Secrets
🚀 What It Does
A Secret in Kubernetes is used to store sensitive information such as passwords, OAuth tokens, SSH keys, and TLS certificates. It allows you to manage confidential data separately from your application code and configuration, helping to keep your workloads secure.
🧩 Key Features
- Base64-Encoded Data: Secrets store data in base64-encoded format (note: this is not encryption, just encoding).
- Types of Secrets:
- Opaque (default): Generic key-value pairs.
- Predefined types for common use cases, e.g.
kubernetes.io/basic-auth,kubernetes.io/ssh-auth, etc.
- Access Control: Kubernetes RBAC can restrict who can view or modify Secrets.
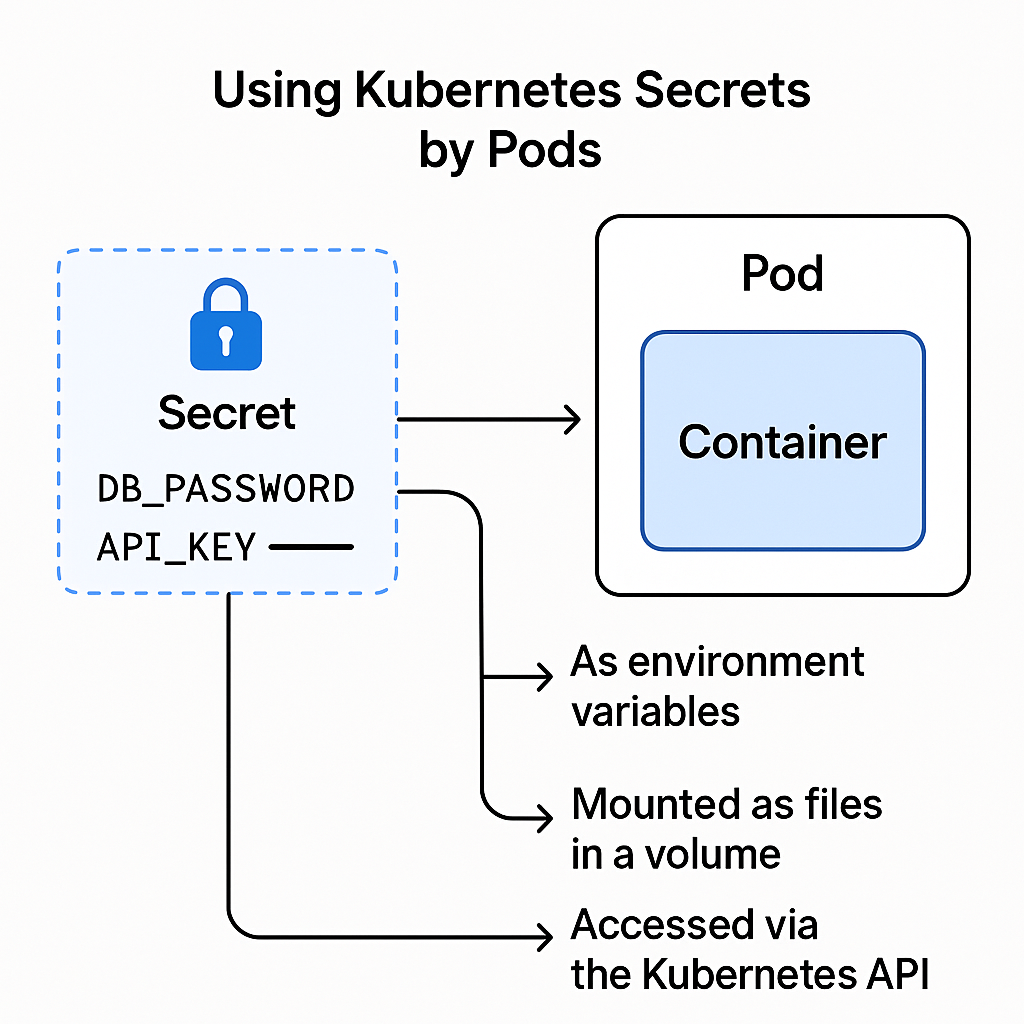
- Multiple Consumption Methods:
- As environment variables
- Mounted as files in a volume
- Accessed via the Kubernetes API (with proper permissions)
⚙️ How It Works
- You create a Secret using
kubectlor a YAML manifest. - The Secret is stored in the Kubernetes API server and can be encrypted at rest.
- Pods reference the Secret to inject sensitive data at runtime.
- If the Secret is updated, changes can be reflected in the pod (depending on how it’s consumed and how the app handles it).