ai-agents-for-beginners
探索 Microsoft Agent Framework

簡介
本課程將涵蓋:
- 理解 Microsoft Agent Framework:主要功能與價值
- 探索 Microsoft Agent Framework 的核心概念
- 比較 MAF 與 Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen:遷移指南
學習目標
完成本課程後,您將能夠:
- 使用 Microsoft Agent Framework 建立可投入生產的 AI 代理
- 將 Microsoft Agent Framework 的核心功能應用於您的代理使用案例
- 遷移並整合現有的代理框架和工具
程式碼範例
Microsoft Agent Framework (MAF) 的程式碼範例可在此存儲庫中找到,位於 xx-python-agent-framework 和 xx-dotnet-agent-framework 文件中。
理解 Microsoft Agent Framework
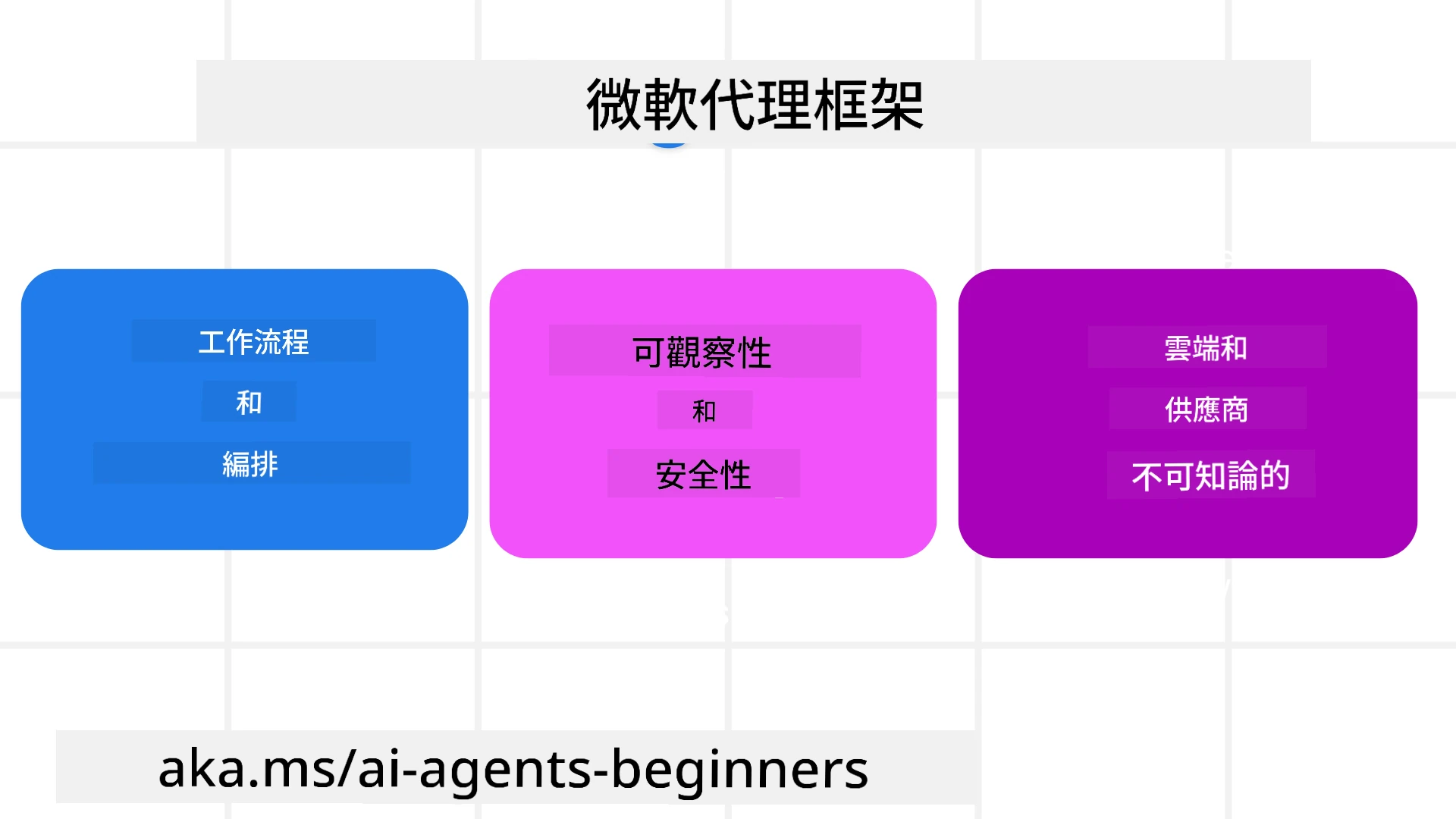
Microsoft Agent Framework (MAF) 建立在 Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen 的經驗和學習之上。它提供了靈活性以應對生產和研究環境中各種代理使用案例,包括:
- 順序代理編排:適用於需要逐步工作流程的場景。
- 並行編排:適用於代理需要同時完成任務的場景。
- 群組聊天編排:適用於代理可以共同協作完成一項任務的場景。
- 交接編排:適用於代理在完成子任務後將任務交接給其他代理的場景。
- 磁性編排:適用於管理代理創建並修改任務列表,並協調子代理完成任務的場景。
為了在生產環境中交付 AI 代理,MAF 還包含以下功能:
- 可觀測性:通過使用 OpenTelemetry,AI 代理的每個操作(包括工具調用、編排步驟、推理流程和性能監控)都可以在 Azure AI Foundry 儀表板中進行追蹤。
- 安全性:代理原生託管於 Azure AI Foundry,包含角色基於訪問控制、私密數據處理和內建內容安全等安全控制。
- 持久性:代理線程和工作流程可以暫停、恢復並從錯誤中恢復,支持長時間運行的過程。
- 控制:支持人類介入的工作流程,任務可標記為需要人類批准。
Microsoft Agent Framework 還專注於互操作性,具體表現為:
- 雲端無依賴性:代理可以在容器、內部部署以及多個不同的雲端中運行。
- 提供者無依賴性:代理可以通過您偏好的 SDK 創建,包括 Azure OpenAI 和 OpenAI。
- 整合開放標準:代理可以利用 Agent-to-Agent (A2A) 和 Model Context Protocol (MCP) 等協議來發現和使用其他代理和工具。
- 插件和連接器:可以連接到數據和記憶服務,例如 Microsoft Fabric、SharePoint、Pinecone 和 Qdrant。
接下來,我們將探討這些功能如何應用於 Microsoft Agent Framework 的核心概念。
Microsoft Agent Framework 的核心概念
代理
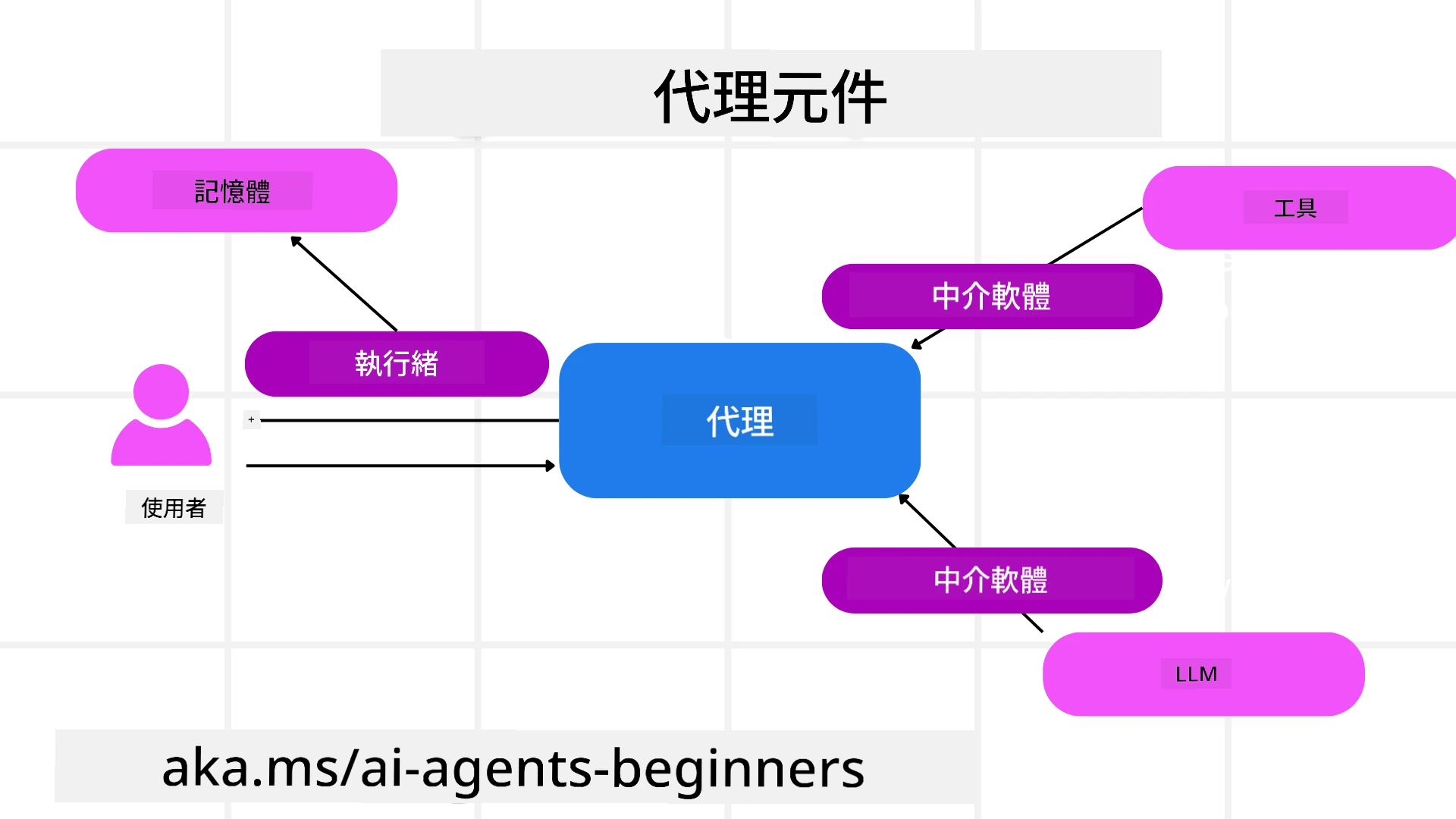
創建代理
代理的創建是通過定義推理服務(LLM 提供者)、一組 AI 代理需要遵循的指令以及分配的 name 來完成:
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at recommending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
上述範例使用了 Azure OpenAI,但代理也可以使用多種服務創建,包括 Azure AI Foundry Agent Service:
AzureAIAgentClient(async_credential=credential).create_agent( name="HelperAgent", instructions="You are a helpful assistant." ) as agent
OpenAI 的 Responses 和 ChatCompletion API:
agent = OpenAIResponsesClient().create_agent( name="WeatherBot", instructions="You are a helpful weather assistant.", )
agent = OpenAIChatClient().create_agent( name="HelpfulAssistant", instructions="You are a helpful assistant.", )
或者使用 A2A 協議的遠程代理:
agent = A2AAgent( name=agent_card.name, description=agent_card.description, agent_card=agent_card, url="https://your-a2a-agent-host" )
運行代理
代理可以通過 .run 或 .run_stream 方法運行,分別用於非流式或流式響應。
result = await agent.run("What are good places to visit in Amsterdam?")
print(result.text)
async for update in agent.run_stream("What are the good places to visit in Amsterdam?"):
if update.text:
print(update.text, end="", flush=True)
每次代理運行還可以選擇自定義參數,例如代理使用的 max_tokens、代理可以調用的 tools,甚至是代理使用的 model。
這在需要特定模型或工具來完成用戶任務的情況下非常有用。
工具
工具可以在定義代理時設置:
def get_attractions( location: Annotated[str, Field(description="The location to get the top tourist attractions for")], ) -> str: """Get the top tourist attractions for a given location.""" return f"The top attractions for {location} are."
# When creating a ChatAgent directly
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
也可以在運行代理時設置:
result1 = await agent.run( "What's the best place to visit in Seattle?", tools=[get_attractions] # Tool provided for this run only )
代理線程
代理線程用於處理多輪對話。線程可以通過以下方式創建:
- 使用
get_new_thread(),使線程可以隨時間保存。 - 在運行代理時自動創建線程,線程僅在當前運行期間存在。
創建線程的程式碼如下:
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
然後可以序列化線程以供以後使用:
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread()
# Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, how are you?", thread=thread)
# Serialize the thread for storage.
serialized_thread = await thread.serialize()
# Deserialize the thread state after loading from storage.
resumed_thread = await agent.deserialize_thread(serialized_thread)
代理中介軟件
代理通過工具和 LLM 完成用戶的任務。在某些場景中,我們希望在這些交互之間執行或追蹤操作。代理中介軟件使我們能夠做到這一點:
功能中介軟件
此中介軟件允許我們在代理調用的功能或工具之間執行操作。例如,您可能希望在功能調用時進行一些日誌記錄。
在以下程式碼中,next 定義是否應調用下一個中介軟件或實際功能。
async def logging_function_middleware(
context: FunctionInvocationContext,
next: Callable[[FunctionInvocationContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Function middleware that logs function execution."""
# Pre-processing: Log before function execution
print(f"[Function] Calling {context.function.name}")
# Continue to next middleware or function execution
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after function execution
print(f"[Function] {context.function.name} completed")
聊天中介軟件
此中介軟件允許我們在代理與 LLM 之間的請求中執行或記錄操作。
這包含重要信息,例如發送到 AI 服務的 messages。
async def logging_chat_middleware(
context: ChatContext,
next: Callable[[ChatContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Chat middleware that logs AI interactions."""
# Pre-processing: Log before AI call
print(f"[Chat] Sending {len(context.messages)} messages to AI")
# Continue to next middleware or AI service
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after AI response
print("[Chat] AI response received")
代理記憶
如 Agentic Memory 課程中所述,記憶是使代理能夠在不同上下文中運作的重要元素。MAF 提供了幾種不同類型的記憶:
內存存儲
這是在應用程序運行期間存儲在線程中的記憶。
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
持久消息
此記憶用於在不同會話中存儲對話歷史。它是通過 chat_message_store_factory 定義的:
from agent_framework import ChatMessageStore
# Create a custom message store
def create_message_store():
return ChatMessageStore()
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a Travel assistant.",
chat_message_store_factory=create_message_store
)
動態記憶
此記憶在代理運行之前添加到上下文中。這些記憶可以存儲在外部服務中,例如 mem0:
from agent_framework.mem0 import Mem0Provider
# Using Mem0 for advanced memory capabilities
memory_provider = Mem0Provider(
api_key="your-mem0-api-key",
user_id="user_123",
application_id="my_app"
)
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a helpful assistant with memory.",
context_providers=memory_provider
)
代理可觀測性
可觀測性對於構建可靠且可維護的代理系統至關重要。MAF 與 OpenTelemetry 集成,提供追蹤和計量以提高可觀測性。
from agent_framework.observability import get_tracer, get_meter
tracer = get_tracer()
meter = get_meter()
with tracer.start_as_current_span("my_custom_span"):
# do something
pass
counter = meter.create_counter("my_custom_counter")
counter.add(1, {"key": "value"})
工作流程
MAF 提供了預定義的步驟來完成任務,並將 AI 代理作為這些步驟中的組件。
工作流程由不同的組件組成,允許更好的控制流。工作流程還支持 多代理編排 和 檢查點 以保存工作流程狀態。
工作流程的核心組件包括:
執行器
執行器接收輸入消息,執行分配的任務,然後生成輸出消息。這使工作流程向完成更大的任務邁進。執行器可以是 AI 代理或自定義邏輯。
邊
邊用於定義工作流程中的消息流。這些可以是:
直接邊 - 執行器之間的簡單一對一連接:
from agent_framework import WorkflowBuilder
builder = WorkflowBuilder()
builder.add_edge(source_executor, target_executor)
builder.set_start_executor(source_executor)
workflow = builder.build()
條件邊 - 在滿足某些條件後激活。例如,當酒店房間不可用時,執行器可以建議其他選項。
Switch-case 邊 - 根據定義的條件將消息路由到不同的執行器。例如,如果旅行客戶具有優先訪問權,他們的任務將通過另一個工作流程處理。
Fan-out 邊 - 將一條消息發送到多個目標。
Fan-in 邊 - 收集來自不同執行器的多條消息並發送到一個目標。
事件
為了更好地觀測工作流程,MAF 提供了內建的執行事件,包括:
WorkflowStartedEvent- 工作流程執行開始WorkflowOutputEvent- 工作流程生成輸出WorkflowErrorEvent- 工作流程遇到錯誤ExecutorInvokeEvent- 執行器開始處理ExecutorCompleteEvent- 執行器完成處理RequestInfoEvent- 發出請求
從其他框架遷移(Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen)
MAF 與 Semantic Kernel 的差異
簡化的代理創建
Semantic Kernel 需要為每個代理創建一個 Kernel 實例。MAF 使用擴展為主要提供者提供簡化的方法。
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at reccomending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
代理線程創建
Semantic Kernel 需要手動創建線程。在 MAF 中,代理直接分配線程。
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
工具註冊
在 Semantic Kernel 中,工具註冊到 Kernel,然後將 Kernel 傳遞給代理。在 MAF 中,工具直接在代理創建過程中註冊。
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
MAF 與 AutoGen 的差異
Teams vs 工作流程
Teams 是 AutoGen 中代理事件驅動活動的結構。MAF 使用 Workflows,通過基於圖形的架構將數據路由到執行器。
工具創建
AutoGen 使用 FunctionTool 封裝代理調用的功能。MAF 使用 @ai_function,操作類似,但還能自動推斷每個功能的架構。
代理行為
在 AutoGen 中,代理默認是單輪代理,除非 max_tool_iterations 設置為更高值。在 MAF 中,ChatAgent 默認是多輪代理,意味著它會持續調用工具直到完成用戶的任務。
程式碼範例
Microsoft Agent Framework 的程式碼範例可在此存儲庫中找到,位於 xx-python-agent-framework 和 xx-dotnet-agent-framework 文件中。
有更多關於 Microsoft Agent Framework 的問題?
加入 Azure AI Foundry Discord,與其他學習者交流,參加辦公時間並解答您的 AI 代理相關問題。
免責聲明:
本文件已使用 AI 翻譯服務 Co-op Translator 進行翻譯。儘管我們致力於提供準確的翻譯,請注意自動翻譯可能包含錯誤或不準確之處。原始文件的母語版本應被視為權威來源。對於關鍵資訊,建議使用專業人工翻譯。我們對因使用此翻譯而引起的任何誤解或誤釋不承擔責任。