Gaze
Gaze is a form of input that interacts with the world based on where the user is looking. Gaze exists in two different flavors
Head gaze
This type of gaze is based on the direction that the head/camera is looking at. Head gaze is active on systems that don't support eye gaze, or in cases where the hardware may support eye gaze, but the right set of permissions and setup has not been performed.
Head gaze is usually associated with HoloLens 1 style interactions involving looking at object by placing it in the center of the Holographic Frame and then performing the air tap gesture.
Eye gaze
This type of gaze is based on where the user's eyes are looking. Eye gaze is only present on systems that support eye tracking. See the eye tracking documentation for more details on how to use eye gaze.
GazeProvider
Gaze functionality (both head and eye) is provided by the GazeProvider. This provider can be configured in the Pointer section of the input system profile:
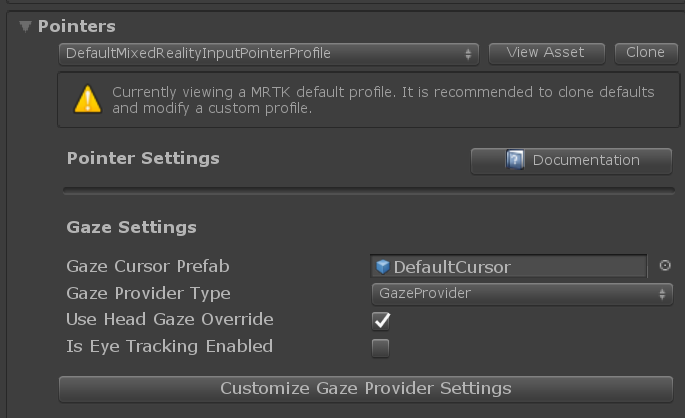
Like other sources of input, the gaze provider interacts with objects in the scene
through use of a pointer (see this document for information on pointers).
In the case of the gaze provider, its pointer is implemented via InternalGazePointer
and is not configured through a profile.
It is possible to replace the stock GazeProvider with an alternate implementation by changing Gaze Provider Type to reference a different class that implements IMixedRealityGazeProvider and IMixedRealityEyeGazeProvider. It's generally recommended to use the stock GazeProvider (and filing issues in when finding bugs) as re-implementing the GazeProvider is non-trivial.
Alternative platform-provided gaze poses
By default, the MRTK GazeProvider uses the center of the camera's frame as the gaze origin. Some platforms, like Windows Mixed Reality on HoloLens 2, provide an alternatively defined gaze pose. This is managed via the Use Head Gaze Override setting in the gaze settings. When enabled, the alternative gaze override will be used. When disabled, the default frame center origin will be used. Specifically, for HoloLens 2, the gaze angle will be raised several degrees to account for user comfort in using their head for targeting.
Usage
How get the current gaze target
This sample shows how to get the current game object that is targeted by the user gaze.
void LogCurrentGazeTarget()
{
if (CoreServices.InputSystem.GazeProvider.GazeTarget)
{
Debug.Log("User gaze is currently over game object: "
+ CoreServices.InputSystem.GazeProvider.GazeTarget)
}
}
How to get the current gaze direction and origin
This sample shows how to get the Vector3 representing the direction of the user gaze and the origin (the point from which the direction is going).
void LogGazeDirectionOrigin()
{
Debug.Log("Gaze is looking in direction: "
+ CoreServices.InputSystem.GazeProvider.GazeDirection);
Debug.Log("Gaze origin is: "
+ CoreServices.InputSystem.GazeProvider.GazeOrigin);
}