AKS Ingress Controllers
Ingress and Gateway API are Kubernetes features designed to provide controlled, secure external access to services running inside a cluster. They enable you to define rules for how incoming traffic from outside the cluster is routed to your internal applications, making it possible to expose web services, APIs, or other endpoints to users and systems outside of Kubernetes.
An Ingress Controller is a specialized Kubernetes component that manages external access to services in a cluster - typically HTTP/HTTPS traffic. It watches for Ingress resources and configures the underlying load balancer or proxy to route traffic to the appropriate services based on rules like hostnames and paths.
Ingress or Gateway API
With the evolution of Kubernetes networking, the traditional Ingress resource has been the standard way to manage external HTTP(S) access to services in a cluster. However, the new Gateway API is emerging as the next-generation solution for ingress traffic management. Gateway API offers more flexibility, advanced routing capabilities, and better integration with modern cloud-native architectures. While Gateway API is designed to eventually supersede the older Ingress resource, Ingress controllers remain widely used and fully supported in AKS.
For new projects, we recommend considering Gateway API for its enhanced features and future-proof design - but Ingress remains a reliable and familiar option for many existing workloads.
Ingress
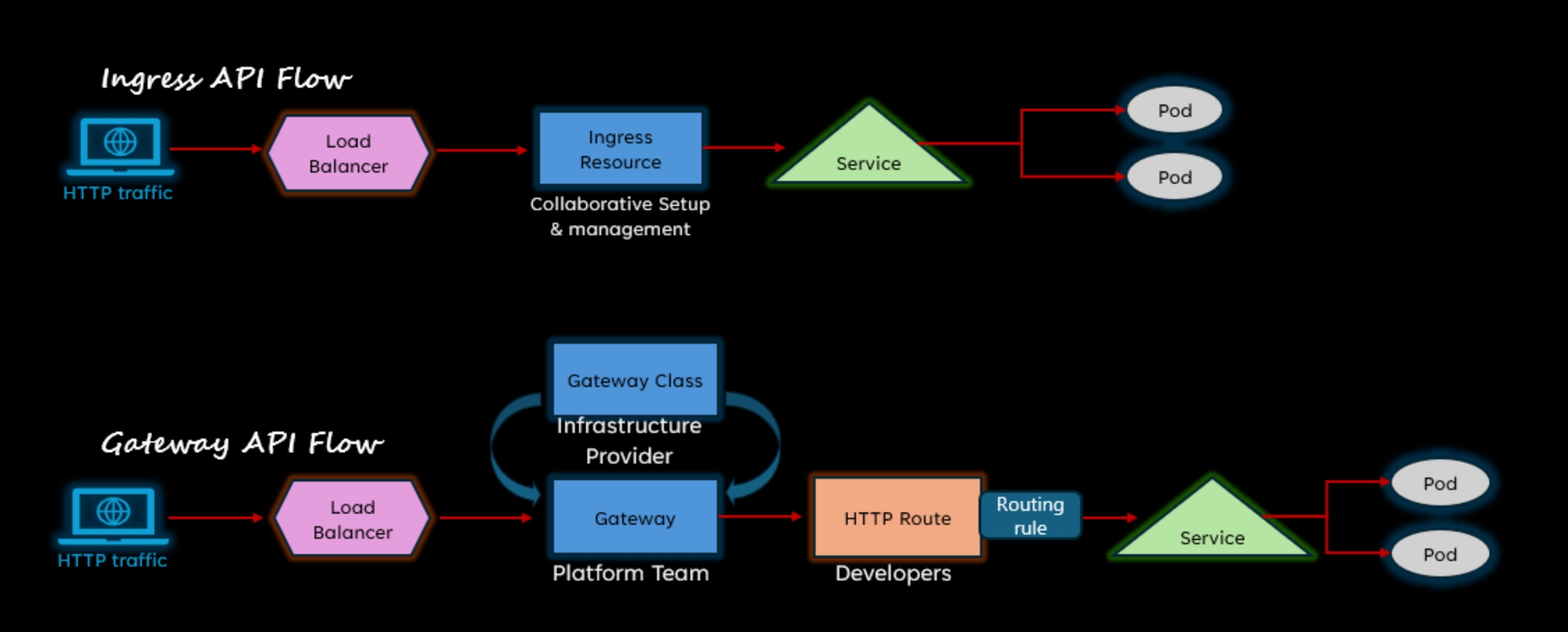
Ingress is a Kubernetes resource that manages external HTTP and HTTPS access to services within a cluster. By defining Ingress rules, you can control routing based on hostnames and paths, enabling multiple services to be exposed under a single IP address. Ingress relies on an ingress controller, such as Nginx or Azure Application Gateway, to implement these rules and handle the actual traffic routing. It has been the standard approach for managing web traffic into Kubernetes clusters and remains widely supported and used.
With the traditional Ingress approach, a single Ingress resource typically handles multiple aspects of external traffic management. This resource defines routing rules (such as hostnames and paths), associates those rules with backend services, and can also specify TLS/SSL settings for secure connections. As a result, domain management, routing logic, and SSL configuration are all bundled together in one resource. This simplicity makes Ingress easy to use for straightforward scenarios, but it can become limiting or unwieldy as requirements grow more complex.
Gateway API
Gateway API is the next-generation Kubernetes standard for service networking and traffic management. It builds on the concepts of Ingress but introduces more expressive, flexible, and extensible routing capabilities. Gateway API supports advanced features like traffic splitting, header-based routing, and integration with modern cloud-native gateways. Designed to address the limitations of the original Ingress resource, Gateway API is becoming the preferred solution for new deployments, offering better scalability and future-proofing for evolving application architectures.
Gateway API introduces a more modular and flexible model by splitting responsibilities across several resource types. Instead of a single resource, you define a Gateway (representing the entry point and infrastructure), GatewayClass (the type of gateway), HTTPRoute (routing rules), and separate resources for TLS configuration and domain management. This separation allows for clearer roles, better scalability, and more granular control over routing, security, and infrastructure. It also enables teams to manage different aspects of traffic independently, supporting advanced use cases and larger, multi-team environments.