MSCCL++ Torch Integration Guide
This guide shows how to use MSCCL++ with PyTorch for high-performance collective communication.
Quick Start
MSCCL++ provides three ways to implement collective algorithms with PyTorch:
Approach |
Best For |
Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Default Algorithms |
Quick integration, standard use cases |
Low |
DSL-based |
Custom communication patterns without C++ |
Medium |
Native C++/CUDA |
Maximum control, custom kernels |
High |
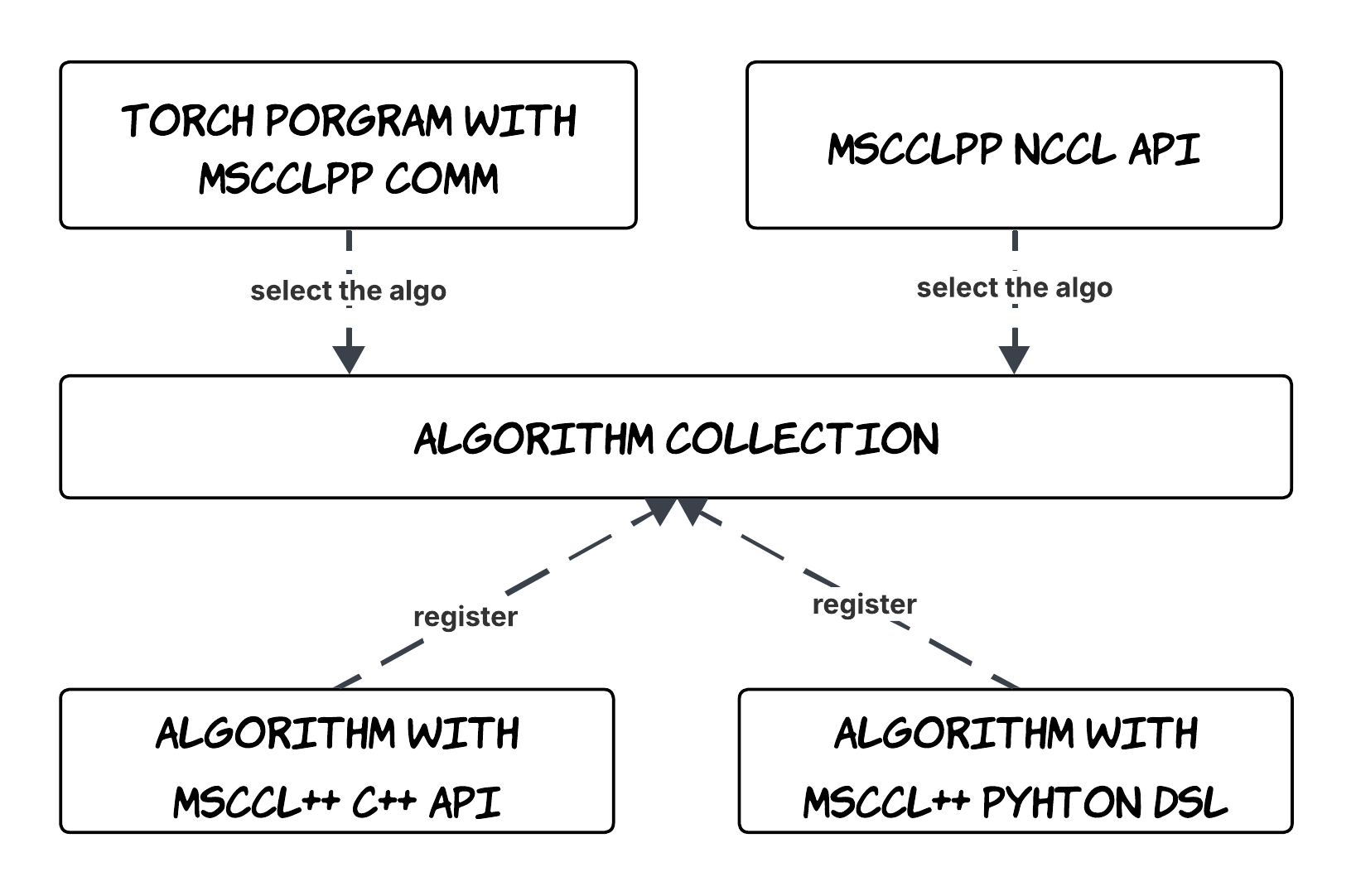
MSCCL++ Customization Algorithm Selection Overview
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
MSCCL++ installed with Python bindings
PyTorch with CUDA support
Required Environment Variables:
export MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR=<master_node_ip> # IP address of master node
export MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT=<port> # Port for communication (e.g., 29500)
Common Setup: Creating a Communicator
All approaches require initializing an MSCCL++ communicator. Here’s a reusable setup:
import os
import torch
import netifaces as ni
import ipaddress
def get_network_interface(ip: str):
"""Find the network interface for the given IP address."""
target = ipaddress.ip_address(ip)
for interface in ni.interfaces():
addresses = ni.ifaddresses(interface)
if ni.AF_INET in addresses:
for link in addresses[ni.AF_INET]:
if "addr" in link:
if ipaddress.ip_address(link["addr"]) == target:
return interface
return None
def init_communicator():
"""Initialize MSCCL++ communicator from environment variables."""
rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", rank))
torch.cuda.set_device(local_rank)
master_addr = os.environ["MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR"]
master_port = os.environ["MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT"]
interface = get_network_interface(master_addr)
if interface is None:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot find network interface for IP {master_addr}")
interface_trio = f"{interface}:{master_addr}:{master_port}"
comm_group = mscclpp.CommGroup(
interfaceIpPortTrio=interface_trio,
rank=rank,
size=world_size
)
return comm_group
Approach 1: Default Built-in Algorithms (Easiest)
Use pre-built, optimized algorithms from MSCCL++. Best for standard collective operations.
Example: customized_comm_with_default_algo.py
Step 1: Load Default Algorithms
import mscclpp
import mscclpp.utils as mscclpp_utils
def load_algorithms(scratch_buffer: torch.Tensor, rank: int):
"""Load MSCCL++ default algorithm collection."""
collection_builder = mscclpp.AlgorithmCollectionBuilder()
return collection_builder.build_default_algorithms(
scratch_buffer=scratch_buffer.data_ptr(),
scratch_buffer_size=scratch_buffer.nbytes,
rank=rank
)
Step 2: Create a Custom Communicator Class
class CustomizedComm:
def __init__(self, comm: mscclpp.CommGroup):
self.comm = comm
# Allocate scratch buffer (required by some algorithms)
dlpack = mscclpp.RawGpuBuffer(1 << 27).to_dlpack(data_type=str(torch.float16))
self.scratch_buffer = torch.utils.dlpack.from_dlpack(dlpack)
# Load and select algorithms
algorithms = load_algorithms(self.scratch_buffer, comm.my_rank)
# Select specific algorithms by name
self._algo_small = [
algo for algo in algorithms
if algo.collective == "allreduce"
and algo.name == "default_allreduce_nvls_packet"
][0]
self._algo_large = [
algo for algo in algorithms
if algo.collective == "allreduce"
and algo.name == "default_allreduce_nvls_with_copy"
][0]
def all_reduce(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, stream=None):
# Select algorithm based on message size
algo = self._algo_small if tensor.nbytes < (1 << 20) else self._algo_large
algo.execute(
comm=self.comm.communicator,
input_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
output_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
input_size=tensor.nbytes,
output_size=tensor.nbytes,
dtype=mscclpp_utils.torch_dtype_to_mscclpp_dtype(tensor.dtype),
op=mscclpp.ReduceOp.SUM,
stream=stream.cuda_stream if stream else 0
)
Step 3: Run
MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR=<ip> MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT=<port> \
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=8 customized_comm_with_default_algo.py
Approach 2: DSL-based Algorithms (Medium)
Define custom communication patterns using MSCCL++ Python DSL. No C++ required.
Example: customized_comm_with_dsl.py
Step 1: Define the Collective Program
import mscclpp
from mscclpp.language.collectives import AllReduce
from mscclpp.language.channel import SwitchChannel, MemoryChannel, BufferType, SyncType
from mscclpp.language.program import CollectiveProgram
from mscclpp.language.rank import Rank
def allreduce_nvls(spec: mscclpp.AlgoSpec) -> CollectiveProgram:
"""Define an allreduce using NVLS (NVLink SHARP)."""
gpu_size = spec.world_size
with CollectiveProgram(
spec.name,
spec.collective,
gpu_size,
instances=spec.instances,
protocol=spec.protocol,
num_threads_per_block=spec.num_threads_per_block,
min_message_size=spec.min_message_size,
max_message_size=spec.max_message_size,
) as program:
# Create NVLS channel for all GPUs
nvls_chan = SwitchChannel(
rank_list=[gpu for gpu in range(gpu_size)],
buffer_type=BufferType.input
)
# Create memory channels for synchronization
channels = {}
for gpu in range(gpu_size):
for peer in range(gpu_size):
if peer != gpu:
channels[(peer, gpu)] = MemoryChannel(peer, gpu)
# Synchronize before operation
for gpu in range(gpu_size):
for peer in range(gpu_size):
if peer != gpu:
channels[(peer, gpu)].signal(tb=0, relaxed=True)
for peer in range(gpu_size):
if peer != gpu:
channels[(peer, gpu)].wait(tb=0, relaxed=True, data_sync=SyncType.after)
# Perform reduce and broadcast
for gpu in range(gpu_size):
rank = Rank(gpu)
input_buffer = rank.get_input_buffer()
nvls_chan.at_rank(gpu).reduce(
buffer_offset=gpu, size=1,
dst_chunk=input_buffer[gpu:gpu+1], tb=0
)
nvls_chan.at_rank(gpu).broadcast(
src_chunk=input_buffer[gpu:gpu+1],
buffer_offset=gpu, size=1, tb=0
)
# Synchronize after operation
for gpu in range(gpu_size):
for peer in range(gpu_size):
if peer != gpu:
channels[(peer, gpu)].signal(tb=0, relaxed=True, data_sync=SyncType.before)
for peer in range(gpu_size):
if peer != gpu:
channels[(peer, gpu)].wait(tb=0, relaxed=True)
return program
Step 2: Compile the Algorithm
def setup_algorithm(rank: int, world_size: int, nranks_per_node: int):
"""Compile the DSL algorithm for this rank."""
spec = mscclpp.language.AlgoSpec(
name="allreduce_nvls",
collective=AllReduce(world_size, 1, True),
nranks_per_node=nranks_per_node,
world_size=world_size,
in_place=True,
instances=nranks_per_node,
protocol="Simple",
num_threads_per_block=1024,
min_message_size=1 << 20,
max_message_size=48 << 30,
tags={"nvls": 1},
)
return mscclpp.compile(algo=allreduce_nvls, algo_spec=spec, rank=rank)
Step 3: Execute with Executor
DSL algorithms require an Executor:
class CustomizedComm:
def __init__(self, comm: mscclpp.CommGroup, algorithm):
self.comm = comm
self.executor = mscclpp.Executor(comm.communicator) # Required for DSL
self.algorithm = algorithm
def all_reduce(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, stream=None):
self.algorithm.execute(
comm=self.comm.communicator,
executor=self.executor, # Pass executor for DSL algorithms
input_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
output_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
input_size=tensor.nbytes,
output_size=tensor.nbytes,
dtype=mscclpp_utils.torch_dtype_to_mscclpp_dtype(tensor.dtype),
stream=stream.cuda_stream if stream else 0
)
Step 4: Run
MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR=<ip> MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT=<port> \
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=8 customized_comm_with_dsl.py
Approach 3: Native C++/CUDA Kernels (Advanced)
Write custom CUDA kernels for maximum performance and control.
Example: customized_allgather.py + customized_allgather.cu
Step 1: Implement the CUDA Kernel and Algorithm Builder
Create a .cu file with your kernel and algorithm builder:
// customized_allgather.cu
#include <mscclpp/algorithm.hpp>
#include <mscclpp/core.hpp>
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>
namespace py = pybind11;
// Your CUDA kernel
__global__ void allgather(
mscclpp::DeviceHandle<mscclpp::PortChannel>* channels,
int rank,
size_t nbytesPerGPU
) {
// Kernel implementation...
}
// Algorithm builder class
class AllgatherAlgoBuilder : public mscclpp::AlgorithmBuilder {
public:
std::shared_ptr<mscclpp::Algorithm> build() override {
auto self = std::make_shared<AllgatherAlgoBuilder>();
return std::make_shared<mscclpp::NativeAlgorithm>(
"allgather", // Algorithm name
"allgather", // Collective type
// Initialize function
[self](std::shared_ptr<mscclpp::Communicator> comm) {
self->initialize(comm);
},
// Kernel execution function
[self](const std::shared_ptr<void> ctx,
const void* input, void* output,
size_t inputSize, size_t outputSize,
mscclpp::DataType dtype, mscclpp::ReduceOp op,
cudaStream_t stream, int nBlocks, int nThreadsPerBlock,
const std::unordered_map<std::string, uintptr_t>& extras) {
return self->kernelFunc(ctx, input, output, inputSize, dtype, stream);
},
// Context initialization function
[self](std::shared_ptr<mscclpp::Communicator> comm,
const void* input, void* output,
size_t inputSize, size_t outputSize, mscclpp::DataType dtype) {
return self->initContext(comm, input, output, inputSize, dtype);
},
// Context key generation function
[self](const void* input, void* output,
size_t inputSize, size_t outputSize, mscclpp::DataType dtype, bool symmetricMemory) {
return self->generateContextKey(input, output, inputSize, outputSize, dtype, symmetricMemory);
}
);
}
private:
void initialize(std::shared_ptr<mscclpp::Communicator> comm) { /* ... */ }
mscclpp::CommResult kernelFunc(const std::shared_ptr<void> ctx, /* ... */) { /* ... */ }
std::shared_ptr<void> initContext(/* ... */) { /* ... */ }
mscclpp::AlgorithmCtxKey generateContextKey(/* ... */) { /* ... */ }
};
// Expose to Python
PYBIND11_MODULE(mscclpp_native, m) {
m.def("create_allgather_algorithm", []() {
auto builder = std::make_shared<AllgatherAlgoBuilder>();
auto algo = builder->build();
// Return as PyCapsule (see full example for capsule handling)
return py::reinterpret_steal<py::capsule>(getCapsule(algo));
});
}
Step 2: Compile and Load in Python
import mscclpp
import os
# MSCCL++ compiles the .cu file at runtime using JIT
mscclpp_native = mscclpp.compile_native(
name="mscclpp_native",
file=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "customized_allgather.cu")
)
# Get the algorithm from the compiled module
capsule = mscclpp_native.create_allgather_algorithm()
algorithm = mscclpp.Algorithm.create_from_native_capsule(capsule)
Step 3: Execute
class CustomizedComm:
def __init__(self, comm: mscclpp.CommGroup):
self.comm = comm
# Compile and load native algorithm
mscclpp_native = mscclpp.compile_native(
name="mscclpp_native",
file="customized_allgather.cu"
)
capsule = mscclpp_native.create_allgather_algorithm()
self.algorithm = mscclpp.Algorithm.create_from_native_capsule(capsule)
def all_gather(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, out_tensor: torch.Tensor, stream=None):
self.algorithm.execute(
self.comm.communicator,
tensor.data_ptr(),
out_tensor.data_ptr(),
tensor.nbytes,
out_tensor.nbytes,
mscclpp_utils.torch_dtype_to_mscclpp_dtype(tensor.dtype),
stream=stream.cuda_stream if stream else 0
)
Step 4: Run
MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR=<ip> MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT=<port> \
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=8 customized_allgather.py
Algorithm.execute() API Reference
All algorithms use the same execute() interface:
algorithm.execute(
comm, # mscclpp.Communicator (required)
input_buffer, # int: input data pointer from tensor.data_ptr()
output_buffer, # int: output data pointer
input_size, # int: input size in bytes (tensor.nbytes)
output_size, # int: output size in bytes
dtype, # mscclpp.DataType: data type
op=mscclpp.ReduceOp.NOP, # Reduction operation (for reduce collectives)
stream=0, # CUDA stream handle
executor=None, # mscclpp.Executor (required for DSL algorithms)
nblocks=0, # Thread blocks (0 = auto)
nthreads_per_block=0, # Threads per block (0 = auto)
extras=None # dict[str, int]: extra pointer parameters
)
Data Type Conversion:
import mscclpp.utils as mscclpp_utils
# Convert PyTorch dtype to MSCCL++ dtype
mscclpp_dtype = mscclpp_utils.torch_dtype_to_mscclpp_dtype(tensor.dtype)
Getting CUDA Stream:
stream_handle = torch.cuda.current_stream().cuda_stream
Summary
Approach |
When to Use |
Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
Default |
Standard operations, quick setup |
Scratch buffer |
DSL |
Custom patterns, no C++ needed |
Executor |
Native |
Custom kernels, max performance |
|
All examples are in examples/torch-integration/.
Performance Tuning
The default algorithms use a fixed heuristic to select algorithms based on message size. For production workloads, you can achieve significantly better performance by auto-tuning — benchmarking every candidate algorithm, block count, and thread count for each message size at startup, then using the fastest configuration at runtime.
Full example: customized_comm_with_tuning.py
How It Works
Candidate selection — For each power-of-two message size from 1 KB to 128 MB, the tuner picks the applicable algorithms:
Small messages (≤ 4 MB):
default_allreduce_nvls_packet,default_allreduce_packetLarge messages (≥ 512 KB):
default_allreduce_rsag_zero_copyOverlapping sizes get all three candidates.
Grid search — Each candidate is run with every combination of block counts (
4, 8, 16, … 128) and thread counts (512, 768, 1024). Results are captured in a CUDA graph and timed.Cross-rank consensus — Elapsed times are averaged across all ranks with an allreduce so every GPU selects the same configuration.
Runtime dispatch —
get_tuned_config()rounds the actual message size up to the next power of two and returns the winning(algorithm, nblocks, nthreads)triple.
Loading Candidate Algorithms
The same load_algorithms helper from Approach 1 is reused. The tuner extracts multiple algorithm objects:
algorithms = load_algorithms(scratch_buffer=self.scratch_buffer, rank=self.rank)
self._algorithm_nvls_packet = [
algo for algo in algorithms
if algo.collective == "allreduce" and algo.name == "default_allreduce_nvls_packet"
][0]
self._algorithm_rsag_zero_copy = [
algo for algo in algorithms
if algo.collective == "allreduce" and algo.name == "default_allreduce_rsag_zero_copy"
][0]
self._algorithm_packet = [
algo for algo in algorithms
if algo.collective == "allreduce" and algo.name == "default_allreduce_packet"
][0]
The Tuning Loop
The tuning loop iterates over message sizes, candidate algorithms, and kernel launch parameters. CUDA graphs are used for accurate timing:
def _tune(self, n_warmup, n_graph_launches, n_ops_per_graph):
sizes = [1 << i for i in range(10, 28)]
self.best_configs = {1024: (self._algorithm_nvls_packet, 0, 0)}
tune_tensor = torch.rand(1 << 27, dtype=torch.float16, device="cuda")
candidates_nblocks = [4, 8, 16, 24, 32, 48, 64, 128]
candidates_nthreads = [512, 768, 1024]
for size in sizes:
algos = []
if size <= 4 * 1024 * 1024:
algos.append(self._algorithm_nvls_packet)
algos.append(self._algorithm_packet)
if size >= 512 * 1024:
algos.append(self._algorithm_rsag_zero_copy)
best_time = float("inf")
best_config = None
for algo in algos:
for nb in candidates_nblocks:
for nt in candidates_nthreads:
if self._run_algo(algo, tune_tensor, size, nb, nt) != 0:
continue # skip unsupported configs
# Warmup, then time with CUDA graphs
# ... (see full example for graph capture logic)
# Average timing across ranks
time_tensor = torch.full(
(self.world_size,), elapsed, dtype=torch.float64, device="cuda"
).to(dtype=torch.float32)
self.all_reduce(time_tensor, op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM)
avg_time = time_tensor[self.rank].item() / self.world_size
if avg_time < best_time:
best_time = avg_time
best_config = (algo, nb, nt)
if best_config:
self.best_configs[size] = best_config
Dispatching with Tuned Configuration
At runtime, round the message size to the next power of two and look up the best configuration:
def get_tuned_config(self, size):
if size < 1024:
target_size = 1024
elif size > 256 * 1024 * 1024:
target_size = 256 * 1024 * 1024
else:
target_size = 1 << (size - 1).bit_length()
return self.best_configs.get(target_size)
def all_reduce(self, tensor, op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM, stream=None):
config = self.get_tuned_config(tensor.nbytes)
algo, nblocks, nthreads = config if config else (self._algorithm_nvls_packet, 0, 0)
algo.execute(
comm=self.comm.communicator,
input_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
output_buffer=tensor.data_ptr(),
input_size=tensor.nbytes,
output_size=tensor.nbytes,
dtype=mscclpp_utils.torch_dtype_to_mscclpp_dtype(tensor.dtype),
op=mscclpp.ReduceOp.SUM,
stream=stream.cuda_stream if stream else torch.cuda.current_stream().cuda_stream,
nblocks=nblocks,
nthreads_per_block=nthreads,
)
Running the Tuning Example
MSCCLPP_MASTER_ADDR=<ip> MSCCLPP_MASTER_PORT=<port> \
torchrun --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=8 customized_comm_with_tuning.py