Azure Workload Identity
Azure Workload Identity is a secure and scalable way to provide Azure identities to Kubernetes workloads running in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). It allows pods to authenticate with Azure services using Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) service principal identities without storing credentials in the cluster.
What is Azure Workload Identity?
Azure Workload Identity enables Kubernetes workloads to access Azure resources using Entra ID identities. It replaces the need for storing service principal credentials or managed identity credentials directly in pods, secrets, or environment variables.
This technology is based on industry-standard OpenID Connect (OIDC) federation and provides a bridge between Kubernetes service accounts and Azure Entra ID applications, enabling secure authentication without credential storage.
Key Benefits
Enhanced Security
- No Credential Storage: Eliminates the need to store secrets, service principal credentials, or managed identity credentials in the cluster.
- Short-lived Tokens: Uses temporary tokens that are automatically refreshed.
- No Secret Rotation: Removes the operational burden of rotating stored credentials.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Minimizes the risk of credential theft or exposure.
Simplified Management
- Native Integration: Leverages both Kubernetes and Azure identity mechanisms.
- Automatic Token Management: Handles token acquisition and renewal transparently.
- Standard SDK Support: Works with existing Azure SDKs without code changes.
- Consistent Experience: Provides the same authentication experience across different Azure services.
Fine-grained Access Control
- Principle of Least Privilege: Enables precise resource-level permissions.
- Azure RBAC Integration: Leverages Azure’s role-based access control system.
- Conditional Access: Supports Azure conditional access policies.
- Audit and Compliance: Provides full audit trails of identity usage and resource access.
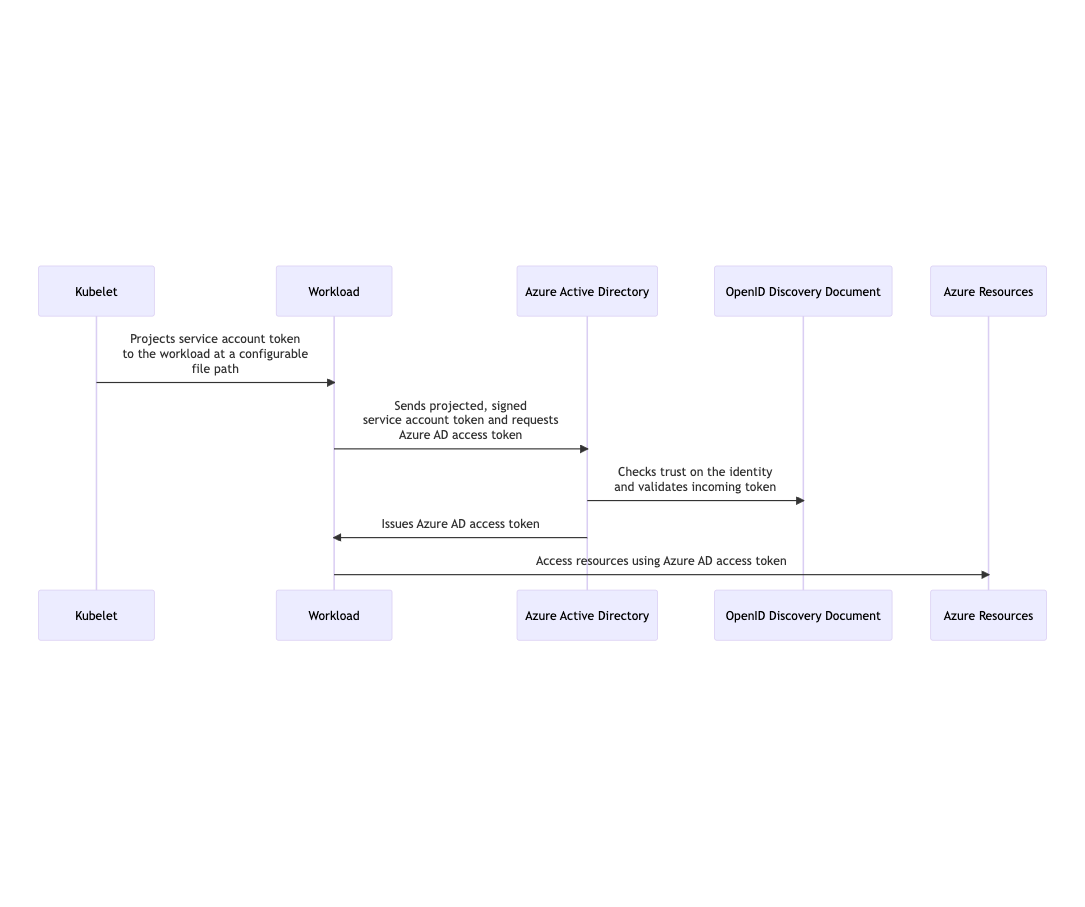
How Azure Workload Identity Works
Azure Workload Identity operates through a secure token exchange mechanism based on OpenID Connect federation.
1. Trust Establishment
A federated identity credential creates a trust relationship between:
- An Entra ID application (representing your workload’s identity in Azure)
- A Kubernetes service account (representing your workload’s identity in Kubernetes)
This trust relationship is established through OIDC federation, allowing Azure to trust tokens issued by the Kubernetes cluster.
2. Token Issuance
When a pod starts:
- Kubernetes automatically mounts a service account token into the pod
- This token contains claims that identify the service account and namespace
- The token is signed by the Kubernetes cluster’s OIDC issuer
3. Token Exchange
When the application needs to access Azure resources:
- The Azure SDK detects the presence of the service account token
- It sends the Kubernetes token to Azure’s Security Token Service (STS)
- Azure validates the token signature and federation configuration
- Azure issues a new Azure access token for the federated Entra ID application
4. Resource Access
- The application uses the Azure access token to authenticate with Azure services
- Azure services validate the token and apply the configured RBAC permissions
- The access token has a limited lifetime and is automatically refreshed as needed
Architecture Components
Kubernetes Side
- Service Account: Standard Kubernetes identity primitive
- OIDC Issuer: Kubernetes cluster component that signs service account tokens
- Azure Workload Identity Webhook: Mutating admission controller that injects necessary configurations
Azure Side
- Entra ID Application/Service Principal: Represents the workload’s identity in Azure
- Federated Identity Credential: Configuration that establishes trust with Kubernetes
- Azure RBAC: Role assignments that define what resources the identity can access