Cluster Autoscaler
The Cluster Autoscaler, or Node Autoscaler, is a core Kubernetes component that automatically adjusts the number of nodes in a cluster based on the resource requirements of scheduled pods. In AKS, the Cluster Autoscaler helps ensure that workloads have sufficient resources to run efficiently, scaling the cluster up or down in response to changes in demand.
How Cluster Autoscaler Works
Cluster Autoscaler continuously monitors the state of pods and nodes in the cluster. When it detects unschedulable pods—pods that cannot be placed due to insufficient resources—it attempts to add nodes to the cluster. Conversely, if it finds nodes that are underutilized and can safely be removed without affecting running workloads, it will scale the cluster down by removing those nodes.
The autoscaler makes decisions based on resource requests and limits defined in pod specifications. It does not consider actual usage, but rather the requested resources, ensuring that scheduling decisions are predictable and consistent. The autoscaler respects node pool boundaries and scaling limits, only adding or removing nodes within the configured minimum and maximum node counts for each pool.
| Scenario | Autoscaler Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Unschedulable pods | Add nodes | Cluster scales up to accommodate new pods |
| Underutilized nodes | Remove nodes | Cluster scales down, reducing resource waste |
| Node pool limits reached | No action | Cluster remains at configured boundaries |
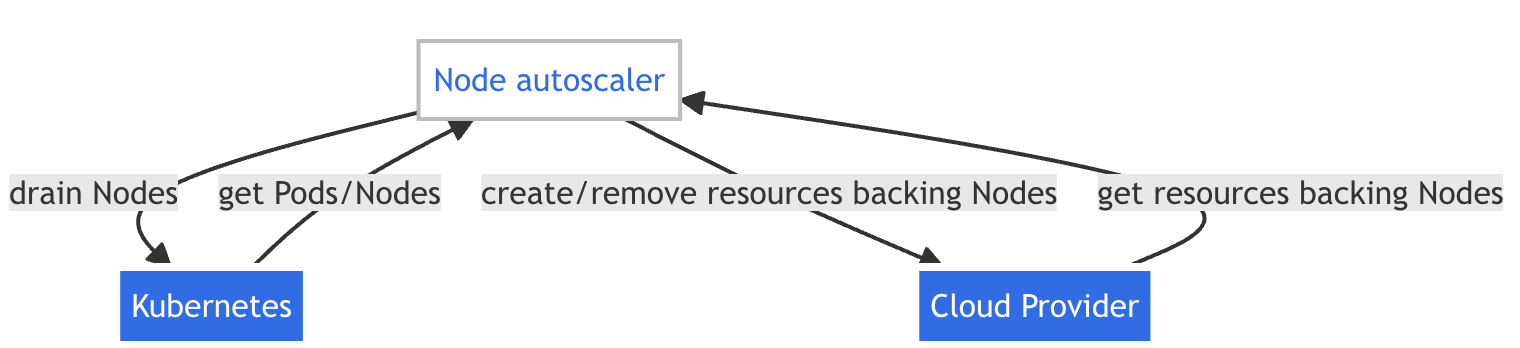
When nodes need to be added or removed, the autoscaler interacts with the underlying cloud provider’s API (in AKS, this is Azure) to provision or deallocate virtual machines.
Key Features and Behaviors
- Pod Scheduling Awareness: The autoscaler reacts only to pods that cannot be scheduled due to resource constraints, not to actual resource usage or performance metrics.
- Node Pool Integration: Works with AKS node pools, scaling each pool independently within its configured limits.
- Graceful Node Removal: When scaling down, the autoscaler drains nodes, evicts pods, and ensures workloads are rescheduled before node removal.
- Resource Request Reliance: Decisions are based on pod resource requests and limits, so accurate resource specification is critical for effective scaling.
- No Impact on Running Pods: The autoscaler will not remove nodes if doing so would disrupt running pods that cannot be rescheduled elsewhere.
Cluster Autoscaler in AKS
In AKS, the Cluster Autoscaler integrates directly with Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) to manage the underlying compute resources for each node pool. Each node pool in AKS is backed by a VMSS, which allows the autoscaler to dynamically adjust the number of virtual machines based on the cluster’s needs.
When the autoscaler determines that additional nodes are required, it instructs the VMSS to provision new VMs, which are then joined to the Kubernetes cluster and made available for scheduling pods. Conversely, when nodes are underutilized and can be safely removed, the autoscaler coordinates with the VMSS to deallocate and remove those VMs, ensuring that workloads are gracefully rescheduled before node removal.
Limitations and Considerations
Cluster Autoscaler is designed for general-purpose scaling and may not be suitable for all workload types. It does not respond to custom metrics, queue depth, or business logic; its decisions are strictly based on scheduling feasibility. Any additional logic needs to be built into your pod scaling process, which will in turn trigger the cluster autoscaler to adjust the node count. There are other open source and third party autoscalers that can scale clusters in a different manner.
Node pool configuration is important: minimum and maximum node counts must be set appropriately to allow the autoscaler to function effectively. Overly restrictive limits can prevent scaling, while overly permissive limits may lead to resource waste if not managed carefully.
The autoscaler may take several minutes to react to changes, as node provisioning and draining are not instantaneous. This delay should be considered when designing applications with strict performance or availability requirements. Adding new VMs to VMSS in Azure can take between 2-10 minutes depending on node choices and availability.