
Challenge 03 - Create Resources
< Previous Challenge - Home - Next Challenge >
Introduction
As per the diagram below, the TollBooth application is composed of multiple Azure “Platform As A Service” (aka PaaS) services including:
- Azure Functions
- Cosmos DB
- Azure Event Grid
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Computer Vision API (aka “Azure AI Vision Service” as of 2024)
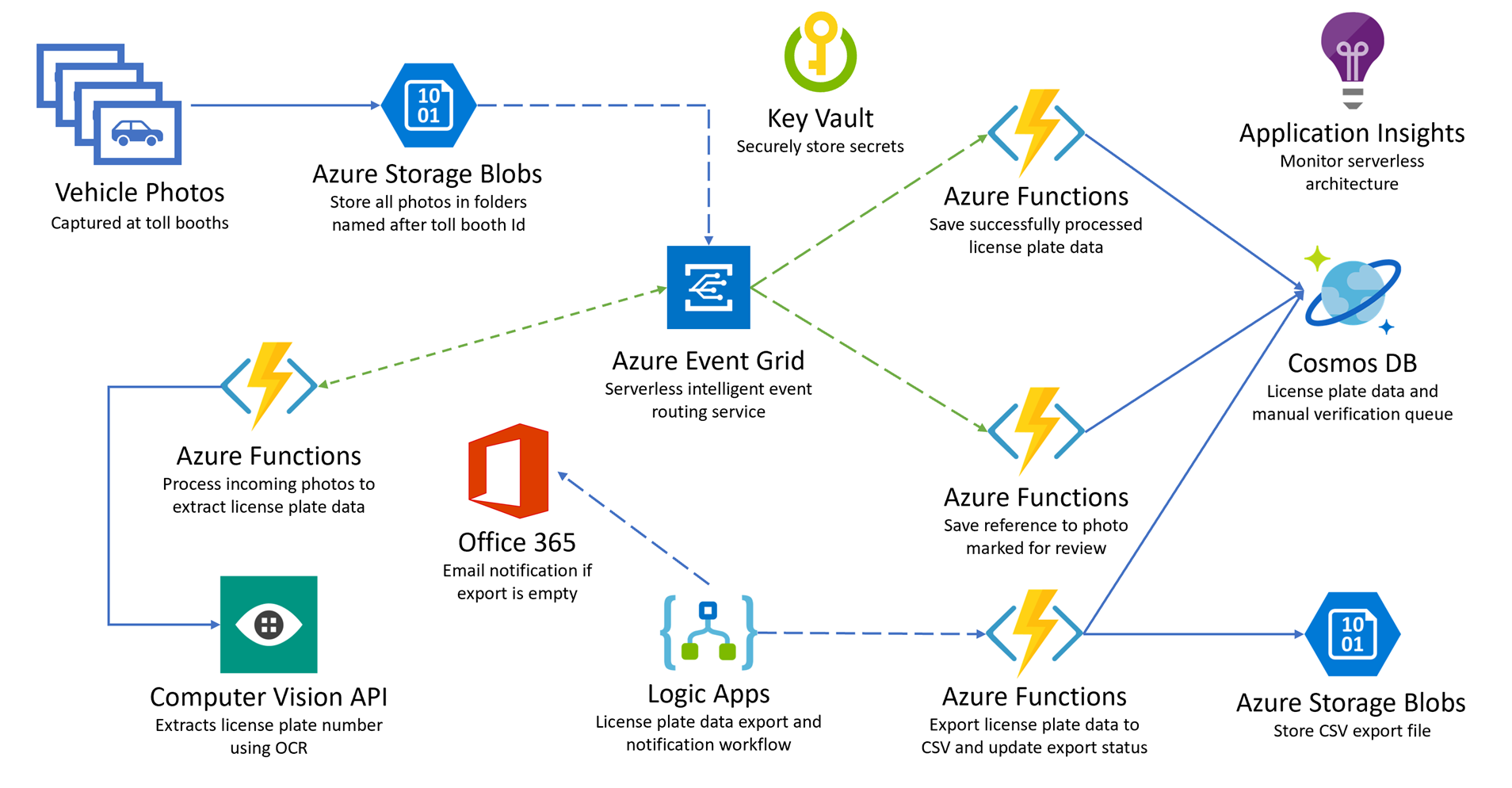
The TollBooth application’s Azure Function source code is just one piece of the overall solution. That code depends on each of these PaaS services being deployed in Azure and configured properly.
Description
In this challenge, you must provision & configure each of the PaaS resources in Azure before you can start developing & deploying the TollBooth application’s Azure Functions code in the next challenge. Each of the Azure PaaS services have secrets that the Azure Function application code needs to access those services. You will also configure Key Vault to host those secrets and grant permission to the Azure Function application so it can access those keys.
While deploying each resource is a challenge in and of itself, there are two high-level tasks for this challenge:
Deploy Azure PaaS Resources
In this challenge, you will provision a blob storage account using the Hot tier, and create two containers within to store uploaded photos and exported CSV files. You will then provision two Function Apps instances, one you will host the “App” function code, and one will host the “Events” function code. Next, you will create a new Event Grid topic. After that, you will create an Azure Cosmos DB account with two collections. Then, you will provision a new Cognitive Services Computer Vision API service (aka Azure AI Vision Service) for applying object character recognition (OCR) on the license plates. Lastly, you will implement Key Vault for secure some of the resource keys.
TIP: It is recommended that you ensure all resources use the same resource group for easier cleanup.
TIP: Deploy resources in the same region as the resource group.
TIP: Remember that some resources need to have unique names.
TIP: Record names and keys as you go, you will need these later.
You can deploy the resources however you like (Azure Portal, Bicep, Azure CLI, Terraform, etc). However, it is a good idea to use the Azure Portal so that you can learn the available settings for each resource.
Create the resources in Azure according the following specifications:
- Create a resource group
- Create an Azure Cosmos DB account
If this takes a while, move ahead and come back to finish the containers
- API : Core (SQL)
- Disable Geo-redundancy and multi-region writes
- Create a container
- Database ID
LicensePlates - Uncheck Provision database throughput
- Container ID
Processed - Partition key :
/licensePlateText
- Database ID
- Create a second container
- Database ID created above
LicensePlates - Container ID
NeedsManualReview - Partition key :
/fileName
- Database ID created above
- Create a storage account (refer to this one as INIT)
- Create a container
images - Create a container
export
- Create a container
- Create a function app (put
Appin the name)- For your tollbooth app, consumption plan, .NET runtime stack
- Create new storage and disable application insights
- Create a function app (put
Eventsin the name)- For your tollbooth events, consumption plan, Node.js runtime stack
- Create new storage and disable application insights
- Create an Event Grid Topic (leave schema as Event Grid Schema)
- Create a Computer Vision API service (S1 pricing tier), nowadays called Azure AI Vision
- Create a Key Vault
- Pricing Tier : Standard
Configure Azure Key Vault
Each of the Azure PaaS services have secrets that the Azure Function application code needs to access those services. The easy thing would be to just put those secrets in the source code so the functions can access each service. However, the easy way is rarely the CORRECT way to do things.
NOTE: Placing secrets in plain-text code files could result in your company or organization being in the news headlines for all the wrong reasons.
It is a best practice to store secrets in a key management service like Azure Key Vault, and then have the application request those secret values from Key Vault on demand as needed. This solution has multiple benefits, including:
- The secrets are not placed in plain text code files where they can be compromised (by committing them to a Git repository)
- The application developer does not need to know or see the secret values
- The secrets can be managed by an operations team independently of application developers
With the Key Vault you created above, you will need to complete the following tasks:
- Store the keys for the Azure PaaS services listed in the table below as secrets in the key vault
- Grant yourself & the Azure Function apps access to the secrets in the key vault
- There are two ways to do this:
- Using “Access Keys”
- Using Azure RBAC (Role Based Access Control)
- It is recommended you use Azure RBAC
Secret Name Value computerVisionApiKeyComputer Vision API key eventGridTopicKeyEvent Grid Topic access key cosmosDBAuthorizationKeyCosmos DB Primary Key cosmosDBConnectionStringCosmos DB Primary Connection String blobStorageConnectionBlob storage connection string - There are two ways to do this:
HINT: You have to configure a Managed Identity for the Function to be able to read from the Key Vault secrets using Azure RBAC.
HINT: Secrets can be referenced in Azure Portal using a specially formatted Secret URI. Also, the Secret URI must finish with a trailing “/” when not referring a version. For example: @Microsoft.KeyVault(SecretUri=https://wth-serverless-kv.vault.azure.net/secrets/blobStorageConnection/)
HINT: Configure the RBAC role “KeyVault Administrator” for yourself, to read and write secrets via the portal, which is a more privileged role than the “KeyVault Secrets User” role that the functions will use to just read secrets using a Managed Identity.
Success Criteria
- Validate that you have 11 resources in your resource group in the same region (This includes the 2 storage accounts associated to your function apps). If you enabled Application Insights on any of your functions, it’s OK, we’ll change it later.
- Ensure you have permissions to read/write the Key Vault Secrets using the Portal
- Validate that you are able see all of the secret values from the above table stored in Key Vault