Exercise 2: Troubleshooting AKS Issues
Task 1 - Common Troubleshooting Commands
Familiarize yourself with key troubleshooting commands:
# Get pod status kubectl get pods # Get detailed pod information kubectl describe pod <pod-name> # Get pod logs kubectl logs <pod-name> # Get logs from previous instance of a pod (if it restarted) kubectl logs <pod-name> --previous # Get events across the cluster kubectl get events --sort-by='.lastTimestamp' # Check node status kubectl get nodes kubectl describe node <node-name> # Get resource usage kubectl top pods kubectl top nodes# Get pod status kubectl get pods # Get detailed pod information kubectl describe pod <pod-name> # Get pod logs kubectl logs <pod-name> # Get logs from previous instance of a pod (if it restarted) kubectl logs <pod-name> --previous # Get events across the cluster kubectl get events --sort-by='.lastTimestamp' # Check node status kubectl get nodes kubectl describe node <node-name> # Get resource usage kubectl top pods kubectl top nodes
Task 2 - Simulate and Troubleshoot a Crashing Pod
Create and examine the crasher pod manifest:
$crasherPod = @" apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: crasher-pod spec: containers: - name: crasher image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/busybox command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "echo 'Starting pod...'; echo 'Pod running normally...'; sleep 10; echo 'WARNING: Memory corruption detected!'; echo 'ERROR: Critical system failure!'; echo 'Pod will now terminate with error...'; exit 1"] # This will output logs and crash after 10 seconds resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "200m" restartPolicy: Always # The pod will continuously restart and crash "@ # Output the manifest to review it $crasherPodcat << EOF > crasher-pod.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: crasher-pod spec: containers: - name: crasher image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/busybox command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "echo 'Starting pod...'; echo 'Pod running normally...'; sleep 10; echo 'WARNING: Memory corruption detected!'; echo 'ERROR: Critical system failure!'; echo 'Pod will now terminate with error...'; exit 1"] # This will output logs and crash after 10 seconds resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "200m" restartPolicy: Always # The pod will continuously restart and crash EOF # Output the manifest to review it cat crasher-pod.yamlThis pod is designed to output several log messages and then exit with an error after 10 seconds, causing it to crash and restart.
Deploy the crashing pod:
$crasherPod | kubectl apply -f -kubectl apply -f crasher-pod.yamlObserve the pod’s status:
kubectl get pods -wkubectl get pods -wYou should see the pod status cycle through
Running→Error→CrashLoopBackOff→Runningagain.Terminate the watch by pressing Ctrl+C.
Diagnose the issue:
# Check the pod status kubectl describe pod crasher-pod # Look at the restart count and last state # Check the logs kubectl logs crasher-pod# Check the pod status kubectl describe pod crasher-pod # Look at the restart count and last state # Check the logs kubectl logs crasher-podYou should see error messages in the logs that provide clues about why the pod is crashing, such as
WARNING: Memory corruption detected!andERROR: Critical system failure!.Fix the issue by creating a new pod that doesn’t crash:
$fixedPod = @" apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: fixed-pod spec: containers: - name: fixed image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/busybox command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "while true; do echo 'Running stably'; sleep 30; done"] resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "200m" "@ $fixedPod | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: fixed-pod spec: containers: - name: fixed image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/busybox command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "while true; do echo 'Running stably'; sleep 30; done"] resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "200m" EOFVerify the fixed pod is running stably:
kubectl get pods fixed-pod -wkubectl get pods fixed-pod -wWait for a minute or so to confirm it doesn’t restart.
Terminate the watch by pressing Ctrl+C.
Task 3 - Troubleshoot Application Connectivity with Network Policies
Create a dedicated namespace for network policy testing:
kubectl create namespace netpolicy-testkubectl create namespace netpolicy-testCreate a simple web application and service in the namespace:
# Create a deployment kubectl create deployment web --image=nginx -n netpolicy-test # Add the app=web label to the deployment kubectl label deployment web app=web -n netpolicy-test # Expose the deployment with a service kubectl expose deployment web --port=80 --type=ClusterIP -n netpolicy-test# Create a deployment kubectl create deployment web --image=nginx -n netpolicy-test # Add the app=web label to the deployment kubectl label deployment web app=web -n netpolicy-test # Expose the deployment with a service kubectl expose deployment web --port=80 --type=ClusterIP -n netpolicy-testInfo
If the
kubectl labelcommand returnsdeployment.apps/web not labeledthis is OK. It indicates that the deployment was already labelled.Create a debugging pod in the same namespace:
kubectl run debug --image=busybox -n netpolicy-test -- sleep 3600kubectl run debug --image=busybox -n netpolicy-test -- sleep 3600Wait for the pod to be ready:
kubectl wait --for=condition=Ready pod/debug --timeout=60s -n netpolicy-testkubectl wait --for=condition=Ready pod/debug --timeout=60s -n netpolicy-testVerify connectivity before applying network policies:
kubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- http://webkubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- http://webYou should see the HTML output from the nginx welcome page.
Create a default deny-all policy for the namespace:
Info
We will cover network policies in more detail in the next section, but for now, these policies will be used for our lab to block all traffic and then allow specific traffic.
$denyAllPolicy = @" apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: default-deny-ingress namespace: netpolicy-test spec: podSelector: {} # This selects ALL pods in the namespace policyTypes: - Ingress "@ $denyAllPolicy | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: default-deny-ingress namespace: netpolicy-test spec: podSelector: {} # This selects ALL pods in the namespace policyTypes: - Ingress EOFThis policy denies all ingress traffic to all pods in the namespace.
Try to access the web service again:
kubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- --timeout=5 http://webkubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- --timeout=5 http://webThis should fail due to the network policy blocking all traffic, and you should find that the attempt times out.
Create a policy that allows traffic from the debug pod to the web service:
$allowPolicy = @" apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-debug-to-web namespace: netpolicy-test spec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: web policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: run: debug "@ $allowPolicy | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-debug-to-web namespace: netpolicy-test spec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: web policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: run: debug EOFTest connectivity again:
kubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- http://webkubectl exec -it debug -n netpolicy-test -- wget -O- http://webThis should succeed now because the network policy specifically allows traffic from the debug pod to the web service.
Task 4 - Troubleshoot Resource Constraints
Create a pod with insufficient resources:
$memoryHogPod = @" apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: memory-hog spec: containers: - name: memory-hog image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/nginx resources: requests: memory: "100Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "100Mi" cpu: "100m" command: ["sh", "-c", "apt-get update && apt-get install -y stress && stress --vm 1 --vm-bytes 200M"] "@ $memoryHogPod | kubectl apply -f -cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: memory-hog spec: containers: - name: memory-hog image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/nginx resources: requests: memory: "100Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "100Mi" cpu: "100m" command: ["sh", "-c", "apt-get update && apt-get install -y stress && stress --vm 1 --vm-bytes 200M"] EOFCheck the pod status:
kubectl get pods memory-hog -wkubectl get pods memory-hog -wThe pod should eventually be killed due to OOM (Out of Memory).
Terminate the watch with Ctrl+C.
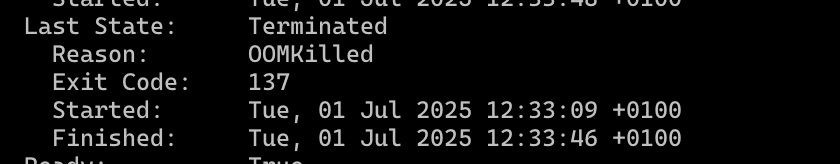
Diagnose the issue:
kubectl describe pod memory-hogkubectl describe pod memory-hogLook for the termination reason, which should indicate an OOM kill.
Fix the issue by increasing the memory limit:
kubectl delete pod memory-hog $memoryFixedPod = @" apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: memory-fixed spec: containers: - name: memory-fixed image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/nginx resources: requests: memory: "250Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "300Mi" cpu: "100m" command: ["sh", "-c", "apt-get update && apt-get install -y stress && stress --vm 1 --vm-bytes 200M"] "@ $memoryFixedPod | kubectl apply -f -kubectl delete pod memory-hog cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: memory-fixed spec: containers: - name: memory-fixed image: k8sonazureworkshoppublic.azurecr.io/nginx resources: requests: memory: "250Mi" cpu: "100m" limits: memory: "300Mi" cpu: "100m" command: ["sh", "-c", "apt-get update && apt-get install -y stress && stress --vm 1 --vm-bytes 200M"] EOFCheck that the pod runs correctly:
kubectl get pods memory-fixed -wkubectl get pods memory-fixed -wTerminate the watch with Ctrl+C after a couple of minutes.
Task 5 - Using Kubectl Debug
Create a deployment with multiple replicas:
kubectl create deployment debug-demo --image=nginx --replicas=3kubectl create deployment debug-demo --image=nginx --replicas=3Use
kubectl debugto troubleshoot a pod:# Get pod names $POD_NAME = kubectl get pods -l app=debug-demo -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}' # Create a debug container in the pod kubectl debug $POD_NAME -it --image=busybox --target=nginx# Get pod names POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods -l app=debug-demo -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') # Create a debug container in the pod kubectl debug $POD_NAME -it --image=busybox --target=nginxInside the debug container, run some diagnostics:
# Check processes ps aux # Check network netstat -tulpn # Check the nginx config in main container cat /proc/1/root/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf # Exit when done exit
Task 6 - Clean Up
Clean up the resources created in this exercise:
# Delete regular resources kubectl delete pod crasher-pod fixed-pod memory-fixed kubectl delete deployment debug-demo # Delete network policy test resources kubectl delete namespace netpolicy-test# Delete regular resources kubectl delete pod crasher-pod fixed-pod memory-fixed kubectl delete deployment debug-demo # Delete network policy test resources kubectl delete namespace netpolicy-test