ai-agents-for-beginners
การสำรวจ Microsoft Agent Framework

บทนำ
บทเรียนนี้จะครอบคลุม:
- การทำความเข้าใจ Microsoft Agent Framework: คุณสมบัติสำคัญและคุณค่า
- การสำรวจแนวคิดหลักของ Microsoft Agent Framework
- การเปรียบเทียบ MAF กับ Semantic Kernel และ AutoGen: คู่มือการย้ายข้อมูล
เป้าหมายการเรียนรู้
หลังจากจบบทเรียนนี้ คุณจะสามารถ:
- สร้าง AI Agents ที่พร้อมใช้งานในระดับการผลิตด้วย Microsoft Agent Framework
- ใช้คุณสมบัติหลักของ Microsoft Agent Framework กับกรณีการใช้งาน Agentic ของคุณ
- ย้ายและผสานรวมเฟรมเวิร์กและเครื่องมือ Agentic ที่มีอยู่
ตัวอย่างโค้ด
ตัวอย่างโค้ดสำหรับ Microsoft Agent Framework (MAF) สามารถพบได้ใน repository นี้ภายใต้ไฟล์ xx-python-agent-framework และ xx-dotnet-agent-framework
การทำความเข้าใจ Microsoft Agent Framework
Microsoft Agent Framework (MAF) ถูกพัฒนาขึ้นจากประสบการณ์และการเรียนรู้จาก Semantic Kernel และ AutoGen โดยมีความยืดหยุ่นในการตอบสนองต่อกรณีการใช้งาน Agentic ที่หลากหลายในทั้งสภาพแวดล้อมการผลิตและการวิจัย เช่น:
- การจัดลำดับขั้นตอนของ Agent ในสถานการณ์ที่ต้องการการทำงานแบบทีละขั้นตอน
- การจัดลำดับพร้อมกัน ในสถานการณ์ที่ Agent ต้องทำงานหลายอย่างในเวลาเดียวกัน
- การจัดลำดับการสนทนากลุ่ม ในสถานการณ์ที่ Agent สามารถร่วมมือกันทำงานในงานเดียว
- การจัดลำดับการส่งต่อ ในสถานการณ์ที่ Agent ส่งต่อภารกิจให้กันเมื่อเสร็จสิ้นงานย่อย
- การจัดลำดับแบบแม่เหล็ก ในสถานการณ์ที่ Agent ผู้จัดการสร้างและปรับเปลี่ยนรายการงานและจัดการการประสานงานของ Subagents เพื่อให้งานเสร็จสมบูรณ์
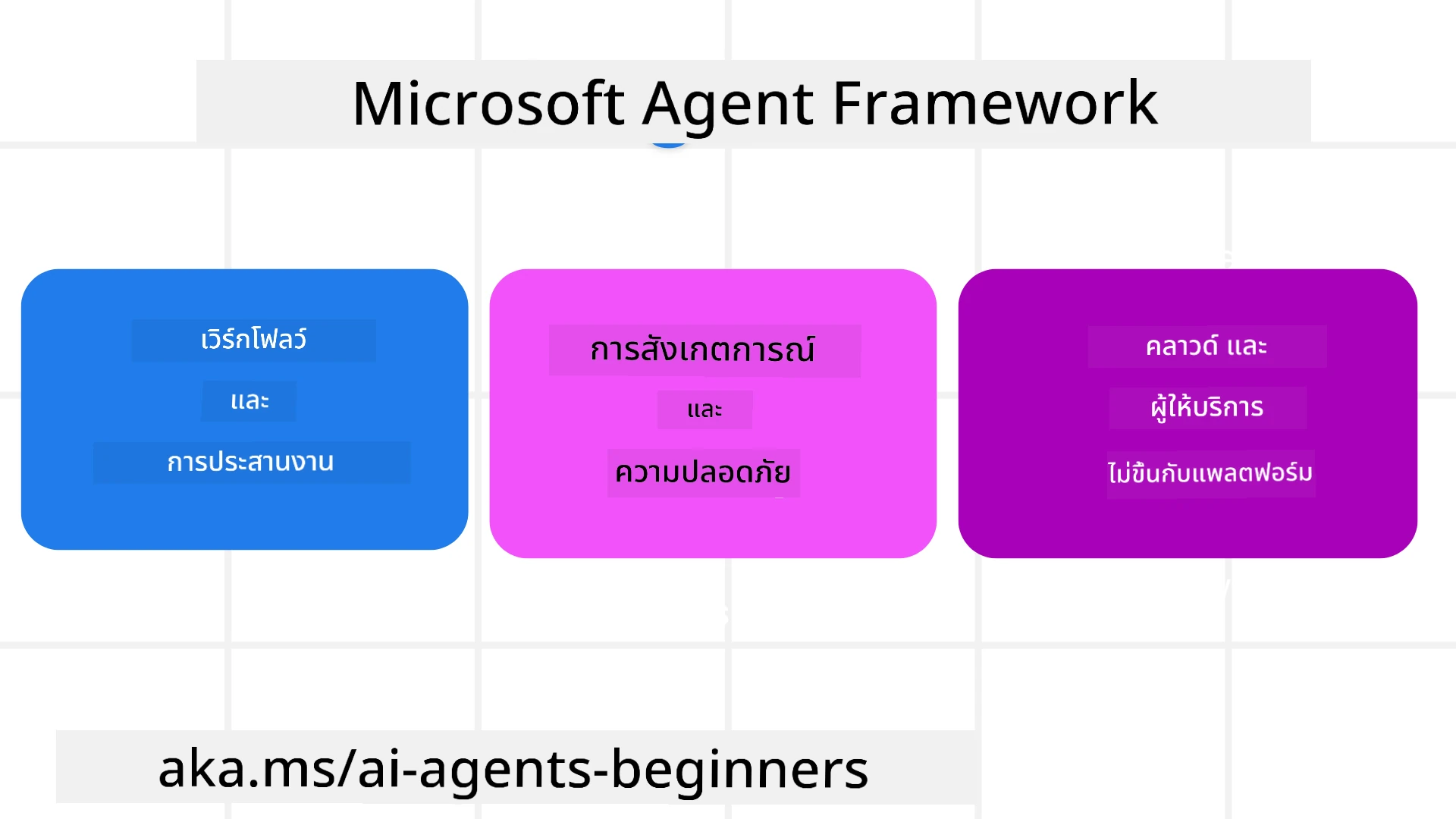
เพื่อส่งมอบ AI Agents ในระดับการผลิต MAF ยังมีคุณสมบัติที่รวมถึง:
- การสังเกตการณ์ ผ่านการใช้ OpenTelemetry ซึ่งทุกการกระทำของ AI Agent รวมถึงการเรียกใช้เครื่องมือ ขั้นตอนการจัดลำดับ การไหลของเหตุผล และการติดตามประสิทธิภาพผ่านแดชบอร์ด Azure AI Foundry
- ความปลอดภัย โดยการโฮสต์ Agent บน Azure AI Foundry ซึ่งมีการควบคุมความปลอดภัย เช่น การเข้าถึงตามบทบาท การจัดการข้อมูลส่วนตัว และความปลอดภัยของเนื้อหาในตัว
- ความทนทาน เนื่องจากเธรดและขั้นตอนการทำงานของ Agent สามารถหยุดชั่วคราว ดำเนินการต่อ และกู้คืนจากข้อผิดพลาด ซึ่งช่วยให้กระบวนการที่ใช้เวลานานดำเนินต่อไปได้
- การควบคุม เนื่องจากรองรับขั้นตอนการทำงานที่มีมนุษย์เข้ามาเกี่ยวข้อง โดยงานจะถูกทำเครื่องหมายว่าต้องการการอนุมัติจากมนุษย์
Microsoft Agent Framework ยังมุ่งเน้นที่การทำงานร่วมกันได้โดย:
- การไม่ยึดติดกับคลาวด์ - Agent สามารถทำงานในคอนเทนเนอร์ ในองค์กร และในคลาวด์ที่หลากหลาย
- การไม่ยึดติดกับผู้ให้บริการ - Agent สามารถสร้างผ่าน SDK ที่คุณชื่นชอบ รวมถึง Azure OpenAI และ OpenAI
- การผสานรวมมาตรฐานเปิด - Agent สามารถใช้โปรโตคอล เช่น Agent-to-Agent (A2A) และ Model Context Protocol (MCP) เพื่อค้นหาและใช้ Agent และเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
- ปลั๊กอินและตัวเชื่อมต่อ - สามารถเชื่อมต่อกับบริการข้อมูลและหน่วยความจำ เช่น Microsoft Fabric, SharePoint, Pinecone และ Qdrant
มาดูกันว่าคุณสมบัติเหล่านี้ถูกนำไปใช้กับแนวคิดหลักของ Microsoft Agent Framework อย่างไร
แนวคิดหลักของ Microsoft Agent Framework
Agents
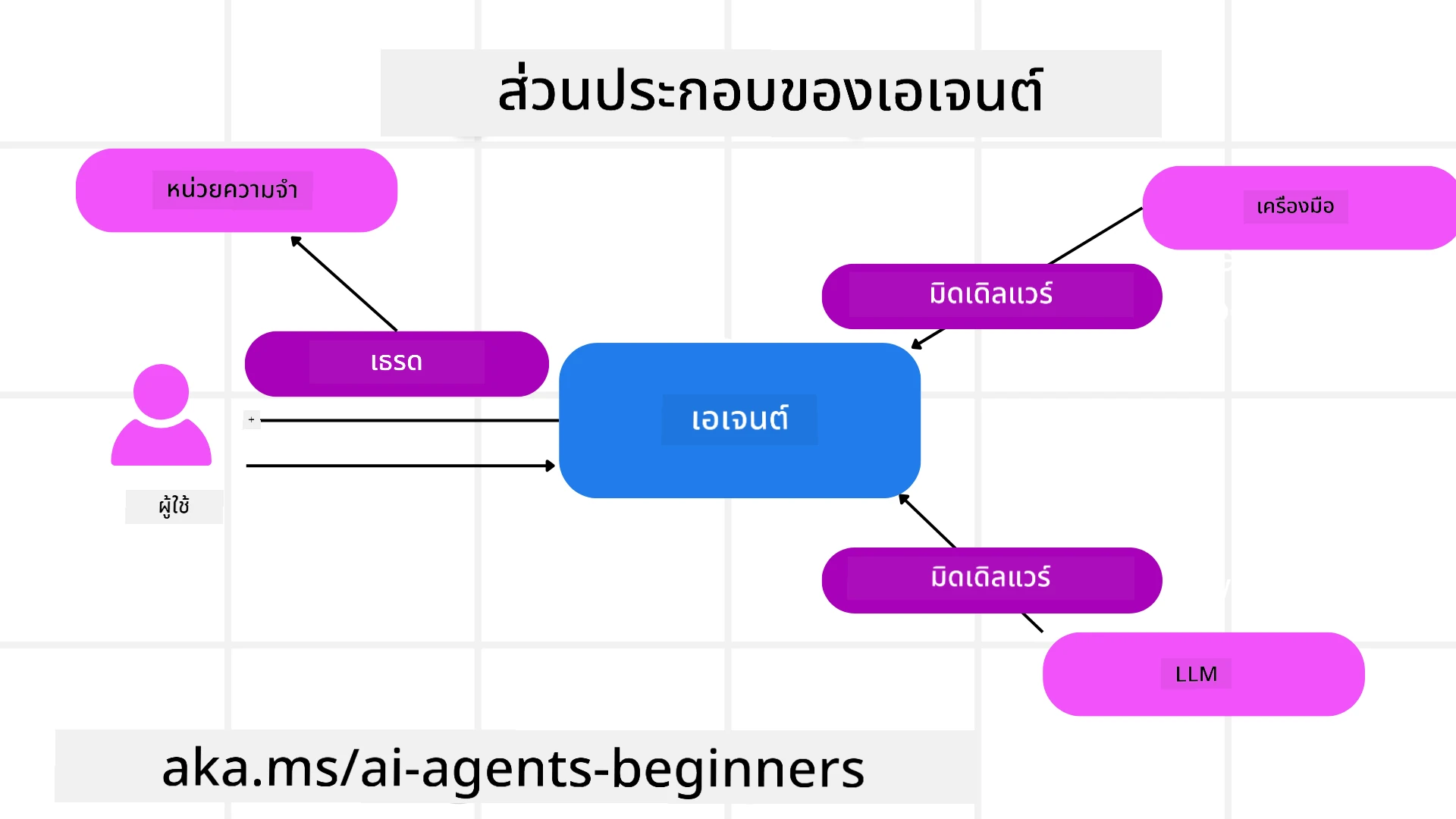
การสร้าง Agent
การสร้าง Agent ทำได้โดยการกำหนดบริการการอนุมาน (LLM Provider) ชุดคำสั่งที่ AI Agent ต้องปฏิบัติตาม และ name ที่กำหนด:
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at recommending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
ตัวอย่างด้านบนใช้ Azure OpenAI แต่ Agent สามารถสร้างได้โดยใช้บริการหลากหลาย รวมถึง Azure AI Foundry Agent Service:
AzureAIAgentClient(async_credential=credential).create_agent( name="HelperAgent", instructions="You are a helpful assistant." ) as agent
OpenAI Responses, ChatCompletion APIs
agent = OpenAIResponsesClient().create_agent( name="WeatherBot", instructions="You are a helpful weather assistant.", )
agent = OpenAIChatClient().create_agent( name="HelpfulAssistant", instructions="You are a helpful assistant.", )
หรือ Agent ระยะไกลโดยใช้โปรโตคอล A2A:
agent = A2AAgent( name=agent_card.name, description=agent_card.description, agent_card=agent_card, url="https://your-a2a-agent-host" )
การเรียกใช้งาน Agent
Agent ถูกเรียกใช้งานโดยใช้เมธอด .run หรือ .run_stream สำหรับการตอบสนองแบบไม่สตรีมและแบบสตรีม
result = await agent.run("What are good places to visit in Amsterdam?")
print(result.text)
async for update in agent.run_stream("What are the good places to visit in Amsterdam?"):
if update.text:
print(update.text, end="", flush=True)
การเรียกใช้งาน Agent แต่ละครั้งยังสามารถปรับแต่งพารามิเตอร์ เช่น max_tokens ที่ Agent ใช้ tools ที่ Agent สามารถเรียกใช้ และแม้กระทั่ง model ที่ใช้สำหรับ Agent
สิ่งนี้มีประโยชน์ในกรณีที่ต้องการโมเดลหรือเครื่องมือเฉพาะสำหรับการทำงานของผู้ใช้ให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์
Tools
เครื่องมือสามารถกำหนดได้ทั้งเมื่อกำหนด Agent:
def get_attractions( location: Annotated[str, Field(description="The location to get the top tourist attractions for")], ) -> str: """Get the top tourist attractions for a given location.""" return f"The top attractions for {location} are."
# When creating a ChatAgent directly
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
และเมื่อเรียกใช้งาน Agent:
result1 = await agent.run( "What's the best place to visit in Seattle?", tools=[get_attractions] # Tool provided for this run only )
Agent Threads
Agent Threads ถูกใช้เพื่อจัดการการสนทนาแบบหลายรอบ Threads สามารถสร้างได้โดย:
- ใช้
get_new_thread()ซึ่งช่วยให้ Thread ถูกบันทึกไว้ในระยะยาว - สร้าง Thread โดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อเรียกใช้งาน Agent และมี Thread อยู่เพียงในระหว่างการเรียกใช้งานปัจจุบัน
การสร้าง Thread มีลักษณะดังนี้:
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
จากนั้นคุณสามารถทำการ serialize Thread เพื่อบันทึกไว้ใช้ในภายหลัง:
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread()
# Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, how are you?", thread=thread)
# Serialize the thread for storage.
serialized_thread = await thread.serialize()
# Deserialize the thread state after loading from storage.
resumed_thread = await agent.deserialize_thread(serialized_thread)
Agent Middleware
Agent โต้ตอบกับเครื่องมือและ LLMs เพื่อทำงานของผู้ใช้ให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์ ในบางสถานการณ์ เราอาจต้องการดำเนินการหรือบันทึกระหว่างการโต้ตอบเหล่านี้ Agent middleware ช่วยให้เราทำสิ่งนี้ได้ผ่าน:
Function Middleware
Middleware นี้ช่วยให้เราดำเนินการระหว่าง Agent และฟังก์ชัน/เครื่องมือที่มันจะเรียกใช้ ตัวอย่างของการใช้งานคือเมื่อคุณต้องการบันทึกการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
ในโค้ดด้านล่าง next กำหนดว่าควรเรียกใช้ middleware ถัดไปหรือฟังก์ชันจริง
async def logging_function_middleware(
context: FunctionInvocationContext,
next: Callable[[FunctionInvocationContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Function middleware that logs function execution."""
# Pre-processing: Log before function execution
print(f"[Function] Calling {context.function.name}")
# Continue to next middleware or function execution
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after function execution
print(f"[Function] {context.function.name} completed")
Chat Middleware
Middleware นี้ช่วยให้เราดำเนินการหรือบันทึกระหว่าง Agent และคำขอระหว่าง LLM
สิ่งนี้มีข้อมูลสำคัญ เช่น messages ที่ถูกส่งไปยังบริการ AI
async def logging_chat_middleware(
context: ChatContext,
next: Callable[[ChatContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Chat middleware that logs AI interactions."""
# Pre-processing: Log before AI call
print(f"[Chat] Sending {len(context.messages)} messages to AI")
# Continue to next middleware or AI service
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after AI response
print("[Chat] AI response received")
Agent Memory
ตามที่ครอบคลุมในบทเรียน Agentic Memory หน่วยความจำเป็นองค์ประกอบสำคัญที่ช่วยให้ Agent ทำงานในบริบทต่าง ๆ MAF มีหน่วยความจำหลายประเภท:
In-Memory Storage
นี่คือหน่วยความจำที่ถูกเก็บไว้ใน Threads ระหว่างการทำงานของแอปพลิเคชัน
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
Persistent Messages
หน่วยความจำนี้ถูกใช้เมื่อเก็บประวัติการสนทนาในหลายเซสชัน มันถูกกำหนดโดยใช้ chat_message_store_factory:
from agent_framework import ChatMessageStore
# Create a custom message store
def create_message_store():
return ChatMessageStore()
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a Travel assistant.",
chat_message_store_factory=create_message_store
)
Dynamic Memory
หน่วยความจำนี้ถูกเพิ่มลงในบริบทก่อนที่ Agent จะถูกเรียกใช้ หน่วยความจำเหล่านี้สามารถเก็บไว้ในบริการภายนอก เช่น mem0:
from agent_framework.mem0 import Mem0Provider
# Using Mem0 for advanced memory capabilities
memory_provider = Mem0Provider(
api_key="your-mem0-api-key",
user_id="user_123",
application_id="my_app"
)
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a helpful assistant with memory.",
context_providers=memory_provider
)
Agent Observability
การสังเกตการณ์เป็นสิ่งสำคัญในการสร้างระบบ Agentic ที่เชื่อถือได้และดูแลรักษาได้ MAF ผสานรวมกับ OpenTelemetry เพื่อให้การติดตามและการวัดผลสำหรับการสังเกตการณ์ที่ดีขึ้น
from agent_framework.observability import get_tracer, get_meter
tracer = get_tracer()
meter = get_meter()
with tracer.start_as_current_span("my_custom_span"):
# do something
pass
counter = meter.create_counter("my_custom_counter")
counter.add(1, {"key": "value"})
Workflows
MAF มี workflows ที่เป็นขั้นตอนที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าเพื่อทำงานให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์และรวม AI Agents เป็นส่วนประกอบในขั้นตอนเหล่านั้น
Workflows ประกอบด้วยส่วนประกอบต่าง ๆ ที่ช่วยให้การควบคุมการไหลดีขึ้น Workflows ยังช่วยให้ การจัดลำดับหลาย Agent และ การบันทึกสถานะ เพื่อบันทึกสถานะ workflow
ส่วนประกอบหลักของ workflow ได้แก่:
Executors
Executors รับข้อความนำเข้า ดำเนินการงานที่ได้รับมอบหมาย และผลิตข้อความส่งออก ซึ่งช่วยให้ workflow ก้าวไปสู่การทำงานที่ใหญ่ขึ้นให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์ Executors สามารถเป็น AI Agent หรือ logic ที่กำหนดเอง
Edges
Edges ถูกใช้เพื่อกำหนดการไหลของข้อความใน workflow ซึ่งสามารถเป็น:
Direct Edges - การเชื่อมต่อแบบง่าย ๆ ระหว่าง Executors:
from agent_framework import WorkflowBuilder
builder = WorkflowBuilder()
builder.add_edge(source_executor, target_executor)
builder.set_start_executor(source_executor)
workflow = builder.build()
Conditional Edges - ถูกเปิดใช้งานเมื่อเงื่อนไขบางอย่างถูกตอบสนอง ตัวอย่างเช่น เมื่อห้องพักโรงแรมไม่ว่าง Executor สามารถแนะนำตัวเลือกอื่น ๆ
Switch-case Edges - ส่งข้อความไปยัง Executors ต่าง ๆ ตามเงื่อนไขที่กำหนด ตัวอย่างเช่น หากลูกค้าการเดินทางมีสิทธิ์เข้าถึงพิเศษ งานของพวกเขาจะถูกจัดการผ่าน workflow อื่น
Fan-out Edges - ส่งข้อความหนึ่งไปยังเป้าหมายหลายแห่ง
Fan-in Edges - รวบรวมข้อความหลายข้อความจาก Executors ต่าง ๆ และส่งไปยังเป้าหมายเดียว
Events
เพื่อให้การสังเกตการณ์ใน workflows ดีขึ้น MAF มี events ในตัวสำหรับการดำเนินการ เช่น:
WorkflowStartedEvent- การดำเนินการ workflow เริ่มต้นWorkflowOutputEvent- Workflow ผลิตผลลัพธ์WorkflowErrorEvent- Workflow พบข้อผิดพลาดExecutorInvokeEvent- Executor เริ่มดำเนินการExecutorCompleteEvent- Executor เสร็จสิ้นการดำเนินการRequestInfoEvent- มีการออกคำขอ
การย้ายจากเฟรมเวิร์กอื่น (Semantic Kernel และ AutoGen)
ความแตกต่างระหว่าง MAF และ Semantic Kernel
การสร้าง Agent ที่ง่ายขึ้น
Semantic Kernel ต้องการการสร้าง Kernel instance สำหรับทุก Agent ในขณะที่ MAF ใช้แนวทางที่ง่ายขึ้นโดยใช้ extensions สำหรับผู้ให้บริการหลัก
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at reccomending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
การสร้าง Agent Thread
Semantic Kernel ต้องการการสร้าง Threads ด้วยตนเอง ใน MAF Agent จะถูกกำหนด Thread โดยตรง
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
การลงทะเบียนเครื่องมือ
ใน Semantic Kernel เครื่องมือจะถูกลงทะเบียนกับ Kernel และ Kernel จะถูกส่งต่อไปยัง Agent ใน MAF เครื่องมือจะถูกลงทะเบียนโดยตรงในระหว่างกระบวนการสร้าง Agent
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
ความแตกต่างระหว่าง MAF และ AutoGen
Teams vs Workflows
Teams เป็นโครงสร้างเหตุการณ์สำหรับกิจกรรมที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วยเหตุการณ์กับ Agent ใน AutoGen ในขณะที่ MAF ใช้ Workflows ที่ส่งข้อมูลไปยัง Executors ผ่านสถาปัตยกรรมแบบกราฟ
การสร้างเครื่องมือ
AutoGen ใช้ FunctionTool เพื่อห่อหุ้มฟังก์ชันสำหรับ Agent ในการเรียกใช้ ในขณะที่ MAF ใช้ @ai_function ซึ่งทำงานคล้ายกันแต่ยังสามารถอนุมาน schemas โดยอัตโนมัติสำหรับแต่ละฟังก์ชัน
พฤติกรรมของ Agent
Agent ใน AutoGen เป็น Agent แบบรอบเดียวโดยค่าเริ่มต้น เว้นแต่ max_tool_iterations จะถูกตั้งค่าให้สูงกว่า ใน MAF ChatAgent เป็น Agent แบบหลายรอบโดยค่าเริ่มต้น ซึ่งหมายความว่ามันจะเรียกใช้เครื่องมือจนกว่างานของผู้ใช้จะเสร็จสมบูรณ์
ตัวอย่างโค้ด
ตัวอย่างโค้ดสำหรับ Microsoft Agent Framework สามารถพบได้ใน repository นี้ภายใต้ไฟล์ xx-python-agent-framework และ xx-dotnet-agent-framework
มีคำถามเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ Microsoft Agent Framework?
เข้าร่วม Azure AI Foundry Discord เพื่อพบปะกับผู้เรียนคนอื่น ๆ เข้าร่วมชั่วโมงสำนักงาน และรับคำตอบสำหรับคำถามเกี่ยวกับ AI Agents ของคุณ
ข้อจำกัดความรับผิดชอบ:
เอกสารนี้ได้รับการแปลโดยใช้บริการแปลภาษา AI Co-op Translator แม้ว่าเราจะพยายามให้การแปลมีความถูกต้อง แต่โปรดทราบว่าการแปลอัตโนมัติอาจมีข้อผิดพลาดหรือความไม่ถูกต้อง เอกสารต้นฉบับในภาษาดั้งเดิมควรถือเป็นแหล่งข้อมูลที่เชื่อถือได้ สำหรับข้อมูลที่สำคัญ ขอแนะนำให้ใช้บริการแปลภาษามนุษย์ที่เป็นมืออาชีพ เราไม่รับผิดชอบต่อความเข้าใจผิดหรือการตีความผิดที่เกิดจากการใช้การแปลนี้