ConfigMaps
🚀 What It Does
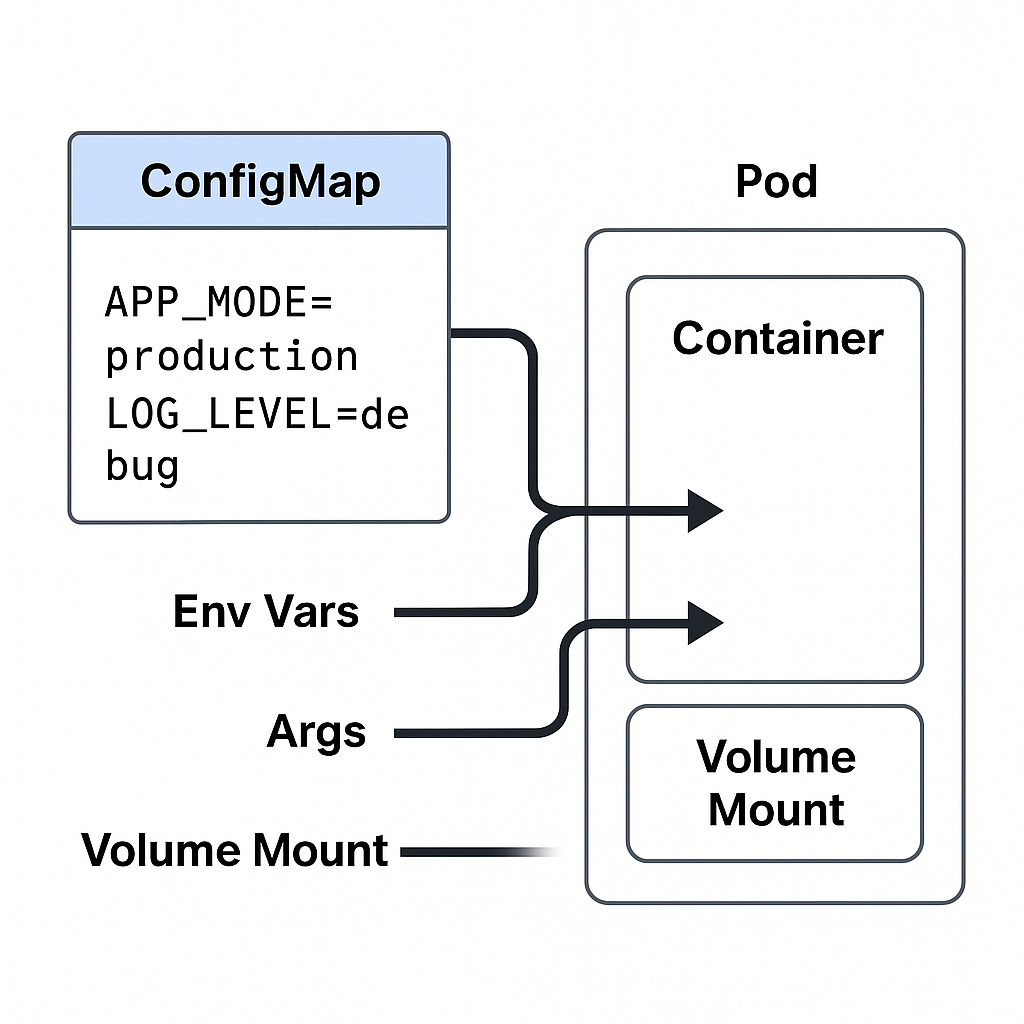
A ConfigMap in Kubernetes is used to externalize configuration data from your application code. It allows you to store key-value pairs or configuration files that your pods can consume at runtime, making your applications more portable and easier to manage.
🧩 Key Features
- Key-Value Storage: Stores configuration as simple key-value pairs or entire files.
- Decoupling: Keeps configuration separate from container images, enabling reuse and flexibility.
- Multiple Consumption Methods:
- As environment variables
- As command-line arguments
- Mounted as files in a volume
- Dynamic Updates: When mounted as volumes, changes to the ConfigMap can be reflected in the pod without restarting it (depending on how the app handles it).
⚙️ How It Works
- You create a ConfigMap using
kubectlor a YAML manifest. - The ConfigMap is stored in the Kubernetes API server.
- Pods reference the ConfigMap to inject configuration at runtime.
- If the ConfigMap is updated, the changes can be picked up by the pods (depending on how it’s consumed).