ai-agents-for-beginners
(Nhấn vào hình ảnh trên để xem video của bài học này)
Siêu nhận thức trong các tác nhân AI
Giới thiệu
Chào mừng bạn đến với bài học về siêu nhận thức trong các tác nhân AI! Chương này được thiết kế dành cho người mới bắt đầu, những người tò mò về cách các tác nhân AI có thể suy nghĩ về quá trình tư duy của chính mình. Sau khi hoàn thành bài học này, bạn sẽ hiểu các khái niệm chính và được trang bị các ví dụ thực tế để áp dụng siêu nhận thức trong thiết kế tác nhân AI.
Mục tiêu học tập
Sau khi hoàn thành bài học này, bạn sẽ có thể:
- Hiểu được tác động của các vòng lặp suy luận trong định nghĩa tác nhân.
- Sử dụng các kỹ thuật lập kế hoạch và đánh giá để hỗ trợ các tác nhân tự sửa lỗi.
- Tạo ra các tác nhân của riêng bạn có khả năng thao tác mã để hoàn thành nhiệm vụ.
Giới thiệu về Siêu Nhận Thức
Siêu nhận thức đề cập đến các quá trình nhận thức cấp cao hơn, liên quan đến việc suy nghĩ về chính quá trình tư duy của mình. Đối với các tác nhân AI, điều này có nghĩa là có khả năng đánh giá và điều chỉnh hành động của mình dựa trên sự tự nhận thức và kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ. Siêu nhận thức, hay “suy nghĩ về suy nghĩ,” là một khái niệm quan trọng trong việc phát triển các hệ thống AI có tính tác nhân. Nó bao gồm việc các hệ thống AI nhận thức được các quá trình nội bộ của chính mình và có khả năng giám sát, điều chỉnh, và thích nghi hành vi của mình. Giống như cách chúng ta đọc tình huống hoặc nhìn nhận một vấn đề. Sự tự nhận thức này có thể giúp các hệ thống AI đưa ra quyết định tốt hơn, xác định lỗi, và cải thiện hiệu suất theo thời gian - một lần nữa liên kết với bài kiểm tra Turing và cuộc tranh luận về việc liệu AI có thể chiếm lĩnh hay không.
Trong bối cảnh các hệ thống AI có tính tác nhân, siêu nhận thức có thể giúp giải quyết một số thách thức, chẳng hạn như:
- Minh bạch: Đảm bảo rằng các hệ thống AI có thể giải thích lý do và quyết định của mình.
- Suy luận: Nâng cao khả năng của các hệ thống AI trong việc tổng hợp thông tin và đưa ra quyết định hợp lý.
- Thích nghi: Cho phép các hệ thống AI điều chỉnh với môi trường mới và điều kiện thay đổi.
- Nhận thức: Cải thiện độ chính xác của các hệ thống AI trong việc nhận diện và diễn giải dữ liệu từ môi trường của chúng.
Siêu Nhận Thức là gì?
Siêu nhận thức, hay “suy nghĩ về suy nghĩ,” là một quá trình nhận thức cấp cao hơn liên quan đến sự tự nhận thức và tự điều chỉnh các quá trình nhận thức của chính mình. Trong lĩnh vực AI, siêu nhận thức trao quyền cho các tác nhân để đánh giá và điều chỉnh chiến lược và hành động của mình, dẫn đến khả năng giải quyết vấn đề và ra quyết định được cải thiện. Bằng cách hiểu siêu nhận thức, bạn có thể thiết kế các tác nhân AI không chỉ thông minh hơn mà còn thích nghi và hiệu quả hơn. Trong siêu nhận thức thực sự, bạn sẽ thấy AI lý luận rõ ràng về chính quá trình lý luận của mình.
Ví dụ: “Tôi ưu tiên các chuyến bay giá rẻ vì… Tôi có thể bỏ lỡ các chuyến bay trực tiếp, vậy hãy kiểm tra lại.” Theo dõi cách hoặc lý do tại sao nó chọn một tuyến đường nhất định.
- Nhận thấy rằng nó đã mắc lỗi vì quá phụ thuộc vào sở thích của người dùng từ lần trước, nên nó điều chỉnh chiến lược ra quyết định của mình chứ không chỉ là khuyến nghị cuối cùng.
- Chẩn đoán các mẫu như, “Bất cứ khi nào tôi thấy người dùng đề cập đến ‘quá đông đúc,’ tôi không chỉ nên loại bỏ một số điểm tham quan mà còn phản ánh rằng phương pháp chọn ‘điểm tham quan hàng đầu’ của tôi bị sai nếu tôi luôn xếp hạng theo mức độ phổ biến.”
Tầm Quan Trọng của Siêu Nhận Thức trong Các Tác Nhân AI
Siêu nhận thức đóng vai trò quan trọng trong thiết kế tác nhân AI vì nhiều lý do:
- Tự Phản Ánh: Các tác nhân có thể đánh giá hiệu suất của chính mình và xác định các lĩnh vực cần cải thiện.
- Thích Nghi: Các tác nhân có thể điều chỉnh chiến lược của mình dựa trên kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ và môi trường thay đổi.
- Sửa Lỗi: Các tác nhân có thể tự động phát hiện và sửa lỗi, dẫn đến kết quả chính xác hơn.
- Quản Lý Tài Nguyên: Các tác nhân có thể tối ưu hóa việc sử dụng tài nguyên, chẳng hạn như thời gian và sức mạnh tính toán, bằng cách lập kế hoạch và đánh giá hành động của mình.
Các Thành Phần của Một Tác Nhân AI
Trước khi đi sâu vào các quá trình siêu nhận thức, điều quan trọng là phải hiểu các thành phần cơ bản của một tác nhân AI. Một tác nhân AI thường bao gồm:
- Persona: Tính cách và đặc điểm của tác nhân, định nghĩa cách nó tương tác với người dùng.
- Công Cụ: Các khả năng và chức năng mà tác nhân có thể thực hiện.
- Kỹ Năng: Kiến thức và chuyên môn mà tác nhân sở hữu.
Các thành phần này phối hợp với nhau để tạo ra một “đơn vị chuyên môn” có thể thực hiện các nhiệm vụ cụ thể.
Ví dụ: Hãy xem xét một tác nhân du lịch, dịch vụ tác nhân không chỉ lập kế hoạch kỳ nghỉ của bạn mà còn điều chỉnh lộ trình của mình dựa trên dữ liệu thời gian thực và kinh nghiệm hành trình của khách hàng trước đó.
Ví dụ: Siêu Nhận Thức trong Dịch Vụ Tác Nhân Du Lịch
Hãy tưởng tượng bạn đang thiết kế một dịch vụ tác nhân du lịch được hỗ trợ bởi AI. Tác nhân này, “Travel Agent,” hỗ trợ người dùng lập kế hoạch kỳ nghỉ của họ. Để tích hợp siêu nhận thức, Travel Agent cần đánh giá và điều chỉnh hành động của mình dựa trên sự tự nhận thức và kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ. Đây là cách siêu nhận thức có thể đóng vai trò:
Nhiệm Vụ Hiện Tại
Nhiệm vụ hiện tại là giúp người dùng lập kế hoạch chuyến đi đến Paris.
Các Bước Hoàn Thành Nhiệm Vụ
- Thu Thập Sở Thích Người Dùng: Hỏi người dùng về ngày đi, ngân sách, sở thích (ví dụ: bảo tàng, ẩm thực, mua sắm), và bất kỳ yêu cầu cụ thể nào.
- Truy Xuất Thông Tin: Tìm kiếm các tùy chọn chuyến bay, chỗ ở, điểm tham quan, và nhà hàng phù hợp với sở thích của người dùng.
- Tạo Khuyến Nghị: Cung cấp một hành trình cá nhân hóa với chi tiết chuyến bay, đặt phòng khách sạn, và các hoạt động được đề xuất.
- Điều Chỉnh Dựa Trên Phản Hồi: Hỏi người dùng về phản hồi đối với các khuyến nghị và thực hiện các điều chỉnh cần thiết.
Tài Nguyên Cần Thiết
- Truy cập cơ sở dữ liệu đặt vé chuyến bay và khách sạn.
- Thông tin về các điểm tham quan và nhà hàng ở Paris.
- Dữ liệu phản hồi của người dùng từ các tương tác trước đó.
Kinh Nghiệm và Tự Phản Ánh
Travel Agent sử dụng siêu nhận thức để đánh giá hiệu suất của mình và học hỏi từ kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ. Ví dụ:
- Phân Tích Phản Hồi Người Dùng: Travel Agent xem xét phản hồi của người dùng để xác định các khuyến nghị nào được đón nhận tốt và các khuyến nghị nào không. Nó điều chỉnh các đề xuất trong tương lai cho phù hợp.
- Thích Nghi: Nếu người dùng trước đây đã đề cập đến việc không thích những nơi đông đúc, Travel Agent sẽ tránh đề xuất các điểm du lịch phổ biến vào giờ cao điểm trong tương lai.
- Sửa Lỗi: Nếu Travel Agent đã mắc lỗi trong một lần đặt vé trước đó, chẳng hạn như đề xuất một khách sạn đã hết phòng, nó học cách kiểm tra kỹ hơn về tình trạng phòng trước khi đưa ra khuyến nghị.
Ví Dụ Thực Tế Cho Nhà Phát Triển
Dưới đây là một ví dụ đơn giản về cách mã của Travel Agent có thể trông như thế nào khi tích hợp siêu nhận thức:
class Travel_Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.user_preferences = {}
self.experience_data = []
def gather_preferences(self, preferences):
self.user_preferences = preferences
def retrieve_information(self):
# Search for flights, hotels, and attractions based on preferences
flights = search_flights(self.user_preferences)
hotels = search_hotels(self.user_preferences)
attractions = search_attractions(self.user_preferences)
return flights, hotels, attractions
def generate_recommendations(self):
flights, hotels, attractions = self.retrieve_information()
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions)
return itinerary
def adjust_based_on_feedback(self, feedback):
self.experience_data.append(feedback)
# Analyze feedback and adjust future recommendations
self.user_preferences = adjust_preferences(self.user_preferences, feedback)
# Example usage
travel_agent = Travel_Agent()
preferences = {
"destination": "Paris",
"dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10",
"budget": "moderate",
"interests": ["museums", "cuisine"]
}
travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences)
itinerary = travel_agent.generate_recommendations()
print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]}
travel_agent.adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback)
Tại Sao Siêu Nhận Thức Quan Trọng
- Tự Phản Ánh: Các tác nhân có thể phân tích hiệu suất của mình và xác định các lĩnh vực cần cải thiện.
- Thích Nghi: Các tác nhân có thể điều chỉnh chiến lược dựa trên phản hồi và điều kiện thay đổi.
- Sửa Lỗi: Các tác nhân có thể tự động phát hiện và sửa lỗi.
- Quản Lý Tài Nguyên: Các tác nhân có thể tối ưu hóa việc sử dụng tài nguyên, chẳng hạn như thời gian và sức mạnh tính toán.
Bằng cách tích hợp siêu nhận thức, Travel Agent có thể cung cấp các khuyến nghị du lịch cá nhân hóa và chính xác hơn, nâng cao trải nghiệm tổng thể của người dùng.
2. Lập Kế Hoạch trong Các Tác Nhân
Lập kế hoạch là một thành phần quan trọng trong hành vi của tác nhân AI. Nó liên quan đến việc phác thảo các bước cần thiết để đạt được mục tiêu, xem xét trạng thái hiện tại, tài nguyên, và các trở ngại có thể xảy ra.
Các Yếu Tố của Lập Kế Hoạch
- Nhiệm Vụ Hiện Tại: Xác định rõ nhiệm vụ.
- Các Bước Hoàn Thành Nhiệm Vụ: Chia nhỏ nhiệm vụ thành các bước có thể quản lý được.
- Tài Nguyên Cần Thiết: Xác định các tài nguyên cần thiết.
- Kinh Nghiệm: Sử dụng kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ để thông báo cho việc lập kế hoạch.
Ví dụ: Dưới đây là các bước Travel Agent cần thực hiện để hỗ trợ người dùng lập kế hoạch chuyến đi một cách hiệu quả:
Các Bước cho Travel Agent
- Thu Thập Sở Thích Người Dùng
- Hỏi người dùng về chi tiết ngày đi, ngân sách, sở thích, và bất kỳ yêu cầu cụ thể nào.
- Ví dụ: “Bạn dự định đi du lịch vào thời gian nào?” “Phạm vi ngân sách của bạn là bao nhiêu?” “Bạn thích những hoạt động nào trong kỳ nghỉ?”
- Truy Xuất Thông Tin
- Tìm kiếm các tùy chọn du lịch phù hợp dựa trên sở thích của người dùng.
- Chuyến Bay: Tìm các chuyến bay có sẵn trong phạm vi ngân sách và ngày đi ưa thích của người dùng.
- Chỗ Ở: Tìm khách sạn hoặc nhà thuê phù hợp với sở thích của người dùng về vị trí, giá cả, và tiện nghi.
- Điểm Tham Quan và Nhà Hàng: Xác định các điểm tham quan, hoạt động, và lựa chọn ăn uống phổ biến phù hợp với sở thích của người dùng.
- Tạo Khuyến Nghị
- Biên soạn thông tin đã truy xuất thành một hành trình cá nhân hóa.
- Cung cấp chi tiết như tùy chọn chuyến bay, đặt phòng khách sạn, và các hoạt động được đề xuất, đảm bảo điều chỉnh các khuyến nghị theo sở thích của người dùng.
- Trình Bày Hành Trình cho Người Dùng
- Chia sẻ hành trình được đề xuất với người dùng để họ xem xét.
- Ví dụ: “Đây là hành trình được đề xuất cho chuyến đi của bạn đến Paris. Nó bao gồm chi tiết chuyến bay, đặt phòng khách sạn, và danh sách các hoạt động và nhà hàng được đề xuất. Hãy cho tôi biết suy nghĩ của bạn!”
- Thu Thập Phản Hồi
- Hỏi người dùng về phản hồi đối với hành trình được đề xuất.
- Ví dụ: “Bạn có thích các tùy chọn chuyến bay không?” “Khách sạn có phù hợp với nhu cầu của bạn không?” “Có hoạt động nào bạn muốn thêm hoặc loại bỏ không?”
- Điều Chỉnh Dựa Trên Phản Hồi
- Điều chỉnh hành trình dựa trên phản hồi của người dùng.
- Thực hiện các thay đổi cần thiết đối với các khuyến nghị về chuyến bay, chỗ ở, và hoạt động để phù hợp hơn với sở thích của người dùng.
- Xác Nhận Cuối Cùng
- Trình bày hành trình đã cập nhật cho người dùng để xác nhận cuối cùng.
- Ví dụ: “Tôi đã thực hiện các điều chỉnh dựa trên phản hồi của bạn. Đây là hành trình đã cập nhật. Mọi thứ có ổn không?”
- Đặt Vé và Xác Nhận Đặt Chỗ
- Sau khi người dùng phê duyệt hành trình, tiến hành đặt vé chuyến bay, chỗ ở, và bất kỳ hoạt động nào đã được lên kế hoạch trước.
- Gửi chi tiết xác nhận cho người dùng.
- Cung Cấp Hỗ Trợ Liên Tục
- Luôn sẵn sàng hỗ trợ người dùng với bất kỳ thay đổi hoặc yêu cầu bổ sung nào trước và trong chuyến đi của họ.
- Ví dụ: “Nếu bạn cần bất kỳ sự hỗ trợ nào thêm trong chuyến đi của mình, hãy liên hệ với tôi bất cứ lúc nào!”
Tương Tác Ví Dụ
class Travel_Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.user_preferences = {}
self.experience_data = []
def gather_preferences(self, preferences):
self.user_preferences = preferences
def retrieve_information(self):
flights = search_flights(self.user_preferences)
hotels = search_hotels(self.user_preferences)
attractions = search_attractions(self.user_preferences)
return flights, hotels, attractions
def generate_recommendations(self):
flights, hotels, attractions = self.retrieve_information()
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions)
return itinerary
def adjust_based_on_feedback(self, feedback):
self.experience_data.append(feedback)
self.user_preferences = adjust_preferences(self.user_preferences, feedback)
# Example usage within a booing request
travel_agent = Travel_Agent()
preferences = {
"destination": "Paris",
"dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10",
"budget": "moderate",
"interests": ["museums", "cuisine"]
}
travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences)
itinerary = travel_agent.generate_recommendations()
print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]}
travel_agent.adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback)
3. Hệ Thống RAG Sửa Lỗi
Trước tiên, hãy bắt đầu bằng cách hiểu sự khác biệt giữa Công Cụ RAG và Tải Ngữ Cảnh Dự Đoán
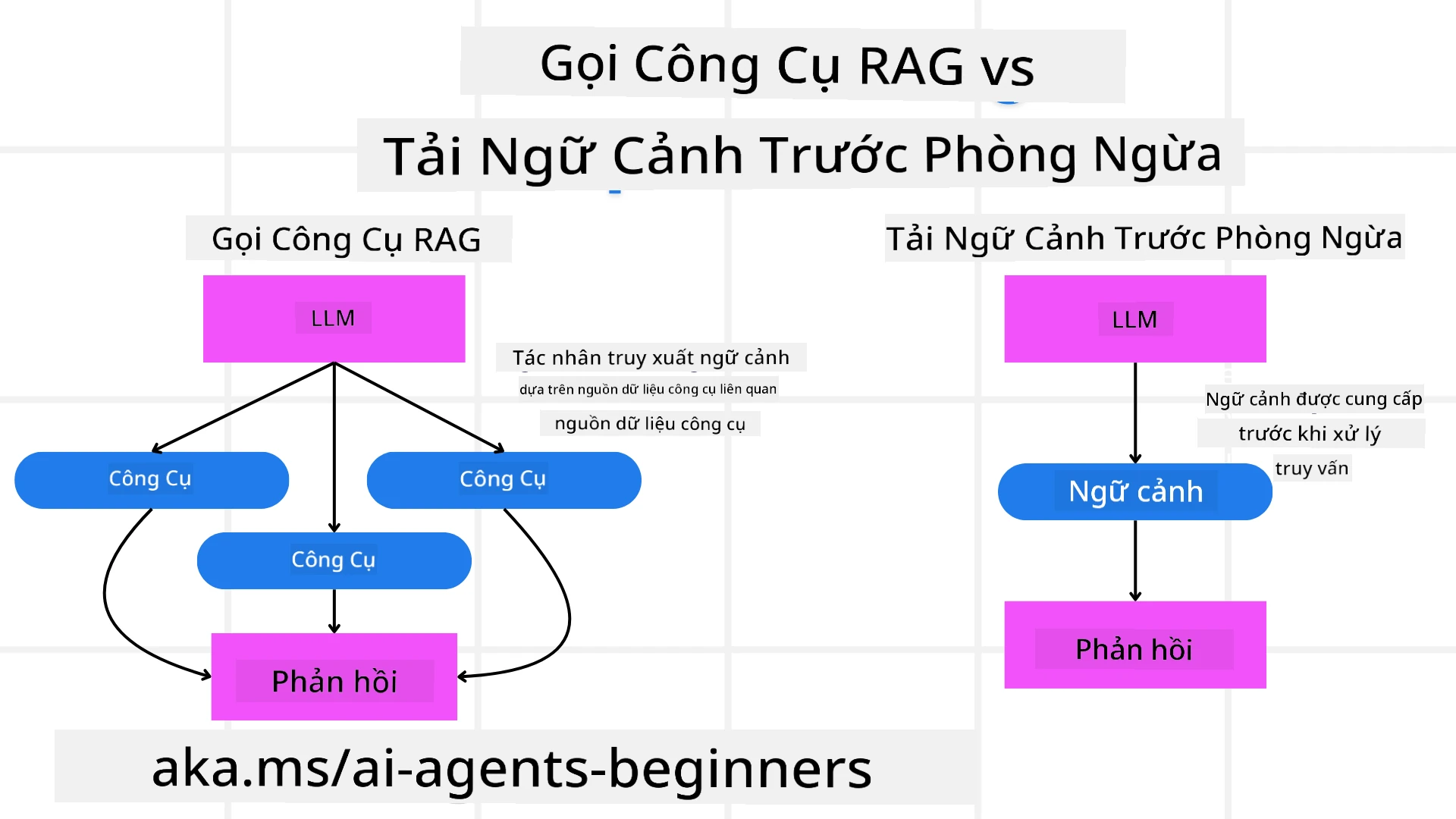
Tạo Dữ Liệu Tăng Cường Truy Xuất (RAG)
RAG kết hợp một hệ thống truy xuất với một mô hình tạo dữ liệu. Khi có một truy vấn, hệ thống truy xuất sẽ lấy các tài liệu hoặc dữ liệu liên quan từ một nguồn bên ngoài, và thông tin được truy xuất này được sử dụng để tăng cường đầu vào cho mô hình tạo dữ liệu. Điều này giúp mô hình tạo ra các phản hồi chính xác và phù hợp với ngữ cảnh hơn.
Trong một hệ thống RAG, tác nhân truy xuất thông tin liên quan từ cơ sở tri thức và sử dụng nó để tạo ra các phản hồi hoặc hành động phù hợp.
Phương Pháp RAG Sửa Lỗi
Phương pháp RAG Sửa Lỗi tập trung vào việc sử dụng các kỹ thuật RAG để sửa lỗi và cải thiện độ chính xác của các tác nhân AI. Điều này bao gồm:
- Kỹ Thuật Nhắc Nhở: Sử dụng các nhắc nhở cụ thể để hướng dẫn tác nhân trong việc truy xuất thông tin liên quan.
- Công Cụ: Triển khai các thuật toán và cơ chế cho phép tác nhân đánh giá mức độ liên quan của thông tin được truy xuất và tạo ra các phản hồi chính xác.
- Đánh Giá: Liên tục đánh giá hiệu suất của tác nhân và thực hiện các điều chỉnh để cải thiện độ chính xác và hiệu quả của nó.
Ví Dụ: RAG Sửa Lỗi trong Tác Nhân Tìm Kiếm
Hãy xem xét một tác nhân tìm kiếm truy xuất thông tin từ web để trả lời các truy vấn của người dùng. Phương pháp RAG Sửa Lỗi có thể bao gồm:
- Kỹ Thuật Nhắc Nhở: Hình thành các truy vấn tìm kiếm dựa trên đầu vào của người dùng.
- Công Cụ: Sử dụng xử lý ngôn ngữ tự nhiên và các thuật toán học máy để xếp hạng và lọc kết quả tìm kiếm.
- Đánh Giá: Phân tích phản hồi của người dùng để xác định và sửa các lỗi trong thông tin được truy xuất.
RAG Sửa Lỗi trong Travel Agent
RAG Sửa Lỗi (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) nâng cao khả năng của AI trong việc truy xuất và tạo thông tin đồng thời sửa các lỗi. Hãy xem Travel Agent có thể sử dụng phương pháp RAG Sửa Lỗi để cung cấp các khuyến nghị du lịch chính xác và phù hợp hơn.
Điều này bao gồm:
- Kỹ Thuật Nhắc Nhở: Sử dụng các nhắc nhở cụ thể để hướng dẫn tác nhân trong việc truy xuất thông tin liên quan.
- Công Cụ: Triển khai các thuật toán và cơ chế cho phép tác nhân đánh giá mức độ liên quan của thông tin được truy xuất và tạo ra các phản hồi chính xác.
- Đánh Giá: Liên tục đánh giá hiệu suất của tác nhân và thực hiện các điều chỉnh để cải thiện độ chính xác và hiệu quả của nó.
Các Bước Triển Khai RAG Sửa Lỗi trong Travel Agent
- Tương Tác Ban Đầu với Người Dùng
- Travel Agent thu thập các sở thích ban đầu từ người dùng, chẳng hạn như điểm đến, ngày đi, ngân sách, và sở thích.
-
Ví dụ:
preferences = { "destination": "Paris", "dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10", "budget": "moderate", "interests": ["museums", "cuisine"] }
- Truy Xuất Thông Tin
- Travel Agent truy xuất thông tin về chuyến bay, chỗ ở, điểm tham quan, và nhà hàng dựa trên sở thích của người dùng.
-
Ví dụ:
flights = search_flights(preferences) hotels = search_hotels(preferences) attractions = search_attractions(preferences)
- Tạo Khuyến Nghị Ban Đầu
- Travel Agent sử dụng thông tin được truy xuất để tạo một hành trình cá nhân hóa.
-
Ví dụ:
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions) print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
class Travel_Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.user_preferences = {}
self.experience_data = []
def gather_preferences(self, preferences):
self.user_preferences = preferences
def retrieve_information(self):
flights = search_flights(self.user_preferences)
hotels = search_hotels(self.user_preferences)
attractions = search_attractions(self.user_preferences)
return flights, hotels, attractions
def generate_recommendations(self):
flights, hotels, attractions = self.retrieve_information()
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions)
return itinerary
def adjust_based_on_feedback(self, feedback):
self.experience_data.append(feedback)
self.user_preferences = adjust_preferences(self.user_preferences, feedback)
new_itinerary = self.generate_recommendations()
return new_itinerary
# Example usage
travel_agent = Travel_Agent()
preferences = {
"destination": "Paris",
"dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10",
"budget": "moderate",
"interests": ["museums", "cuisine"]
}
travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences)
itinerary = travel_agent.generate_recommendations()
print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]}
new_itinerary = travel_agent.adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback)
print("Updated Itinerary:", new_itinerary)
Tải Trước Ngữ Cảnh Một Cách Chủ Động
Tải trước ngữ cảnh một cách chủ động liên quan đến việc nạp thông tin nền hoặc ngữ cảnh liên quan vào mô hình trước khi xử lý truy vấn. Điều này có nghĩa là mô hình sẽ có sẵn thông tin từ đầu, giúp nó tạo ra các phản hồi chính xác hơn mà không cần phải truy xuất thêm dữ liệu trong quá trình xử lý.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ đơn giản về cách tải trước ngữ cảnh có thể được áp dụng cho một ứng dụng đại lý du lịch bằng Python:
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self):
# Pre-load popular destinations and their information
self.context = {
"Paris": {"country": "France", "currency": "Euro", "language": "French", "attractions": ["Eiffel Tower", "Louvre Museum"]},
"Tokyo": {"country": "Japan", "currency": "Yen", "language": "Japanese", "attractions": ["Tokyo Tower", "Shibuya Crossing"]},
"New York": {"country": "USA", "currency": "Dollar", "language": "English", "attractions": ["Statue of Liberty", "Times Square"]},
"Sydney": {"country": "Australia", "currency": "Dollar", "language": "English", "attractions": ["Sydney Opera House", "Bondi Beach"]}
}
def get_destination_info(self, destination):
# Fetch destination information from pre-loaded context
info = self.context.get(destination)
if info:
return f"{destination}:\nCountry: {info['country']}\nCurrency: {info['currency']}\nLanguage: {info['language']}\nAttractions: {', '.join(info['attractions'])}"
else:
return f"Sorry, we don't have information on {destination}."
# Example usage
travel_agent = TravelAgent()
print(travel_agent.get_destination_info("Paris"))
print(travel_agent.get_destination_info("Tokyo"))
Giải Thích
-
Khởi Tạo (phương thức
__init__): LớpTravelAgenttải trước một từ điển chứa thông tin về các điểm đến phổ biến như Paris, Tokyo, New York và Sydney. Từ điển này bao gồm các chi tiết như quốc gia, tiền tệ, ngôn ngữ và các điểm tham quan chính của từng điểm đến. -
Truy Xuất Thông Tin (phương thức
get_destination_info): Khi người dùng hỏi về một điểm đến cụ thể, phương thứcget_destination_infosẽ lấy thông tin liên quan từ từ điển ngữ cảnh đã tải trước.
Bằng cách tải trước ngữ cảnh, ứng dụng đại lý du lịch có thể nhanh chóng phản hồi các truy vấn của người dùng mà không cần phải truy xuất thông tin từ nguồn bên ngoài trong thời gian thực. Điều này làm cho ứng dụng trở nên hiệu quả và phản hồi nhanh hơn.
Khởi Động Kế Hoạch Với Mục Tiêu Trước Khi Lặp
Khởi động kế hoạch với một mục tiêu liên quan đến việc bắt đầu với một mục tiêu rõ ràng hoặc kết quả mong muốn. Bằng cách xác định mục tiêu này từ đầu, mô hình có thể sử dụng nó như một nguyên tắc hướng dẫn trong suốt quá trình lặp. Điều này giúp đảm bảo rằng mỗi lần lặp đều tiến gần hơn đến việc đạt được kết quả mong muốn, làm cho quá trình trở nên hiệu quả và tập trung hơn.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ về cách khởi động kế hoạch du lịch với một mục tiêu trước khi lặp cho một đại lý du lịch bằng Python:
Kịch Bản
Một đại lý du lịch muốn lập kế hoạch kỳ nghỉ tùy chỉnh cho khách hàng. Mục tiêu là tạo ra một lịch trình du lịch tối ưu hóa sự hài lòng của khách hàng dựa trên sở thích và ngân sách của họ.
Các Bước
- Xác định sở thích và ngân sách của khách hàng.
- Khởi động kế hoạch ban đầu dựa trên các sở thích này.
- Lặp lại để tinh chỉnh kế hoạch, tối ưu hóa sự hài lòng của khách hàng.
Mã Python
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self, destinations):
self.destinations = destinations
def bootstrap_plan(self, preferences, budget):
plan = []
total_cost = 0
for destination in self.destinations:
if total_cost + destination['cost'] <= budget and self.match_preferences(destination, preferences):
plan.append(destination)
total_cost += destination['cost']
return plan
def match_preferences(self, destination, preferences):
for key, value in preferences.items():
if destination.get(key) != value:
return False
return True
def iterate_plan(self, plan, preferences, budget):
for i in range(len(plan)):
for destination in self.destinations:
if destination not in plan and self.match_preferences(destination, preferences) and self.calculate_cost(plan, destination) <= budget:
plan[i] = destination
break
return plan
def calculate_cost(self, plan, new_destination):
return sum(destination['cost'] for destination in plan) + new_destination['cost']
# Example usage
destinations = [
{"name": "Paris", "cost": 1000, "activity": "sightseeing"},
{"name": "Tokyo", "cost": 1200, "activity": "shopping"},
{"name": "New York", "cost": 900, "activity": "sightseeing"},
{"name": "Sydney", "cost": 1100, "activity": "beach"},
]
preferences = {"activity": "sightseeing"}
budget = 2000
travel_agent = TravelAgent(destinations)
initial_plan = travel_agent.bootstrap_plan(preferences, budget)
print("Initial Plan:", initial_plan)
refined_plan = travel_agent.iterate_plan(initial_plan, preferences, budget)
print("Refined Plan:", refined_plan)
Giải Thích Mã
-
Khởi Tạo (phương thức
__init__): LớpTravelAgentđược khởi tạo với danh sách các điểm đến tiềm năng, mỗi điểm đến có các thuộc tính như tên, chi phí và loại hoạt động. -
Khởi Động Kế Hoạch (phương thức
bootstrap_plan): Phương thức này tạo ra một kế hoạch du lịch ban đầu dựa trên sở thích và ngân sách của khách hàng. Nó lặp qua danh sách các điểm đến và thêm chúng vào kế hoạch nếu chúng phù hợp với sở thích của khách hàng và nằm trong ngân sách. -
Khớp Sở Thích (phương thức
match_preferences): Phương thức này kiểm tra xem một điểm đến có phù hợp với sở thích của khách hàng hay không. -
Lặp Kế Hoạch (phương thức
iterate_plan): Phương thức này tinh chỉnh kế hoạch ban đầu bằng cách cố gắng thay thế từng điểm đến trong kế hoạch bằng một lựa chọn tốt hơn, dựa trên sở thích và ngân sách của khách hàng. -
Tính Toán Chi Phí (phương thức
calculate_cost): Phương thức này tính toán tổng chi phí của kế hoạch hiện tại, bao gồm cả điểm đến mới tiềm năng.
Ví Dụ Sử Dụng
- Kế Hoạch Ban Đầu: Đại lý du lịch tạo ra một kế hoạch ban đầu dựa trên sở thích của khách hàng về tham quan và ngân sách $2000.
- Kế Hoạch Tinh Chỉnh: Đại lý du lịch lặp lại kế hoạch, tối ưu hóa theo sở thích và ngân sách của khách hàng.
Bằng cách khởi động kế hoạch với một mục tiêu rõ ràng (ví dụ: tối đa hóa sự hài lòng của khách hàng) và lặp lại để tinh chỉnh kế hoạch, đại lý du lịch có thể tạo ra một lịch trình du lịch tùy chỉnh và tối ưu hóa cho khách hàng. Phương pháp này đảm bảo rằng kế hoạch du lịch phù hợp với sở thích và ngân sách của khách hàng từ đầu và được cải thiện qua từng lần lặp.
Tận Dụng LLM Để Xếp Hạng Lại và Chấm Điểm
Các Mô Hình Ngôn Ngữ Lớn (LLM) có thể được sử dụng để xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm bằng cách đánh giá mức độ liên quan và chất lượng của các tài liệu được truy xuất hoặc các phản hồi được tạo ra. Dưới đây là cách hoạt động:
Truy Xuất: Bước truy xuất ban đầu lấy một tập hợp các tài liệu hoặc phản hồi ứng viên dựa trên truy vấn.
Xếp Hạng Lại: LLM đánh giá các ứng viên này và xếp hạng lại chúng dựa trên mức độ liên quan và chất lượng. Bước này đảm bảo rằng thông tin liên quan và chất lượng cao nhất được trình bày đầu tiên.
Chấm Điểm: LLM gán điểm cho từng ứng viên, phản ánh mức độ liên quan và chất lượng của chúng. Điều này giúp chọn ra phản hồi hoặc tài liệu tốt nhất cho người dùng.
Bằng cách tận dụng LLM để xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm, hệ thống có thể cung cấp thông tin chính xác và phù hợp với ngữ cảnh hơn, cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng tổng thể.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ về cách một đại lý du lịch có thể sử dụng Mô Hình Ngôn Ngữ Lớn (LLM) để xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm các điểm đến du lịch dựa trên sở thích của người dùng bằng Python:
Kịch Bản - Du Lịch Dựa Trên Sở Thích
Một đại lý du lịch muốn đề xuất các điểm đến du lịch tốt nhất cho khách hàng dựa trên sở thích của họ. LLM sẽ giúp xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm các điểm đến để đảm bảo các lựa chọn phù hợp nhất được trình bày.
Các Bước:
- Thu thập sở thích của người dùng.
- Truy xuất danh sách các điểm đến du lịch tiềm năng.
- Sử dụng LLM để xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm các điểm đến dựa trên sở thích của người dùng.
Dưới đây là cách bạn có thể cập nhật ví dụ trước để sử dụng Azure OpenAI Services:
Yêu Cầu
- Bạn cần có một đăng ký Azure.
- Tạo một tài nguyên Azure OpenAI và lấy khóa API của bạn.
Mã Python Ví Dụ
import requests
import json
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self, destinations):
self.destinations = destinations
def get_recommendations(self, preferences, api_key, endpoint):
# Generate a prompt for the Azure OpenAI
prompt = self.generate_prompt(preferences)
# Define headers and payload for the request
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': f'Bearer {api_key}'
}
payload = {
"prompt": prompt,
"max_tokens": 150,
"temperature": 0.7
}
# Call the Azure OpenAI API to get the re-ranked and scored destinations
response = requests.post(endpoint, headers=headers, json=payload)
response_data = response.json()
# Extract and return the recommendations
recommendations = response_data['choices'][0]['text'].strip().split('\n')
return recommendations
def generate_prompt(self, preferences):
prompt = "Here are the travel destinations ranked and scored based on the following user preferences:\n"
for key, value in preferences.items():
prompt += f"{key}: {value}\n"
prompt += "\nDestinations:\n"
for destination in self.destinations:
prompt += f"- {destination['name']}: {destination['description']}\n"
return prompt
# Example usage
destinations = [
{"name": "Paris", "description": "City of lights, known for its art, fashion, and culture."},
{"name": "Tokyo", "description": "Vibrant city, famous for its modernity and traditional temples."},
{"name": "New York", "description": "The city that never sleeps, with iconic landmarks and diverse culture."},
{"name": "Sydney", "description": "Beautiful harbour city, known for its opera house and stunning beaches."},
]
preferences = {"activity": "sightseeing", "culture": "diverse"}
api_key = 'your_azure_openai_api_key'
endpoint = 'https://your-endpoint.com/openai/deployments/your-deployment-name/completions?api-version=2022-12-01'
travel_agent = TravelAgent(destinations)
recommendations = travel_agent.get_recommendations(preferences, api_key, endpoint)
print("Recommended Destinations:")
for rec in recommendations:
print(rec)
Giải Thích Mã - Preference Booker
-
Khởi Tạo: Lớp
TravelAgentđược khởi tạo với danh sách các điểm đến du lịch tiềm năng, mỗi điểm đến có các thuộc tính như tên và mô tả. -
Lấy Đề Xuất (phương thức
get_recommendations): Phương thức này tạo ra một prompt cho dịch vụ Azure OpenAI dựa trên sở thích của người dùng và thực hiện yêu cầu HTTP POST tới API Azure OpenAI để nhận các điểm đến được xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm. -
Tạo Prompt (phương thức
generate_prompt): Phương thức này xây dựng một prompt cho Azure OpenAI, bao gồm sở thích của người dùng và danh sách các điểm đến. Prompt hướng dẫn mô hình xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm các điểm đến dựa trên sở thích được cung cấp. -
Gọi API: Thư viện
requestsđược sử dụng để thực hiện yêu cầu HTTP POST tới endpoint API Azure OpenAI. Phản hồi chứa các điểm đến được xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm. -
Ví Dụ Sử Dụng: Đại lý du lịch thu thập sở thích của người dùng (ví dụ: quan tâm đến tham quan và văn hóa đa dạng) và sử dụng dịch vụ Azure OpenAI để nhận các đề xuất được xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm cho các điểm đến du lịch.
Hãy chắc chắn thay thế your_azure_openai_api_key bằng khóa API Azure OpenAI thực tế của bạn và https://your-endpoint.com/... bằng URL endpoint thực tế của triển khai Azure OpenAI của bạn.
Bằng cách tận dụng LLM để xếp hạng lại và chấm điểm, đại lý du lịch có thể cung cấp các đề xuất du lịch cá nhân hóa và phù hợp hơn cho khách hàng, nâng cao trải nghiệm tổng thể của họ.
Ví dụ thực tế: Tìm kiếm theo ý định trong Travel Agent
Hãy lấy Travel Agent làm ví dụ để xem cách triển khai tìm kiếm theo ý định.
-
Thu thập sở thích của người dùng
class Travel_Agent: def __init__(self): self.user_preferences = {} def gather_preferences(self, preferences): self.user_preferences = preferences -
Hiểu ý định của người dùng
def identify_intent(query): if "book" in query or "purchase" in query: return "transactional" elif "website" in query or "official" in query: return "navigational" else: return "informational" -
Nhận thức ngữ cảnh
def analyze_context(query, user_history): # Combine current query with user history to understand context context = { "current_query": query, "user_history": user_history } return context -
Tìm kiếm và cá nhân hóa kết quả
def search_with_intent(query, preferences, user_history): intent = identify_intent(query) context = analyze_context(query, user_history) if intent == "informational": search_results = search_information(query, preferences) elif intent == "navigational": search_results = search_navigation(query) elif intent == "transactional": search_results = search_transaction(query, preferences) personalized_results = personalize_results(search_results, user_history) return personalized_results def search_information(query, preferences): # Example search logic for informational intent results = search_web(f"best {preferences['interests']} in {preferences['destination']}") return results def search_navigation(query): # Example search logic for navigational intent results = search_web(query) return results def search_transaction(query, preferences): # Example search logic for transactional intent results = search_web(f"book {query} to {preferences['destination']}") return results def personalize_results(results, user_history): # Example personalization logic personalized = [result for result in results if result not in user_history] return personalized[:10] # Return top 10 personalized results -
Ví dụ sử dụng
travel_agent = Travel_Agent() preferences = { "destination": "Paris", "interests": ["museums", "cuisine"] } travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences) user_history = ["Louvre Museum website", "Book flight to Paris"] query = "best museums in Paris" results = search_with_intent(query, preferences, user_history) print("Search Results:", results)
4. Tạo mã như một công cụ
Các tác nhân tạo mã sử dụng mô hình AI để viết và thực thi mã, giải quyết các vấn đề phức tạp và tự động hóa nhiệm vụ.
Tác nhân tạo mã
Tác nhân tạo mã sử dụng mô hình AI sinh để viết và thực thi mã. Những tác nhân này có thể giải quyết các vấn đề phức tạp, tự động hóa nhiệm vụ, và cung cấp những thông tin giá trị bằng cách tạo và chạy mã trong nhiều ngôn ngữ lập trình.
Ứng dụng thực tế
- Tự động tạo mã: Tạo đoạn mã cho các nhiệm vụ cụ thể, như phân tích dữ liệu, thu thập thông tin từ web, hoặc học máy.
- SQL như một RAG: Sử dụng truy vấn SQL để lấy và xử lý dữ liệu từ cơ sở dữ liệu.
- Giải quyết vấn đề: Tạo và thực thi mã để giải quyết các vấn đề cụ thể, như tối ưu hóa thuật toán hoặc phân tích dữ liệu.
Ví dụ: Tác nhân tạo mã cho phân tích dữ liệu
Hãy tưởng tượng bạn đang thiết kế một tác nhân tạo mã. Đây là cách nó có thể hoạt động:
- Nhiệm vụ: Phân tích một tập dữ liệu để xác định xu hướng và mẫu.
- Các bước:
- Tải tập dữ liệu vào công cụ phân tích dữ liệu.
- Tạo truy vấn SQL để lọc và tổng hợp dữ liệu.
- Thực thi các truy vấn và lấy kết quả.
- Sử dụng kết quả để tạo hình ảnh hóa và thông tin chi tiết.
- Tài nguyên cần thiết: Truy cập tập dữ liệu, công cụ phân tích dữ liệu, và khả năng SQL.
- Kinh nghiệm: Sử dụng kết quả phân tích trước đó để cải thiện độ chính xác và sự liên quan của các phân tích trong tương lai.
Ví dụ: Tác nhân tạo mã cho Travel Agent
Trong ví dụ này, chúng ta sẽ thiết kế một tác nhân tạo mã, Travel Agent, để hỗ trợ người dùng lập kế hoạch du lịch bằng cách tạo và thực thi mã. Tác nhân này có thể xử lý các nhiệm vụ như tìm kiếm tùy chọn du lịch, lọc kết quả, và lập kế hoạch hành trình bằng AI sinh.
Tổng quan về tác nhân tạo mã
- Thu thập sở thích của người dùng: Thu thập thông tin đầu vào của người dùng như điểm đến, ngày du lịch, ngân sách, và sở thích.
- Tạo mã để lấy dữ liệu: Tạo đoạn mã để lấy dữ liệu về chuyến bay, khách sạn, và điểm tham quan.
- Thực thi mã đã tạo: Chạy đoạn mã đã tạo để lấy thông tin thời gian thực.
- Tạo hành trình: Tổng hợp dữ liệu đã lấy thành một kế hoạch du lịch cá nhân hóa.
- Điều chỉnh dựa trên phản hồi: Nhận phản hồi từ người dùng và tạo lại mã nếu cần để tinh chỉnh kết quả.
Triển khai từng bước
-
Thu thập sở thích của người dùng
class Travel_Agent: def __init__(self): self.user_preferences = {} def gather_preferences(self, preferences): self.user_preferences = preferences -
Tạo mã để lấy dữ liệu
def generate_code_to_fetch_data(preferences): # Example: Generate code to search for flights based on user preferences code = f""" def search_flights(): import requests response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/flights', params={preferences}) return response.json() """ return code def generate_code_to_fetch_hotels(preferences): # Example: Generate code to search for hotels code = f""" def search_hotels(): import requests response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/hotels', params={preferences}) return response.json() """ return code -
Thực thi mã đã tạo
def execute_code(code): # Execute the generated code using exec exec(code) result = locals() return result travel_agent = Travel_Agent() preferences = { "destination": "Paris", "dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10", "budget": "moderate", "interests": ["museums", "cuisine"] } travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences) flight_code = generate_code_to_fetch_data(preferences) hotel_code = generate_code_to_fetch_hotels(preferences) flights = execute_code(flight_code) hotels = execute_code(hotel_code) print("Flight Options:", flights) print("Hotel Options:", hotels) -
Tạo hành trình
def generate_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions): itinerary = { "flights": flights, "hotels": hotels, "attractions": attractions } return itinerary attractions = search_attractions(preferences) itinerary = generate_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions) print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary) -
Điều chỉnh dựa trên phản hồi
def adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback, preferences): # Adjust preferences based on user feedback if "liked" in feedback: preferences["favorites"] = feedback["liked"] if "disliked" in feedback: preferences["avoid"] = feedback["disliked"] return preferences feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]} updated_preferences = adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback, preferences) # Regenerate and execute code with updated preferences updated_flight_code = generate_code_to_fetch_data(updated_preferences) updated_hotel_code = generate_code_to_fetch_hotels(updated_preferences) updated_flights = execute_code(updated_flight_code) updated_hotels = execute_code(updated_hotel_code) updated_itinerary = generate_itinerary(updated_flights, updated_hotels, attractions) print("Updated Itinerary:", updated_itinerary)
Tận dụng nhận thức môi trường và lý luận
Dựa trên cấu trúc của bảng có thể cải thiện quá trình tạo truy vấn bằng cách tận dụng nhận thức môi trường và lý luận.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ về cách thực hiện:
- Hiểu cấu trúc: Hệ thống sẽ hiểu cấu trúc của bảng và sử dụng thông tin này để làm cơ sở cho việc tạo truy vấn.
- Điều chỉnh dựa trên phản hồi: Hệ thống sẽ điều chỉnh sở thích của người dùng dựa trên phản hồi và lý luận về các trường trong cấu trúc cần được cập nhật.
- Tạo và thực thi truy vấn: Hệ thống sẽ tạo và thực thi truy vấn để lấy dữ liệu chuyến bay và khách sạn cập nhật dựa trên sở thích mới.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ mã Python cập nhật tích hợp các khái niệm này:
def adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback, preferences, schema):
# Adjust preferences based on user feedback
if "liked" in feedback:
preferences["favorites"] = feedback["liked"]
if "disliked" in feedback:
preferences["avoid"] = feedback["disliked"]
# Reasoning based on schema to adjust other related preferences
for field in schema:
if field in preferences:
preferences[field] = adjust_based_on_environment(feedback, field, schema)
return preferences
def adjust_based_on_environment(feedback, field, schema):
# Custom logic to adjust preferences based on schema and feedback
if field in feedback["liked"]:
return schema[field]["positive_adjustment"]
elif field in feedback["disliked"]:
return schema[field]["negative_adjustment"]
return schema[field]["default"]
def generate_code_to_fetch_data(preferences):
# Generate code to fetch flight data based on updated preferences
return f"fetch_flights(preferences={preferences})"
def generate_code_to_fetch_hotels(preferences):
# Generate code to fetch hotel data based on updated preferences
return f"fetch_hotels(preferences={preferences})"
def execute_code(code):
# Simulate execution of code and return mock data
return {"data": f"Executed: {code}"}
def generate_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions):
# Generate itinerary based on flights, hotels, and attractions
return {"flights": flights, "hotels": hotels, "attractions": attractions}
# Example schema
schema = {
"favorites": {"positive_adjustment": "increase", "negative_adjustment": "decrease", "default": "neutral"},
"avoid": {"positive_adjustment": "decrease", "negative_adjustment": "increase", "default": "neutral"}
}
# Example usage
preferences = {"favorites": "sightseeing", "avoid": "crowded places"}
feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]}
updated_preferences = adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback, preferences, schema)
# Regenerate and execute code with updated preferences
updated_flight_code = generate_code_to_fetch_data(updated_preferences)
updated_hotel_code = generate_code_to_fetch_hotels(updated_preferences)
updated_flights = execute_code(updated_flight_code)
updated_hotels = execute_code(updated_hotel_code)
updated_itinerary = generate_itinerary(updated_flights, updated_hotels, feedback["liked"])
print("Updated Itinerary:", updated_itinerary)
Giải thích - Đặt chỗ dựa trên phản hồi
- Nhận thức cấu trúc: Từ điển
schemađịnh nghĩa cách điều chỉnh sở thích dựa trên phản hồi. Nó bao gồm các trường nhưfavoritesvàavoid, với các điều chỉnh tương ứng. - Điều chỉnh sở thích (phương thức
adjust_based_on_feedback): Phương thức này điều chỉnh sở thích dựa trên phản hồi của người dùng và cấu trúc. - Điều chỉnh dựa trên môi trường (phương thức
adjust_based_on_environment): Phương thức này tùy chỉnh các điều chỉnh dựa trên cấu trúc và phản hồi. - Tạo và thực thi truy vấn: Hệ thống tạo mã để lấy dữ liệu chuyến bay và khách sạn cập nhật dựa trên sở thích đã điều chỉnh và mô phỏng việc thực thi các truy vấn này.
- Tạo hành trình: Hệ thống tạo một hành trình cập nhật dựa trên dữ liệu chuyến bay, khách sạn, và điểm tham quan mới.
Bằng cách làm cho hệ thống nhận thức môi trường và lý luận dựa trên cấu trúc, nó có thể tạo ra các truy vấn chính xác và liên quan hơn, dẫn đến các khuyến nghị du lịch tốt hơn và trải nghiệm người dùng cá nhân hóa hơn.
Sử dụng SQL như một kỹ thuật Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
SQL (Structured Query Language) là một công cụ mạnh mẽ để tương tác với cơ sở dữ liệu. Khi được sử dụng như một phần của cách tiếp cận Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), SQL có thể lấy dữ liệu liên quan từ cơ sở dữ liệu để thông tin và tạo ra các phản hồi hoặc hành động trong các tác nhân AI. Hãy khám phá cách SQL có thể được sử dụng như một kỹ thuật RAG trong ngữ cảnh của Travel Agent.
Các khái niệm chính
- Tương tác cơ sở dữ liệu:
- SQL được sử dụng để truy vấn cơ sở dữ liệu, lấy thông tin liên quan, và xử lý dữ liệu.
- Ví dụ: Lấy chi tiết chuyến bay, thông tin khách sạn, và điểm tham quan từ cơ sở dữ liệu du lịch.
- Tích hợp với RAG:
- Các truy vấn SQL được tạo dựa trên đầu vào và sở thích của người dùng.
- Dữ liệu được lấy sau đó được sử dụng để tạo ra các khuyến nghị hoặc hành động cá nhân hóa.
- Tạo truy vấn động:
- Tác nhân AI tạo các truy vấn SQL động dựa trên ngữ cảnh và nhu cầu của người dùng.
- Ví dụ: Tùy chỉnh truy vấn SQL để lọc kết quả dựa trên ngân sách, ngày tháng, và sở thích.
Ứng dụng
- Tự động tạo mã: Tạo đoạn mã cho các nhiệm vụ cụ thể.
- SQL như một RAG: Sử dụng truy vấn SQL để xử lý dữ liệu.
- Giải quyết vấn đề: Tạo và thực thi mã để giải quyết vấn đề.
Ví dụ: Một tác nhân phân tích dữ liệu:
- Nhiệm vụ: Phân tích một tập dữ liệu để tìm xu hướng.
- Các bước:
- Tải tập dữ liệu.
- Tạo truy vấn SQL để lọc dữ liệu.
- Thực thi truy vấn và lấy kết quả.
- Tạo hình ảnh hóa và thông tin chi tiết.
- Tài nguyên: Truy cập tập dữ liệu, khả năng SQL.
- Kinh nghiệm: Sử dụng kết quả trước đó để cải thiện phân tích trong tương lai.
Ví dụ thực tế: Sử dụng SQL trong Travel Agent
-
Thu thập sở thích của người dùng
class Travel_Agent: def __init__(self): self.user_preferences = {} def gather_preferences(self, preferences): self.user_preferences = preferences -
Tạo truy vấn SQL
def generate_sql_query(table, preferences): query = f"SELECT * FROM {table} WHERE " conditions = [] for key, value in preferences.items(): conditions.append(f"{key}='{value}'") query += " AND ".join(conditions) return query -
Thực thi truy vấn SQL
import sqlite3 def execute_sql_query(query, database="travel.db"): connection = sqlite3.connect(database) cursor = connection.cursor() cursor.execute(query) results = cursor.fetchall() connection.close() return results -
Tạo khuyến nghị
def generate_recommendations(preferences): flight_query = generate_sql_query("flights", preferences) hotel_query = generate_sql_query("hotels", preferences) attraction_query = generate_sql_query("attractions", preferences) flights = execute_sql_query(flight_query) hotels = execute_sql_query(hotel_query) attractions = execute_sql_query(attraction_query) itinerary = { "flights": flights, "hotels": hotels, "attractions": attractions } return itinerary travel_agent = Travel_Agent() preferences = { "destination": "Paris", "dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10", "budget": "moderate", "interests": ["museums", "cuisine"] } travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences) itinerary = generate_recommendations(preferences) print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
Ví dụ truy vấn SQL
-
Truy vấn chuyến bay
SELECT * FROM flights WHERE destination='Paris' AND dates='2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10' AND budget='moderate'; -
Truy vấn khách sạn
SELECT * FROM hotels WHERE destination='Paris' AND budget='moderate'; -
Truy vấn điểm tham quan
SELECT * FROM attractions WHERE destination='Paris' AND interests='museums, cuisine';
Bằng cách tận dụng SQL như một phần của kỹ thuật Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), các tác nhân AI như Travel Agent có thể lấy và sử dụng dữ liệu liên quan một cách động để cung cấp các khuyến nghị chính xác và cá nhân hóa.
Ví dụ về siêu nhận thức
Để minh họa việc triển khai siêu nhận thức, hãy tạo một tác nhân đơn giản phản ánh quá trình ra quyết định của mình khi giải quyết vấn đề. Trong ví dụ này, chúng ta sẽ xây dựng một hệ thống nơi tác nhân cố gắng tối ưu hóa việc chọn khách sạn, nhưng sau đó đánh giá lý luận của mình và điều chỉnh chiến lược khi mắc lỗi hoặc lựa chọn không tối ưu.
Chúng ta sẽ mô phỏng điều này bằng một ví dụ cơ bản, nơi tác nhân chọn khách sạn dựa trên sự kết hợp giữa giá cả và chất lượng, nhưng nó sẽ “phản ánh” quyết định của mình và điều chỉnh khi cần.
Cách điều này minh họa siêu nhận thức:
- Quyết định ban đầu: Tác nhân sẽ chọn khách sạn rẻ nhất, mà không hiểu tác động đến chất lượng.
- Phản ánh và đánh giá: Sau khi lựa chọn ban đầu, tác nhân sẽ kiểm tra xem khách sạn có phải là lựa chọn “kém” dựa trên phản hồi của người dùng. Nếu phát hiện chất lượng khách sạn quá thấp, nó sẽ phản ánh lý luận của mình.
- Điều chỉnh chiến lược: Tác nhân điều chỉnh chiến lược của mình dựa trên sự phản ánh, chuyển từ “rẻ nhất” sang “chất lượng cao nhất”, từ đó cải thiện quá trình ra quyết định trong các lần lặp lại sau.
Dưới đây là một ví dụ:
class HotelRecommendationAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.previous_choices = [] # Stores the hotels chosen previously
self.corrected_choices = [] # Stores the corrected choices
self.recommendation_strategies = ['cheapest', 'highest_quality'] # Available strategies
def recommend_hotel(self, hotels, strategy):
"""
Recommend a hotel based on the chosen strategy.
The strategy can either be 'cheapest' or 'highest_quality'.
"""
if strategy == 'cheapest':
recommended = min(hotels, key=lambda x: x['price'])
elif strategy == 'highest_quality':
recommended = max(hotels, key=lambda x: x['quality'])
else:
recommended = None
self.previous_choices.append((strategy, recommended))
return recommended
def reflect_on_choice(self):
"""
Reflect on the last choice made and decide if the agent should adjust its strategy.
The agent considers if the previous choice led to a poor outcome.
"""
if not self.previous_choices:
return "No choices made yet."
last_choice_strategy, last_choice = self.previous_choices[-1]
# Let's assume we have some user feedback that tells us whether the last choice was good or not
user_feedback = self.get_user_feedback(last_choice)
if user_feedback == "bad":
# Adjust strategy if the previous choice was unsatisfactory
new_strategy = 'highest_quality' if last_choice_strategy == 'cheapest' else 'cheapest'
self.corrected_choices.append((new_strategy, last_choice))
return f"Reflecting on choice. Adjusting strategy to {new_strategy}."
else:
return "The choice was good. No need to adjust."
def get_user_feedback(self, hotel):
"""
Simulate user feedback based on hotel attributes.
For simplicity, assume if the hotel is too cheap, the feedback is "bad".
If the hotel has quality less than 7, feedback is "bad".
"""
if hotel['price'] < 100 or hotel['quality'] < 7:
return "bad"
return "good"
# Simulate a list of hotels (price and quality)
hotels = [
{'name': 'Budget Inn', 'price': 80, 'quality': 6},
{'name': 'Comfort Suites', 'price': 120, 'quality': 8},
{'name': 'Luxury Stay', 'price': 200, 'quality': 9}
]
# Create an agent
agent = HotelRecommendationAgent()
# Step 1: The agent recommends a hotel using the "cheapest" strategy
recommended_hotel = agent.recommend_hotel(hotels, 'cheapest')
print(f"Recommended hotel (cheapest): {recommended_hotel['name']}")
# Step 2: The agent reflects on the choice and adjusts strategy if necessary
reflection_result = agent.reflect_on_choice()
print(reflection_result)
# Step 3: The agent recommends again, this time using the adjusted strategy
adjusted_recommendation = agent.recommend_hotel(hotels, 'highest_quality')
print(f"Adjusted hotel recommendation (highest_quality): {adjusted_recommendation['name']}")
Khả năng siêu nhận thức của tác nhân
Điểm mấu chốt ở đây là khả năng của tác nhân:
- Đánh giá các lựa chọn và quá trình ra quyết định trước đó.
- Điều chỉnh chiến lược dựa trên sự phản ánh, tức là siêu nhận thức trong hành động.
Đây là một dạng siêu nhận thức đơn giản, nơi hệ thống có khả năng điều chỉnh quá trình lý luận của mình dựa trên phản hồi nội bộ.
Kết luận
Siêu nhận thức là một công cụ mạnh mẽ có thể nâng cao đáng kể khả năng của các tác nhân AI. Bằng cách tích hợp các quy trình siêu nhận thức, bạn có thể thiết kế các tác nhân thông minh, thích nghi, và hiệu quả hơn. Sử dụng các tài nguyên bổ sung để khám phá thêm về thế giới thú vị của siêu nhận thức trong các tác nhân AI.
Có thêm câu hỏi về mẫu thiết kế siêu nhận thức?
Tham gia Azure AI Foundry Discord để gặp gỡ các học viên khác, tham dự giờ làm việc và nhận câu trả lời cho các câu hỏi về tác nhân AI của bạn.
Bài học trước
Bài học tiếp theo
Tuyên bố miễn trừ trách nhiệm:
Tài liệu này đã được dịch bằng dịch vụ dịch thuật AI Co-op Translator. Mặc dù chúng tôi cố gắng đảm bảo độ chính xác, xin lưu ý rằng các bản dịch tự động có thể chứa lỗi hoặc không chính xác. Tài liệu gốc bằng ngôn ngữ bản địa nên được coi là nguồn tham khảo chính thức. Đối với các thông tin quan trọng, nên sử dụng dịch vụ dịch thuật chuyên nghiệp từ con người. Chúng tôi không chịu trách nhiệm cho bất kỳ sự hiểu lầm hoặc diễn giải sai nào phát sinh từ việc sử dụng bản dịch này.
