Hand menu
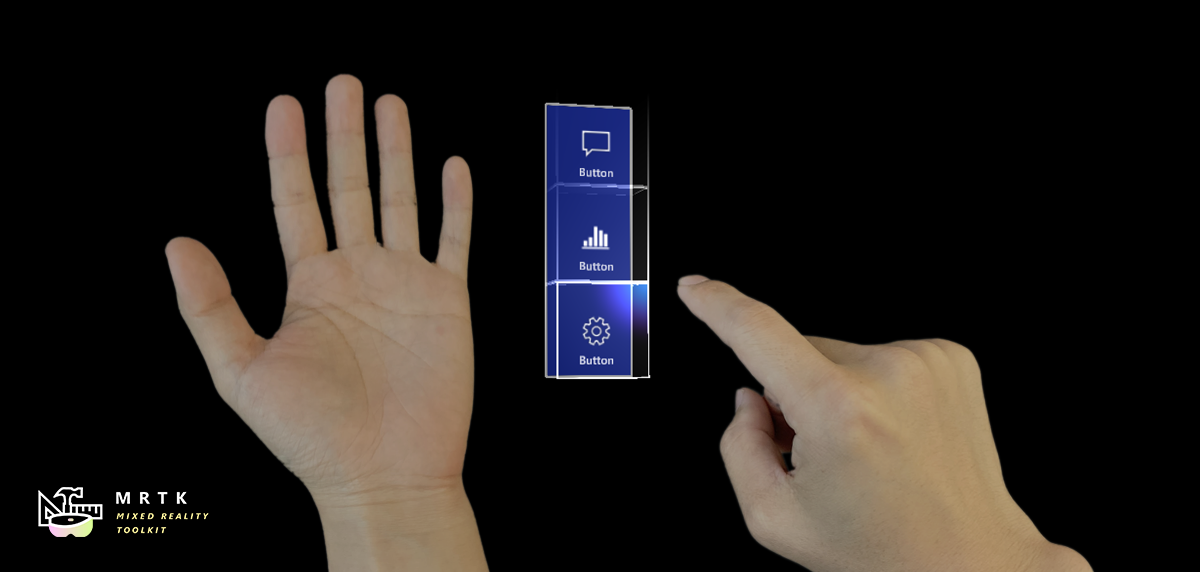
Hand menus allow users to quickly bring up hand-attached UI for frequently used functions. To prevent false activation while interacting with other objects, hand menu provides options such as 'Require Flat Hand' and 'Use Gaze Activation'. It is recommended to use these options to prevent unwanted activation.
Hand menu examples
HandMenuExamples.unity scene is under MRTK/Examples/Demos/HandTracking/Scenes folder. When it is running, the scene will only activate currently selected menu type.

You can find these hand menu prefabs under MRTK/Examples/Demos/HandTracking/Prefabs folder.
HandMenu_Small_HideOnHandDrop and HandMenu_Medium_HideOnHandDrop
These two examples simply activate and deactivate the MenuContent object to show and hide menu on OnFirstHandDetected() and OnLastHandLost() event.
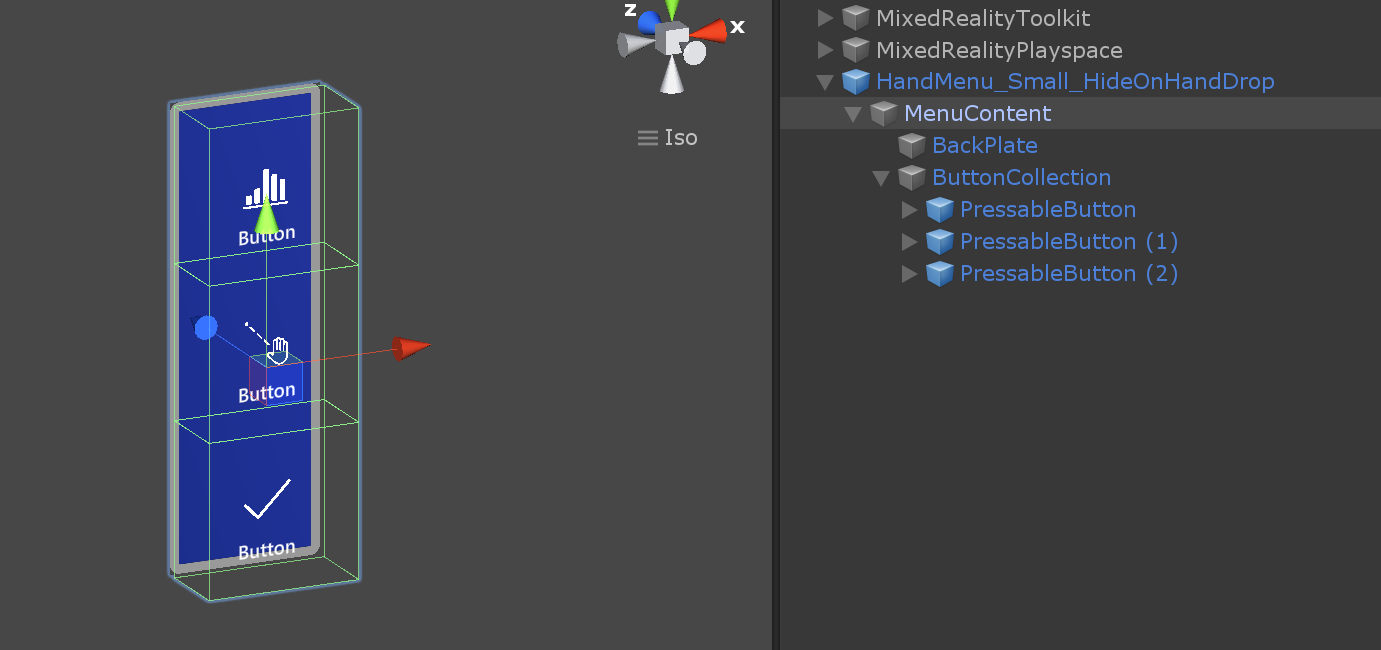
HandMenu_Large_WorldLock_On_GrabAndPull
For more complex menus that require longer interaction time, it is recommended to world-lock the menu. In this example, the user can grab and pull to world-lock the menu, in addition to activating and deactivating the MenuContent on OnFirstHandDetected() and OnLastHandLost() events.
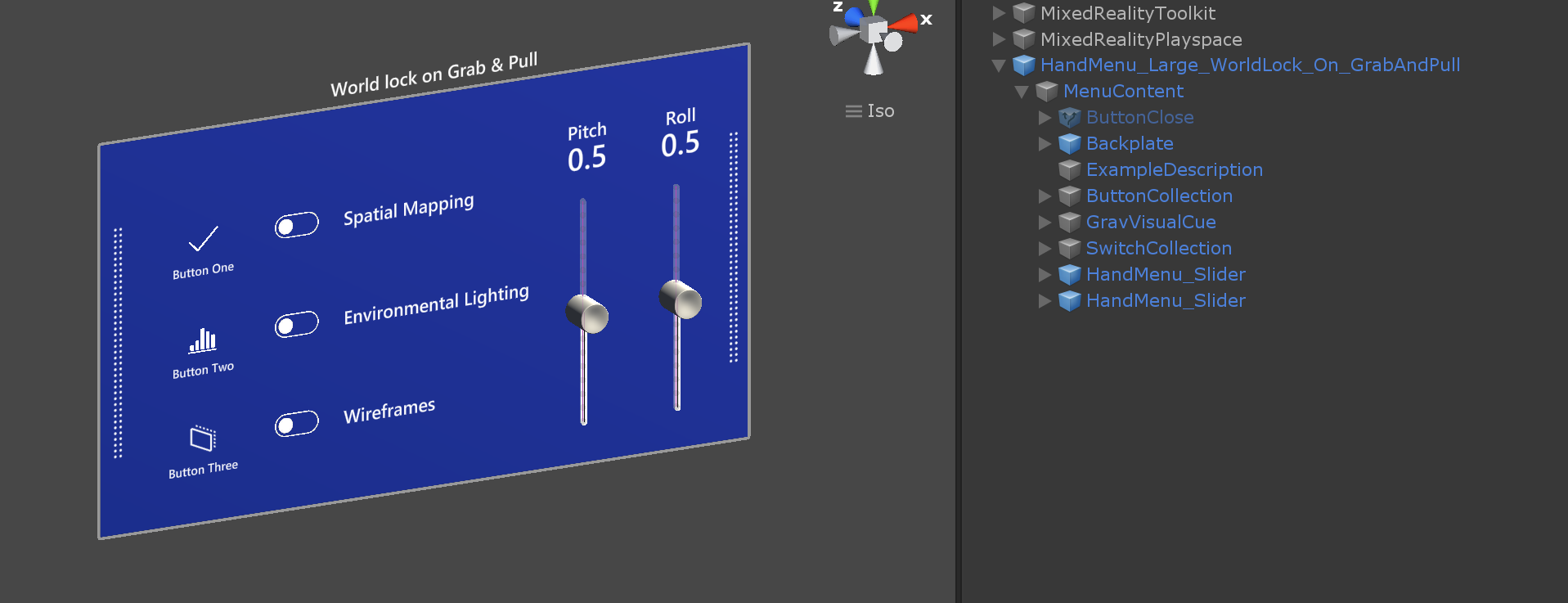
Backplate's ManipulationHandler makes it grabbable and movable. On Manipulation Started event, SolverHandler.UpdateSolvers is deactivated to world-lock the menu. Additionally, it shows the Close button to allow the user to close the menu when the task is finished. On Manipulation Ended event, it calls HandConstraintPalmUp.StartWorldLockReattachCheckCoroutine to allow the user bring the menu back to hand by raising and looking at the palm.
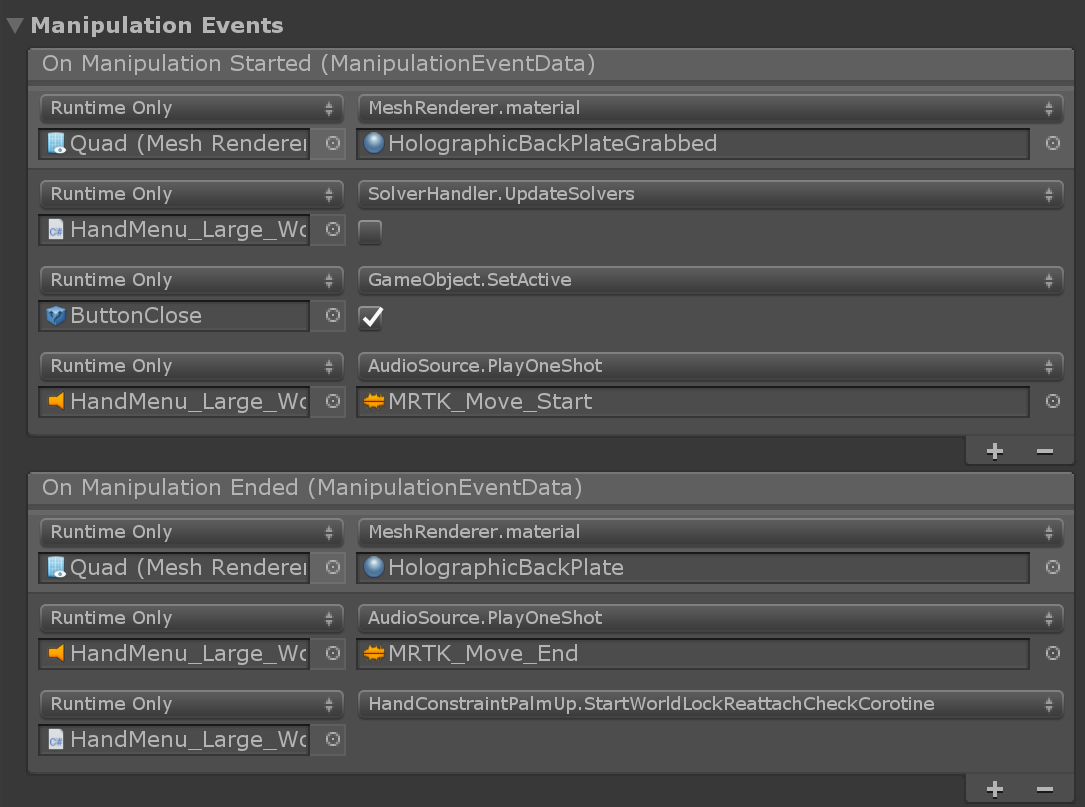
Close button reactivates SolverHandler.UpdateSolvers and hide the MenuContent.
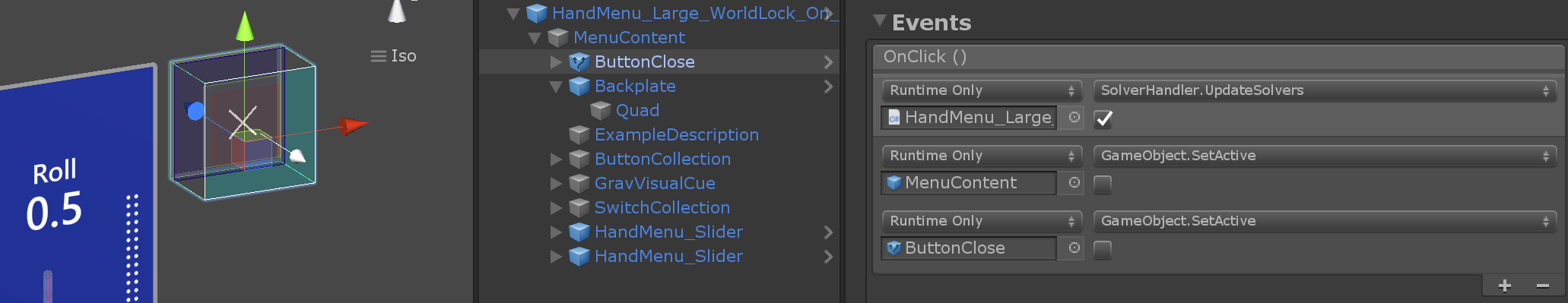
HandMenu_Large_AutoWorldLock_On_HandDrop
This example is similar to HandMenu_Large_WorldLock_On_GrabAndPull. The only difference is that the menu will be automatically world-locked on hand drop. This is done by simply not hiding the MenuContent on OnLastHandLost() event. Grab & pull behavior is same as HandMenu_Large_WorldLock_On_GrabAndPull example.
Scripts
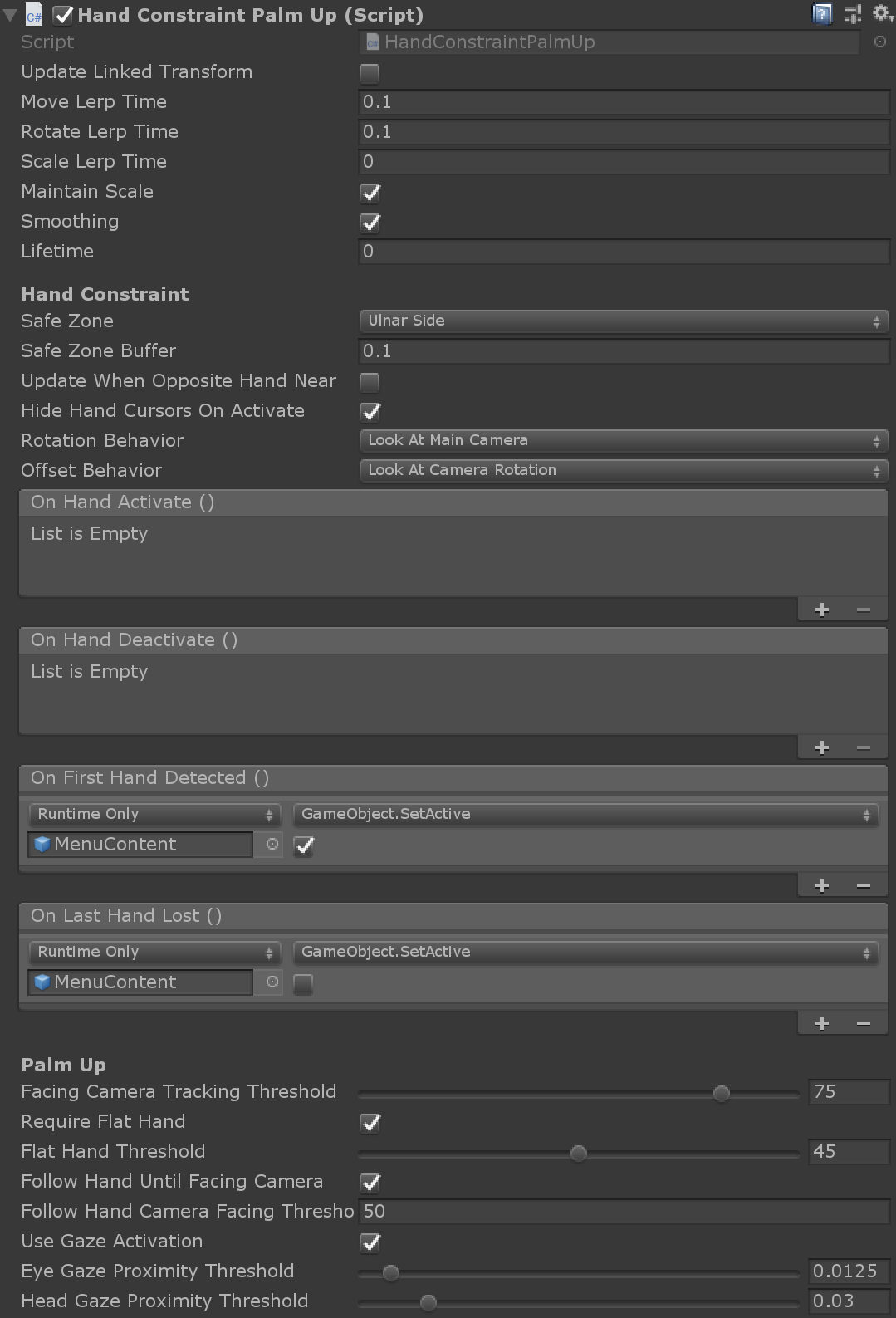
The HandConstraint behavior provides a solver that constrains the tracked object to a region safe for hand constrained content (such as hand UI, menus, etc). Safe regions are considered areas that don't intersect with the hand. A derived class of HandConstraint called HandConstraintPalmUp is also included to demonstrate a common behavior of activating the solver tracked object when the palm is facing the user.
Please see the tool tips available for each HandConstraint property for additional documentation. A few properties are defined in more detail below.
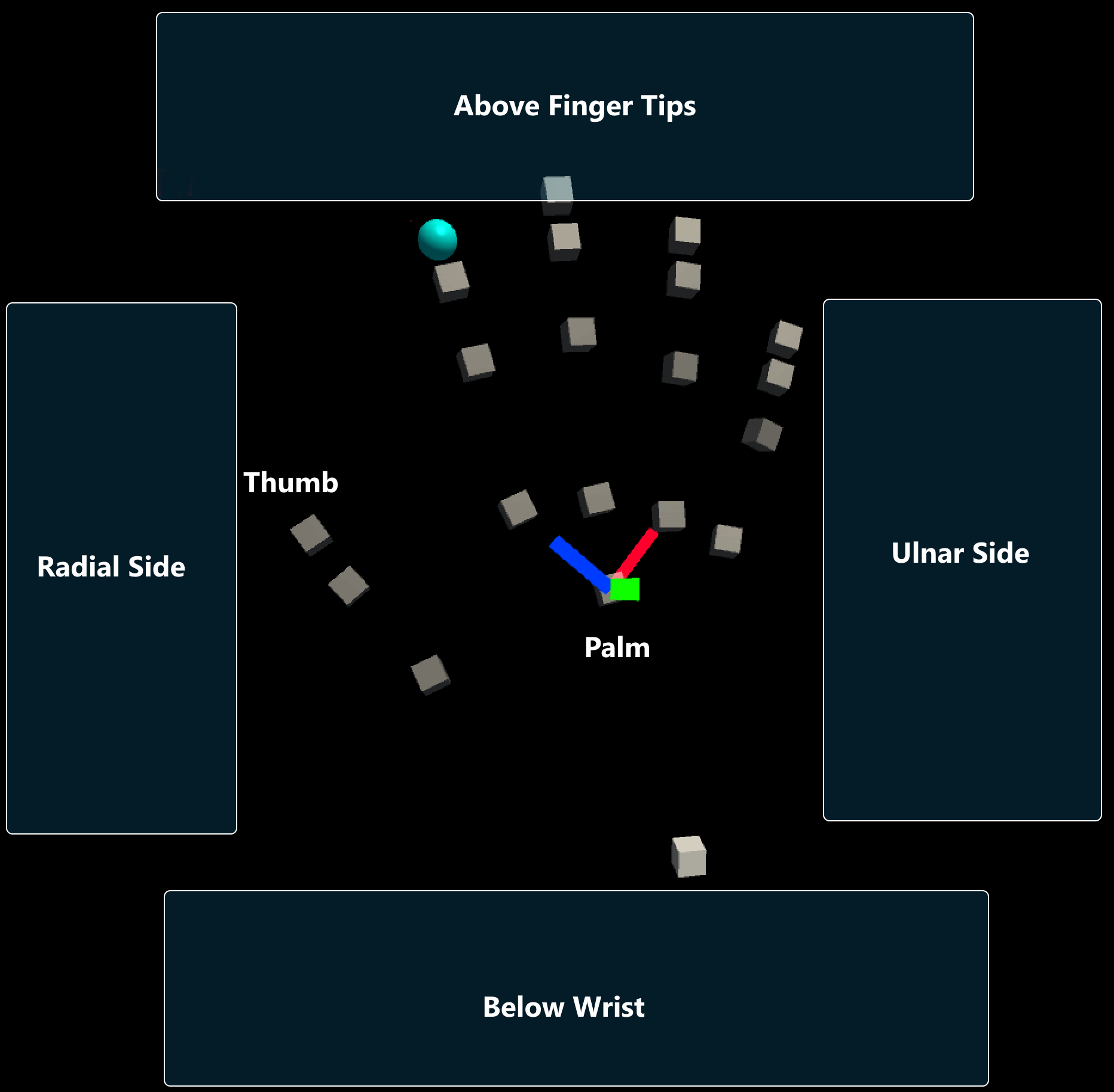
Safe Zone: The safe zone specifies where on the hand to constrain content. It is recommended that content be placed on the Ulnar Side to avoid overlap with the hand and improved interaction quality. Safe zones are calculated by taking the hands orientation projected into a plane orthogonal to the camera's view and raycasting against a bounding box around the hands. Safe zones are defined to work with
IMixedRealityHandbut also works with other controller types. It is recommended to explore what each safe zone represents on different controller types.Follow Hand Until Facing Camera With this active, solver will follow hand rotation until the menu is sufficiently aligned with the gaze, at which point it faces the camera. This works by changing the SolverRotationBehavior in the HandConstraintSolver, from LookAtTrackedObject to LookAtMainCamera as the GazeAlignment angle with the solver varies.
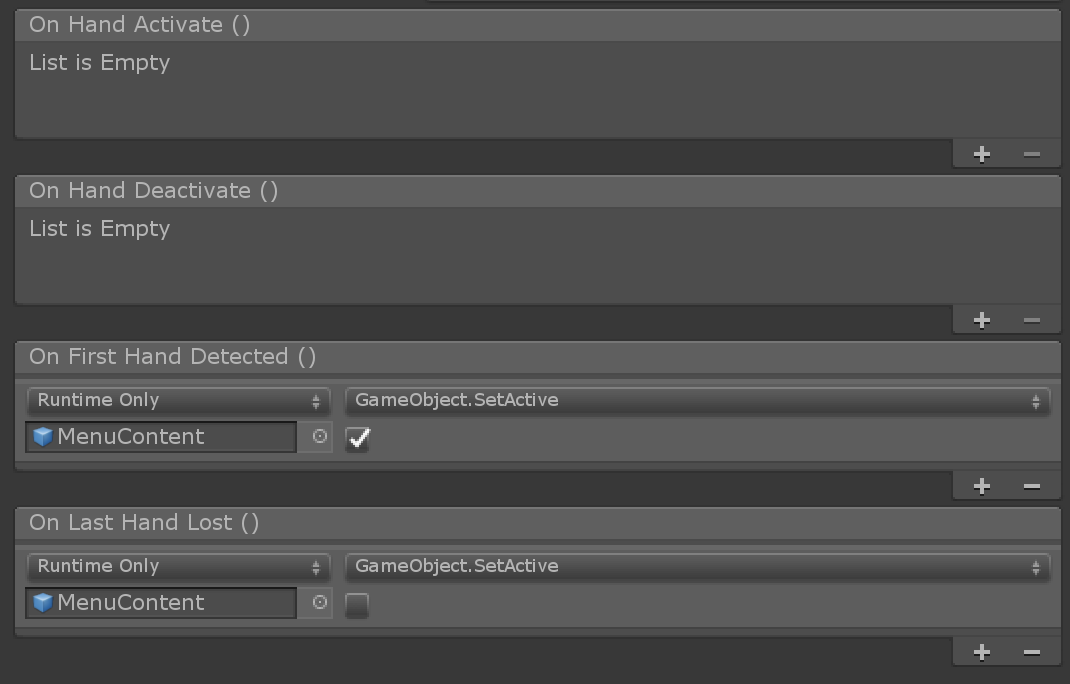
Activation Events: Currently the
HandConstrainttriggers four activation events. These events can be used in many different combinations to create uniqueHandConstraintbehaviors, please see the HandBasedMenuExample scene underMRTK/Examples/Demos/HandTracking/Scenes/for examples of these behaviors.- OnHandActivate: triggers when a hand satisfies the IsHandActive method.
- OnHandDeactivate: triggers when the IsHandActive method is no longer satisfied.
- OnFirstHandDetected: occurs when the hand tracking state changes from no hands in view, to the first hand in view.
- OnLastHandLost: occurs when the hand tracking state changes from at least one hand in view, to no hands in view.
Solver Activation/Deactivation Logic: Currently the recommendation for activating and deactivating
HandConstraintPalmUplogic is to do so through the use of the SolverHandler's UpdateSolver value, rather than by disabling/enabling the object. This can be seen in the example scene through the editor-based hooks triggered after the attached menu's ManipulationHandler "OnManipulationStarted/Ended" events.- Stopping the hand-constraint logic: When trying to set the hand constrained object to stop (as well as not run the activation/deactivation logic), set UpdateSolver to False rather than disabling HandConstraintPalmUp.
- If you want to enable the gaze-based (or even non-gaze-based) Reattach logic, this is then followed by calling the HandConstraintPalmUp.StartWorldLockReattachCheckCoroutine() function. This will trigger a coroutine that then continues to check if the "IsValidController" criteria is met and will set UpdateSolver to True once it is (or the object is disabled)
- Starting the hand-constraint logic: When trying to set the hand constrained object to start following your hand again (based on whether it meets the activation criteria), set the SolverHandler's UpdateSolver to true.
- Stopping the hand-constraint logic: When trying to set the hand constrained object to stop (as well as not run the activation/deactivation logic), set UpdateSolver to False rather than disabling HandConstraintPalmUp.
Reattach Logic: Currently the
HandConstraintPalmUpis able to automatically reattach the target object to the tracked point, regardless of whether the SolverHandler's UpdateSolver is True or not. This is done through calling the HandConstraintPalmUp's StartWorldLockReattachCheckCoroutine() function, after it's been world-locked (which in this case, is effectively setting the SolverHandler's UpdateSolver to False).