ai-agents-for-beginners
(Clique na imagem acima para assistir ao vídeo desta lição)
Planejamento de Design
Introdução
Esta lição abordará:
- Definir um objetivo geral claro e dividir uma tarefa complexa em tarefas gerenciáveis.
- Utilizar saída estruturada para respostas mais confiáveis e legíveis por máquinas.
- Aplicar uma abordagem orientada a eventos para lidar com tarefas dinâmicas e entradas inesperadas.
Objetivos de Aprendizagem
Após concluir esta lição, você terá uma compreensão sobre:
- Identificar e definir um objetivo geral para um agente de IA, garantindo que ele saiba claramente o que precisa ser alcançado.
- Dividir uma tarefa complexa em subtarefas gerenciáveis e organizá-las em uma sequência lógica.
- Equipar agentes com as ferramentas certas (por exemplo, ferramentas de busca ou análise de dados), decidir quando e como usá-las e lidar com situações inesperadas que surgirem.
- Avaliar os resultados das subtarefas, medir o desempenho e iterar nas ações para melhorar o resultado final.
Definindo o Objetivo Geral e Dividindo uma Tarefa
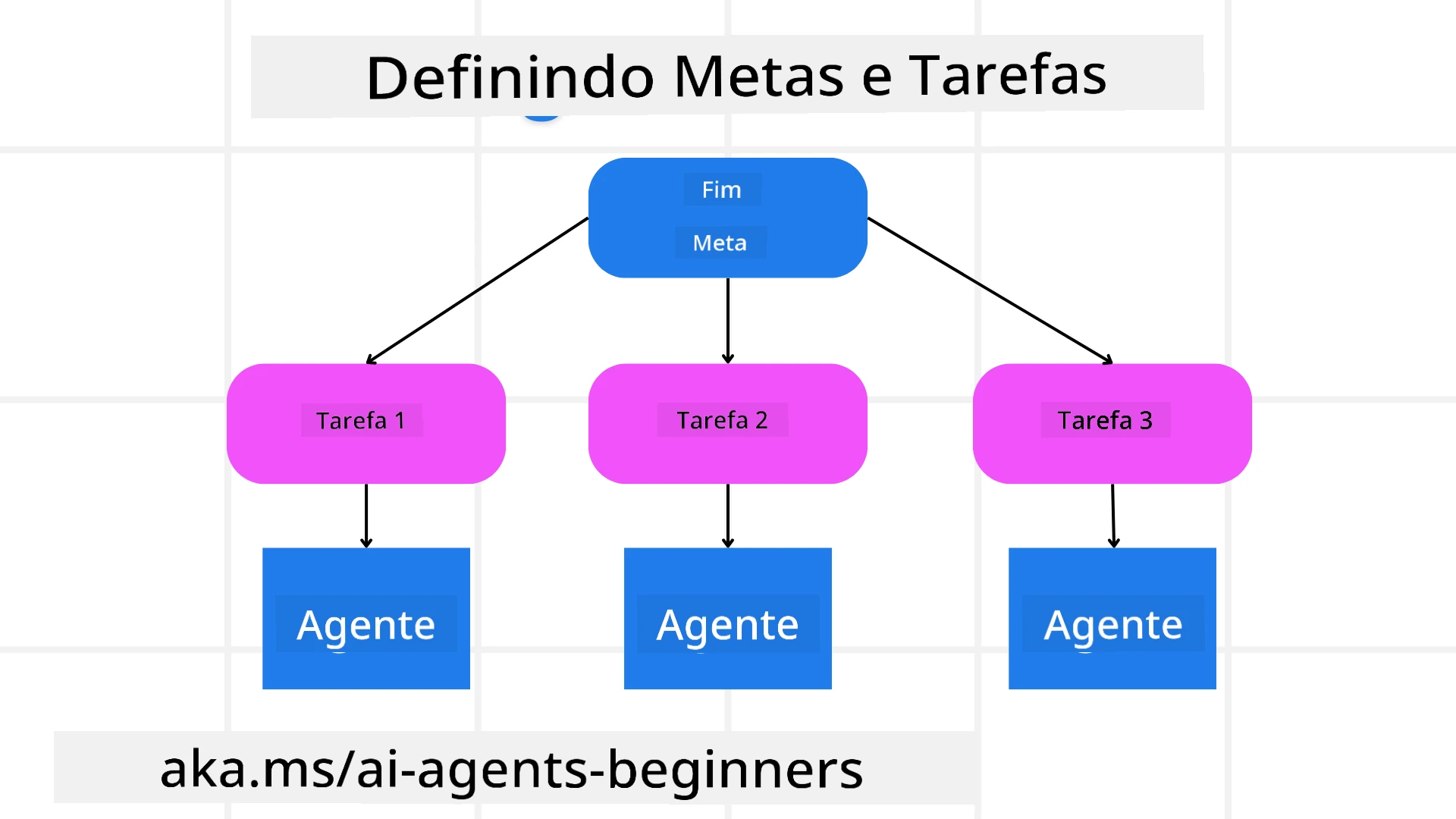
A maioria das tarefas do mundo real é muito complexa para ser resolvida em um único passo. Um agente de IA precisa de um objetivo conciso para orientar seu planejamento e ações. Por exemplo, considere o objetivo:
"Gerar um itinerário de viagem de 3 dias."
Embora seja simples de enunciar, ainda precisa de refinamento. Quanto mais claro for o objetivo, melhor o agente (e qualquer colaborador humano) poderá se concentrar em alcançar o resultado certo, como criar um itinerário abrangente com opções de voo, recomendações de hotéis e sugestões de atividades.
Decomposição de Tarefas
Tarefas grandes ou intrincadas tornam-se mais gerenciáveis quando divididas em subtarefas menores e orientadas a objetivos.
Para o exemplo do itinerário de viagem, você poderia decompor o objetivo em:
- Reserva de Voos
- Reserva de Hotéis
- Aluguel de Carro
- Personalização
Cada subtarefa pode ser tratada por agentes ou processos dedicados. Um agente pode se especializar em buscar as melhores ofertas de voos, outro em reservas de hotéis, e assim por diante. Um agente coordenador ou “downstream” pode então compilar esses resultados em um itinerário coeso para o usuário final.
Essa abordagem modular também permite melhorias incrementais. Por exemplo, você poderia adicionar agentes especializados em Recomendações de Restaurantes ou Sugestões de Atividades Locais e refinar o itinerário ao longo do tempo.
Saída Estruturada
Modelos de Linguagem Grande (LLMs) podem gerar saídas estruturadas (por exemplo, JSON) que são mais fáceis de serem analisadas e processadas por agentes ou serviços subsequentes. Isso é especialmente útil em um contexto de múltiplos agentes, onde podemos executar essas tarefas após receber a saída do planejamento. Para uma visão geral rápida, veja o seguinte trecho de código Python que demonstra um agente de planejamento simples decompondo um objetivo em subtarefas e gerando um plano estruturado:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from enum import Enum
from typing import List, Optional, Union
import json
import os
from typing import Optional
from pprint import pprint
from autogen_core.models import UserMessage, SystemMessage, AssistantMessage
from autogen_ext.models.azure import AzureAIChatCompletionClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
class AgentEnum(str, Enum):
FlightBooking = "flight_booking"
HotelBooking = "hotel_booking"
CarRental = "car_rental"
ActivitiesBooking = "activities_booking"
DestinationInfo = "destination_info"
DefaultAgent = "default_agent"
GroupChatManager = "group_chat_manager"
# Travel SubTask Model
class TravelSubTask(BaseModel):
task_details: str
assigned_agent: AgentEnum # we want to assign the task to the agent
class TravelPlan(BaseModel):
main_task: str
subtasks: List[TravelSubTask]
is_greeting: bool
client = AzureAIChatCompletionClient(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
endpoint="https://models.inference.ai.azure.com",
# To authenticate with the model you will need to generate a personal access token (PAT) in your GitHub settings.
# Create your PAT token by following instructions here: https://docs.github.com/en/authentication/keeping-your-account-and-data-secure/managing-your-personal-access-tokens
credential=AzureKeyCredential(os.environ["GITHUB_TOKEN"]),
model_info={
"json_output": False,
"function_calling": True,
"vision": True,
"family": "unknown",
},
)
# Define the user message
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="""You are an planner agent.
Your job is to decide which agents to run based on the user's request.
Provide your response in JSON format with the following structure:
{'main_task': 'Plan a family trip from Singapore to Melbourne.',
'subtasks': [{'assigned_agent': 'flight_booking',
'task_details': 'Book round-trip flights from Singapore to '
'Melbourne.'}
Below are the available agents specialised in different tasks:
- FlightBooking: For booking flights and providing flight information
- HotelBooking: For booking hotels and providing hotel information
- CarRental: For booking cars and providing car rental information
- ActivitiesBooking: For booking activities and providing activity information
- DestinationInfo: For providing information about destinations
- DefaultAgent: For handling general requests""", source="system"),
UserMessage(
content="Create a travel plan for a family of 2 kids from Singapore to Melboune", source="user"),
]
response = await client.create(messages=messages, extra_create_args={"response_format": 'json_object'})
response_content: Optional[str] = response.content if isinstance(
response.content, str) else None
if response_content is None:
raise ValueError("Response content is not a valid JSON string" )
pprint(json.loads(response_content))
# # Ensure the response content is a valid JSON string before loading it
# response_content: Optional[str] = response.content if isinstance(
# response.content, str) else None
# if response_content is None:
# raise ValueError("Response content is not a valid JSON string")
# # Print the response content after loading it as JSON
# pprint(json.loads(response_content))
# Validate the response content with the MathReasoning model
# TravelPlan.model_validate(json.loads(response_content))
Agente de Planejamento com Orquestração Multi-Agente
Neste exemplo, um Agente de Roteador Semântico recebe uma solicitação do usuário (por exemplo, “Preciso de um plano de hotel para minha viagem.”).
O planejador então:
- Recebe o Plano de Hotel: O planejador pega a mensagem do usuário e, com base em um prompt do sistema (incluindo detalhes dos agentes disponíveis), gera um plano de viagem estruturado.
- Lista os Agentes e Suas Ferramentas: O registro de agentes mantém uma lista de agentes (por exemplo, para voos, hotéis, aluguel de carros e atividades) junto com as funções ou ferramentas que eles oferecem.
- Encaminha o Plano para os Agentes Correspondentes: Dependendo do número de subtarefas, o planejador envia a mensagem diretamente para um agente dedicado (em cenários de tarefa única) ou coordena via um gerenciador de chat em grupo para colaboração multi-agente.
- Resume o Resultado: Por fim, o planejador resume o plano gerado para maior clareza.
O seguinte exemplo de código Python ilustra essas etapas:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from enum import Enum
from typing import List, Optional, Union
class AgentEnum(str, Enum):
FlightBooking = "flight_booking"
HotelBooking = "hotel_booking"
CarRental = "car_rental"
ActivitiesBooking = "activities_booking"
DestinationInfo = "destination_info"
DefaultAgent = "default_agent"
GroupChatManager = "group_chat_manager"
# Travel SubTask Model
class TravelSubTask(BaseModel):
task_details: str
assigned_agent: AgentEnum # we want to assign the task to the agent
class TravelPlan(BaseModel):
main_task: str
subtasks: List[TravelSubTask]
is_greeting: bool
import json
import os
from typing import Optional
from autogen_core.models import UserMessage, SystemMessage, AssistantMessage
from autogen_ext.models.openai import AzureOpenAIChatCompletionClient
# Create the client with type-checked environment variables
client = AzureOpenAIChatCompletionClient(
azure_deployment=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME"),
model=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME"),
api_version=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION"),
azure_endpoint=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"),
api_key=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"),
)
from pprint import pprint
# Define the user message
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="""You are an planner agent.
Your job is to decide which agents to run based on the user's request.
Below are the available agents specialized in different tasks:
- FlightBooking: For booking flights and providing flight information
- HotelBooking: For booking hotels and providing hotel information
- CarRental: For booking cars and providing car rental information
- ActivitiesBooking: For booking activities and providing activity information
- DestinationInfo: For providing information about destinations
- DefaultAgent: For handling general requests""", source="system"),
UserMessage(content="Create a travel plan for a family of 2 kids from Singapore to Melbourne", source="user"),
]
response = await client.create(messages=messages, extra_create_args={"response_format": TravelPlan})
# Ensure the response content is a valid JSON string before loading it
response_content: Optional[str] = response.content if isinstance(response.content, str) else None
if response_content is None:
raise ValueError("Response content is not a valid JSON string")
# Print the response content after loading it as JSON
pprint(json.loads(response_content))
O que segue é a saída do código anterior, e você pode usar essa saída estruturada para encaminhar ao assigned_agent e resumir o plano de viagem para o usuário final.
{
"is_greeting": "False",
"main_task": "Plan a family trip from Singapore to Melbourne.",
"subtasks": [
{
"assigned_agent": "flight_booking",
"task_details": "Book round-trip flights from Singapore to Melbourne."
},
{
"assigned_agent": "hotel_booking",
"task_details": "Find family-friendly hotels in Melbourne."
},
{
"assigned_agent": "car_rental",
"task_details": "Arrange a car rental suitable for a family of four in Melbourne."
},
{
"assigned_agent": "activities_booking",
"task_details": "List family-friendly activities in Melbourne."
},
{
"assigned_agent": "destination_info",
"task_details": "Provide information about Melbourne as a travel destination."
}
]
}
Um notebook de exemplo com o código anterior está disponível aqui.
Planejamento Iterativo
Algumas tarefas exigem um processo de ida e volta ou replanejamento, onde o resultado de uma subtarefa influencia a próxima. Por exemplo, se o agente encontrar um formato de dados inesperado ao reservar voos, ele pode precisar adaptar sua estratégia antes de prosseguir para as reservas de hotéis.
Além disso, o feedback do usuário (por exemplo, um humano decidindo que prefere um voo mais cedo) pode desencadear um replanejamento parcial. Essa abordagem dinâmica e iterativa garante que a solução final esteja alinhada com as restrições do mundo real e as preferências do usuário em evolução.
Exemplo de código:
from autogen_core.models import UserMessage, SystemMessage, AssistantMessage
#.. same as previous code and pass on the user history, current plan
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="""You are a planner agent to optimize the
Your job is to decide which agents to run based on the user's request.
Below are the available agents specialized in different tasks:
- FlightBooking: For booking flights and providing flight information
- HotelBooking: For booking hotels and providing hotel information
- CarRental: For booking cars and providing car rental information
- ActivitiesBooking: For booking activities and providing activity information
- DestinationInfo: For providing information about destinations
- DefaultAgent: For handling general requests""", source="system"),
UserMessage(content="Create a travel plan for a family of 2 kids from Singapore to Melbourne", source="user"),
AssistantMessage(content=f"Previous travel plan - {TravelPlan}", source="assistant")
]
# .. re-plan and send the tasks to respective agents
Para um planejamento mais abrangente, confira Magnetic One para resolver tarefas complexas.
Resumo
Neste artigo, vimos um exemplo de como podemos criar um planejador que pode selecionar dinamicamente os agentes disponíveis definidos. A saída do planejador decompõe as tarefas e atribui os agentes para que possam ser executadas. Assume-se que os agentes têm acesso às funções/ferramentas necessárias para realizar a tarefa. Além dos agentes, você pode incluir outros padrões como reflexão, resumidor e chat round robin para personalizar ainda mais.
Recursos Adicionais
AutoGen Magnetic One - Um sistema multi-agente generalista para resolver tarefas complexas que alcançou resultados impressionantes em vários benchmarks desafiadores de agentes. Referência:
. Nesta implementação, o orquestrador cria um plano específico para a tarefa e delega essas tarefas aos agentes disponíveis. Além do planejamento, o orquestrador também emprega um mecanismo de rastreamento para monitorar o progresso da tarefa e replanejar conforme necessário.
Tem Mais Perguntas sobre o Padrão de Planejamento de Design?
Junte-se ao Discord do Azure AI Foundry para encontrar outros aprendizes, participar de horários de atendimento e tirar suas dúvidas sobre Agentes de IA.
Lição Anterior
Construindo Agentes de IA Confiáveis
Próxima Lição
Aviso Legal:
Este documento foi traduzido utilizando o serviço de tradução por IA Co-op Translator. Embora nos esforcemos para garantir a precisão, esteja ciente de que traduções automatizadas podem conter erros ou imprecisões. O documento original em seu idioma nativo deve ser considerado a fonte autoritativa. Para informações críticas, recomenda-se a tradução profissional realizada por humanos. Não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer mal-entendidos ou interpretações equivocadas decorrentes do uso desta tradução.
