Exercise 6: Services
In this Exercise you will create a simple Service. Services help you expose Pods externally using label selectors.
Task 1 - Create a new Service
Create a deployment:
$sampleDepYaml = @" apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: sample-dep spec: replicas: 4 selector: matchLabels: sample: color template: metadata: name: sample-color-pod labels: sample: color color: blue spec: nodeSelector: kubernetes.io/os: linux containers: - name: nginxcolordemo image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/scubakiz/nginxcolordemo:blue-1.0 ports: - containerPort: 80 protocol: TCP env: - name: NODE_IP valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.hostIP - name: NODE_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: spec.nodeName - name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace - name: POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName - name: POD_CPU_REQUEST valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: requests.cpu - name: POD_CPU_LIMIT valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: limits.cpu - name: POD_MEM_REQUEST valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: requests.memory - name: POD_MEM_LIMIT valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: limits.memory volumeMounts: - name: podinfo mountPath: /etc/podinfo volumes: - name: podinfo downwardAPI: items: - path: "labels" fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels - path: "annotations" fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.annotations "@ $sampleDepYaml | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: sample-dep spec: replicas: 4 selector: matchLabels: sample: color template: metadata: name: sample-color-pod labels: sample: color color: blue spec: nodeSelector: kubernetes.io/os: linux containers: - name: nginxcolordemo image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/scubakiz/nginxcolordemo:blue-1.0 ports: - containerPort: 80 protocol: TCP env: - name: NODE_IP valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.hostIP - name: NODE_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: spec.nodeName - name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace - name: POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName - name: POD_CPU_REQUEST valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: requests.cpu - name: POD_CPU_LIMIT valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: limits.cpu - name: POD_MEM_REQUEST valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: requests.memory - name: POD_MEM_LIMIT valueFrom: resourceFieldRef: containerName: nginxcolordemo resource: limits.memory volumeMounts: - name: podinfo mountPath: /etc/podinfo volumes: - name: podinfo downwardAPI: items: - path: "labels" fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels - path: "annotations" fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.annotations EOFReview running Pods and their labels:
kubectl get pods --show-labelskubectl get pods --show-labelsNote
Notice the label sample=color that is associated with the Pods.
Create a Service manifest with a selector that matches the sample=color label. This Service will track all Pods that have this label and load balance traffic between them:
$sampleSvcYaml = @" apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sample-svc spec: ports: - port: 80 selector: sample: color type: LoadBalancer "@ $sampleSvcYaml | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sample-svc spec: ports: - port: 80 selector: sample: color type: LoadBalancer EOFCheck the newly created service:
kubectl get svc -o widekubectl get svc -o wideTip
The command above will display the details of all available services along with their label selectors. You should see the sample-svc Service with SELECTOR
sample=color. This service should get an external IP that you can use in the next step. It may take several minutes for this IP to appear, it will show<pending>in the meantime.
Task 2 - Access the sample-svc Service
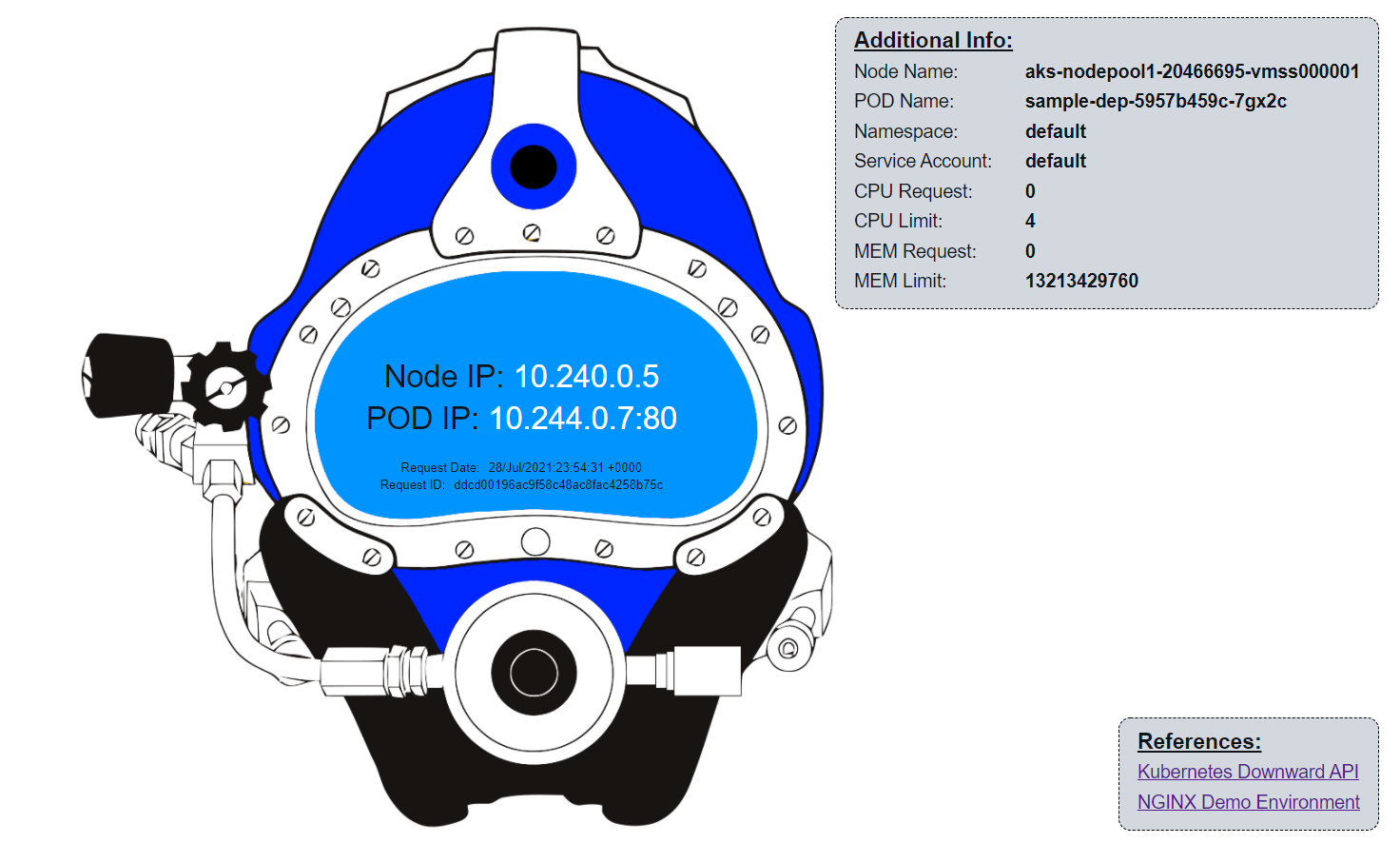
Open a browser and navigate to the IP address shown in the output of the previous command.
The website displays the Node IP/Pod IP address of the pod currently receiving the traffic through the service’s load balancer. The page refreshes every 3 seconds and each request may be directed to a different pod, with a different IP address. This is the service’s internal load balancer at work.
Tip
You may not see the Pod IP address change if you are only accessing the webpage from a single tab in your browser. If this is the case, try opening the same URL in a private browsing window, or a different browser / different device - you should see a different Pod IP on these other devices.
Task 3 - Clean Up
Leave the current deployment and service running for the next exercise. You will clean them up at the end of this lab.