G3000 Weight and Balance
Introduction
The G3000 supports an optional weight and balance feature which extends the base weight and fuel feature with additional capabilities, such as the ability to define and load individual weight stations and carry out center-of-gravity (CG) calculations.
By default, the weight and balance feature is disabled. The following sections describe how to enable and configure the feature. Because weight and balance extends the weight and fuel feature, the latter must still be configured even if weight and balance is enabled. Please refer to this page for more information about the weight and fuel feature.
Configuring Weight and Balance
The weight and balance feature is enabled in panel.xml by including the <WeightBalance> tag. Several global options are defined using attributes on this tag:
Units
The weight-unit and arm-unit attributes define the units with which all weight and moment-arm values in the <WeightBalance> tag and its descendants are parsed. The supported weight units are pounds (lb, lbs, pound, pounds) and kilograms (kg, kgs, kilogram, kilograms). The supported moment arm units are inches (in, inch, inches) and centimeters (cm, centimeter, centimeters).
These units only affect the parsing of values from panel.xml. They do not affect how weight and moment-arm values are displayed by the G3000. The G3000 uses the Weight Units setting (which the user can configure via the GTC Avionics Settings page) to determine the units in which weight and moment-arm values are displayed.
Moment arm labels
The arm-label and arm-label-short attributes define how moment-arm values are labeled. arm-label defines the long-form label text used for moment-arm values, and arm-label-short defines the short-form label text. The short-form label text is recommended to be no longer than 3 characters.
Both attributes are optional. If not explicitly defined, the long-form label text defaults to "CG", and the short-form label text defaults to the long-form label text.
%MAC support
To enable support for %MAC (mean aerodynamic chord) values, both the lemac and temac attributes must be defined. lemac defines the moment arm of the leading edge mean aerodynamic cord (LEMAC) and temac defines the moment arm of the trailing edge mean aerodynamic cord (TEMAC). Both should be expressed in the unit type defined by the arm-unit attribute. LEMAC and TEMAC cannot be equal to each other.
When %MAC support is enabled, moment-arm values will be displayed as %MAC in certain places. Additionally, %MAC support allows envelopes to be defined in terms of %MAC.
Empty weight and moment arm
The empty-weight attribute defines the aircraft's weight when all load stations are disabled (zero empty weight and zero load weight) and with no fuel loaded. It can be any finite non-negative number. It should be expressed in the unit type defined by the weight-unit attribute.
The empty-arm attribute defines the moment arm of the aircraft's center of gravity when all load stations are disabled (zero empty weight and zero load weight) and with no fuel loaded. It can be any finite number. It should be expressed in the unit type defined by the arm-unit attribute.
Example
The following example panel.xml excerpt enables the weight and balance feature and configures global options.
<Performance>
<!--
The <Weights> tag still needs to be defined when enabling the weight and balance feature.
In this case the options defined by the <BasicEmpty> and <MaxPax> tags are informational only and are not used by
the G3000 system.
-->
<Weights>
<BasicEmpty unit='pounds'>3000</BasicEmpty>
<MaxRamp unit='pounds'>5300</MaxRamp>
<MaxTakeoff unit='pounds'>5200</MaxTakeoff>
<MaxLanding unit='pounds'>4750</MaxLanding>
<MaxZeroFuel unit='pounds'>4200</MaxZeroFuel>
<MaxPax>4</MaxPax>
</Weights>
<WeightBalance
weight-unit="lb"
arm-unit="in"
arm-label="Station"
arm-label-short="STA"
empty-weight="3000"
empty-arm="190"
>
<!-- ... -->
</WeightBalance>
</Performance>
Load Stations
With the weight and balance feature, the user adjusts the weight of the airplane by assigning load weight to individual load stations. You may define as many load stations as you wish in panel.xml with the <LoadStations> tag. Each load station is defined using a <Station> tag as a child of <LoadStations>.
A load station can be assigned empty weight and load weight. The empty weight of a station generally does not change from one flight to another and is considered to be part of the aircraft's basic operating weight. For example, the empty weight of a passenger station may include the weight of the seat. The load weight of a station is the weight at that station that typically may change from one flight to another. For example, the load weight of a passenger station would be the weight of the passenger and any of their belongings that are stored with them at the station.
Each station is also assigned a moment arm. The same moment arm applies to both the empty weight and load weight assigned to the station.
Finally, each station can be enabled or disabled. When enabled, the user may adjust its load weight and any weight (empty or load) assigned to it is taken into account when performing weight and balance calculations. When disabled, the user cannot adjust its load weight and any weight (empty or load) assigned to it is ignored when performing weight and balance calculations.
The following sub-sections describe how each load station can be configured.
Basic properties
Each load station requires the following basic properties to be defined using attributes on the <Station> tag:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
id | The load station's ID. Each load station must have a unique ID. The ID is only used internally and is not displayed anywhere. |
type | The load station's type. Can be either 'operating', 'passenger', or 'cargo'. The station's type affects how load weight assigned to it is classified. Note that empty weight assigned to any station is classified as operating weight regardless of the station's type. |
name | The load station's displayed name. |
Weight limits
The max-empty-weight and max-load-weight attributes on the <Station> tag define the maximum empty and load weights, respectively, that can be assigned to the station. Both weights should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute. If either of these values is not defined, then it will default to 99999 (of the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute).
Moment-arm limits
The min-arm and max-arm attributes on the <LoadStations> tag define the global minimum and maximum moment arms, respectively, that can be assigned to any load station. Additionally, the min-arm and max-arm attributes on the <Station> tag define the minimum and maximum moment arms, respectively, that can be assigned to the station associated with that tag. The final moment-arm limits imposed on a station represent the most restrictive range of values that comply with both the global limits and the station limits.
All moment-arm limits should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's arm-unit attribute. If a global or station moment-arm limit is not defined, then it will default to -∞ for the minimum and ∞ for the maximum.
Default parameters
Several default load station parameters can be configured using <Station> tag attributes: default empty weight, default moment arm, and default enabled state. Of these, only the default moment arm must be explicitly defined. The other two will take default values if not defined. These default parameters are assigned to the station before any potential changes are made by the user.
The default empty weight is defined using the empty-weight attribute. It should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute. If not defined, then it defaults to 0.
The default moment arm is defined using the arm attribute. It should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's arm-unit attribute.
The default enabled state is defined using the enabled attribute. If not defined, then it defaults to true.
User-editability
You can configure whether the empty weight, moment arm, and enabled state of a load station are user editable using the <Station> tag's empty-weight-editable, arm-editable, and enabled-editable attributes, respectively. All options default to false if not defined.
When one or more of these parameters are configured to be user editable, the user can change them through the GTC Weight and Balance Configuration page (see image below).
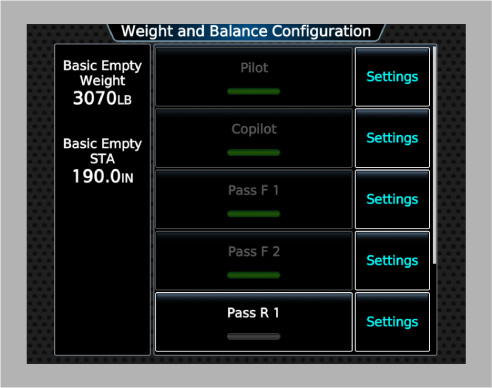
Example
The following example panel.xml excerpt configures seven load stations: pilot, copilot, four passengers, and one baggage. Two passenger stations are optional (they can be disabled by the user) and the rest are required and always enabled. The empty weights and moment arms of all stations except the baggage station are user editable.
<WeightBalance
weight-unit="lb"
arm-unit="in"
...
>
<!-- Apply global moment-arm limits of 100 to 250 inches to all load stations. -->
<LoadStations min-arm="100" max-arm="250">
<!-- Pilot and copilot stations, required -->
<Station
id="pilot" type="operating" name="Pilot"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="0" arm="146.4" enabled="true"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true"
/>
<Station
id="copilot" type="operating" name="Copilot"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="0" arm="146.4" enabled="true"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true"
/>
<!-- Two front-row passenger stations, required -->
<Station
id="passengerF1" type="passenger" name="Pass F 1"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="35" arm="190.1" enabled="true"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true"
/>
<Station
id="passengerF2" type="passenger" name="Pass F 2"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="35" arm="190.1" enabled="true"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true"
/>
<!-- Two rear-row passenger stations, optional -->
<Station
id="passengerR1" type="passenger" name="Pass R 1"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="35" arm="218.2" enabled="false"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true" enabled-editable="true"
/>
<Station
id="passengerR2" type="passenger" name="Pass R 2"
max-load-weight="500"
empty-weight="35" arm="218.2" enabled="false"
empty-weight-editable="true" arm-editable="true" enabled-editable="true"
/>
<!-- Baggage station, required -->
<Station
id="baggage" type="cargo" name="Baggage"
max-load-weight="999"
empty-weight="0" arm="229.0" enabled="true"
/>
</LoadStations>
<!-- ... -->
</WeightBalance>
Fuel Station
The weight and balance feature supports a single fuel station. All weight from loading fuel is assigned to this fuel station.
Configuring the fuel station is done in panel.xml using the <FuelStation> tag. The only configurable value for the fuel station is its moment arm, which is defined using the <Arm> tag. The moment arm should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's arm-unit attribute.
Example
The following example panel.xml excerpt configures a fuel station with a moment arm of 203 inches.
<WeightBalance
weight-unit="lb"
arm-unit="in"
...
>
<FuelStation>
<Arm>203</Arm>
</FuelStation>
<!-- ... -->
</WeightBalance>
Envelopes
One or more envelopes must be defined with the weight and balance feature. An envelope represents the two-dimensional space of allowed weight and center-of-gravity moment-arm values for a given set of conditions. The user selects one envelope as the active envelope through the GTC Weight and Balance page. Weight and center-of-gravity moment-arm pairs calculated by the weight and balance system are compared to the active envelope. If any calculated pairs are found to be outside of the active envelope limits, then the system notifies the user of the exceedance using amber visual cues on the Weight and Balance pane (see image below).
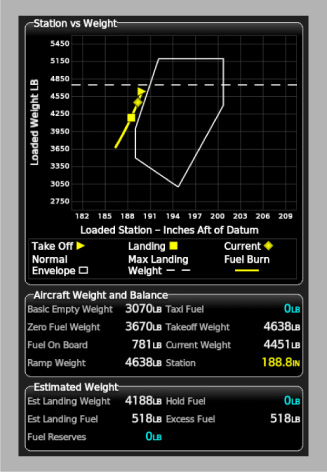
Envelopes are defined in panel.xml with the <Envelopes> tag. Each load station is defined using a <Envelope> tag as a child of <Envelopes>. The <Envelopes> tag's default-index attribute defines the index of the envelope that is selected as the default envelope. Envelopes are indexed in the order they are defined in <Envelopes>, starting at index 0.
The following sub-sections describe how each envelope can be configured.
Envelope parameters
The <Envelope> tag's name attribute defines the displayed name of the envelope.
The <Envelope> tag's min-weight and max-weight attributes define the minimum and maximum weights, respectively, allowed by the envelope. The weights should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute.
The <Envelope> tag's max-zero-fuel-weight, max-ramp-weight, max-takeoff-weight, and max-landing-weight attributes define the maximum zero-fuel, ramp, takeoff, and landing weights that are used when the envelope is active. The weights should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute. If any of these weights are not defined, then it will default to the corresponding weight defined by the <Weights> tag.
Envelope shape
The shape of the envelope between its minimum and maximum weights is defined by the <MinimumArm> and <MaximumArm> tags. The <MinimumArm> tag uses breakpoints to define the minimum moment-arm boundary: the minimum allowed moment arms at all weights between the minimum and maximum weights (below image, red highlight). The <MaximumArm> tag uses breakpoints to define the maximum moment-arm boundary: the maximum allowed moment arms at all weights between the minimum and maximum weights (below image, cyan highlight).
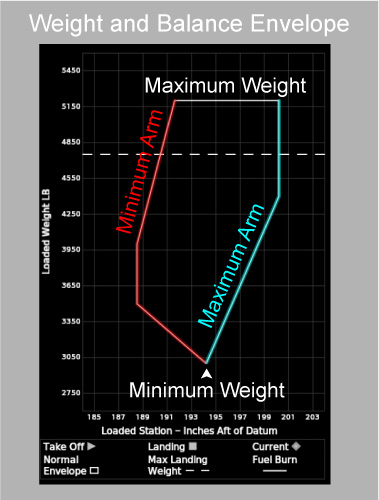
For both the minimum and maximum moment-arm boundaries, breakpoints define anchor points along the boundary and the boundary is linearly interpolated between breakpoints. Breakpoints are expressed as a JSON-formatted array of 2-tuples. Each tuple is one breakpoint. The first tuple member is the breakpoint's moment arm. If the <Envelope> tag's use-mac attribute is true and %MAC support is enabled, then the moment arm should be expressed as a %MAC value. Otherwise, the moment arm should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's arm-unit attribute. The second tuple member is the breakpoint's weight, expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute. Breakpoints should be ordered in the array such that their weights are monotonically increasing (i.e. a breakpoint's weight must be greater than or equal to the weight of the previous breakpoint).
If the first breakpoint in the array has a weight greater than the envelope's minimum weight, then the boundary will extend from the first breakpoint's weight down to the minimum weight at a constant moment-arm value equal to the first breakpoint's moment arm. Likewise, if the last breakpoint in the array has a weight less than the envelope's maximum weight, then the boundary will extend from the last breakpoint's weight up to the maximum weight at a constant moment-arm value equal to the last breakpoint's moment arm.
Graph options
The Weight and Balance pane displays a graph that depicts the active envelope. The scales of this graph must be configured for each envelope. This is done using the <GraphScale>, <LargeGraphScale>, and <SmallGraphScale> tags. The <LargeGraphScale> tag defines scale options for the large-format graph (image, left). The <SmallGraphScale> tag defines scale options for the small-format graph (image, right). If either <LargeGraphScale> or <SmallGraphScale> is not defined, then the options for the missing tag default to those defined by the <GraphScale> tag. If <GraphScale> is not defined, then both <LargeGraphScale> and <SmallGraphScale> must be defined.
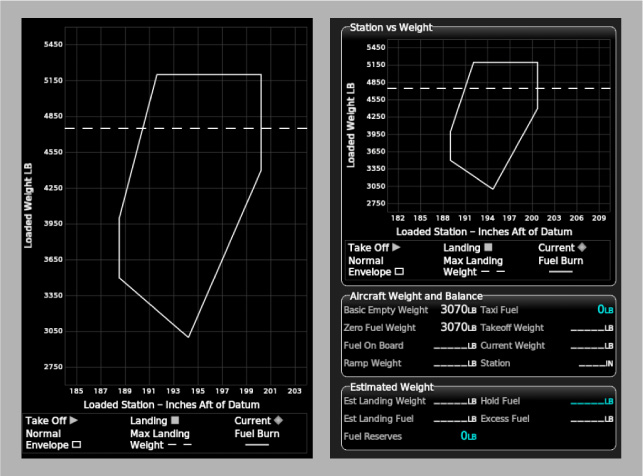
All three graph scale tags share the same syntax. The min-weight and max-weight attributes define the minimum and maximum scale weights, respectively, of the graph's vertical axis. The weights should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's weight-unit attribute. The min-arm and max-arm attributes define the minimum and maximum scale moment arms, respectively, of the graph's horizontal axis. If the <Envelope> tag's use-mac attribute is true and %MAC support is enabled, then the moment arms should be expressed as %MAC values. Otherwise, the moment arms should be expressed in the unit type defined by the <WeightBalance> tag's arm-unit attribute.
If an <Envelope> tag's use-mac attribute is true and %MAC support is enabled, then the Weight and Balance pane graph's moment-arm scale will be displayed in units of %MAC when the envelope is active.
Example
The following example panel.xml excerpt configures the envelope seen in the images in the previous sub-sections.
<WeightBalance
weight-unit="lb"
arm-unit="in"
...
>
<Envelopes>
<Envelope name="Normal" min-weight="3000" max-weight="5200" max-landing-weight="4750">
<MinimumArm>
[
[194.2, 3000],
[188.5, 3500],
[188.5, 4000],
[191.6, 5200]
]
</MinimumArm>
<MaximumArm>
[
[194.2, 3000],
[200.2, 4400],
[200.2, 5200]
]
</MaximumArm>
<LargeGraphScale min-weight="2600" max-weight="5600" min-arm="184" max-arm="204" />
<SmallGraphScale min-weight="2600" max-weight="5600" min-arm="180" max-arm="210" />
</Envelope>
</Envelopes>
<!-- ... -->
</WeightBalance>
Customizing the Weight and Balance Pane
The Weight and Balance pane requires some configuration that is too complex to be defined in panel.xml. This configuration is done using plugins instead. To configure the pane, a PFD and an MFD plugin should return instances of WeightBalancePaneViewModule from their respective getWeightBalancePaneViewModule() methods.
The following sub-sections describe how to customize the Weight and Balance pane using WeightBalancePaneViewModule.
Rendering the Aircraft Loading Panel
The Weight and Balance pane's aircraft loading panel depicts the assigned load weights of all enabled load stations. The load stations are represented graphically and are typically superimposed on a diagram of the airplane.
The content of the loading panel is rendered using WeightBalancePaneViewModule's renderAircraftLoadPanel() method. The method should create and render a component that implements the WeightBalancePaneViewPanel interface and return it as a VNode. A NodeReference is passed to the method as the first argument, which should in turn be passed to the ref prop of the component so that the component instance is assigned to the NodeReference. Additional arguments that may be helpful in creating the component are also passed to the method; these arguments are for convenience only and do not have to be used.
The following code shows how to render a loading panel component using renderAircraftLoadPanel().
class ExampleWeightBalancePaneViewModule implements WeightBalancePaneViewModule {
public renderAircraftLoadPanel(
ref: NodeReference<WeightBalancePaneViewPanel>,
bus: EventBus,
weightBalanceConfig: WeightBalanceConfig,
weightBalanceSettingManager: WeightBalanceUserSettingManager,
unitsSettingManager: UnitsUserSettingManager
): VNode {
return (
<ExampleAircraftLoadPanel
ref={ref} // This prop assignment is required
weightBalanceSettingManager={weightBalanceSettingManager}
unitsSettingManager={unitsSettingManager}
/>
);
}
}
interface ExampleAircraftLoadPanelProps extends ComponentProps {
weightBalanceSettingManager: WeightBalanceUserSettingManager;
unitsSettingManager: UnitsUserSettingManager;
}
class ExampleAircraftLoadPanel
extends DisplayComponent<ExampleAircraftLoadPanelProps>
implements WeightBalancePaneViewPanel {
// ...
}
The total available size of the load panel content area depends on the display pane in which it is contained and whether the pane is full size or half size:
| Pane | Size | Width (px) | Height (px) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PFD | Half | 508 | 778 |
| MFD | Full | 464 | 702 |
| MFD | Half | 495 | 748 |
When styling your load panel component, care should be taken to ensure it supports and fits well into all of these sizes.
When rendering the loading panel component, you may find it helpful to use the WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation to render the graphical representations of the load stations. Each instance of WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation renders a single load station and will automatically show/hide itself when the load station is enabled/disabled and update the displayed load weight as appropriate. The following image shows an example of what a rendered WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation component looks like.
The root element of WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation is assigned the weight-balance-pane-load-station class. Therefore, to apply CSS styling to the root element you can select it with the following selector:
.weight-balance-pane-load-station { }
You can also add additional classes to the root elements of individual WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation components using the class prop.
The following code shows how to use WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation to render two load stations.
interface ExampleAircraftLoadPanelProps extends ComponentProps {
weightBalanceSettingManager: WeightBalanceUserSettingManager;
unitsSettingManager: UnitsUserSettingManager;
}
class ExampleAircraftLoadPanel
extends DisplayComponent<ExampleAircraftLoadPanelProps>
implements WeightBalancePaneViewPanel {
// ...
public render(): VNode {
return (
<div>
// ...
{this.renderStation('pilot', 'weight-balance-pane-load-station-pilot')}
{this.renderStation('copilot', 'weight-balance-pane-load-station-copilot')}
</div>
);
}
/**
* Renders one of this panel's load station displays.
* @param id The ID of the load station for which to render a display.
* @param cssClass CSS class(es) to apply to the display's root element.
* @returns A display for the specified load station.
*/
private renderStation(id: string, cssClass?: string): VNode | null {
const settingManager = this.props.weightBalanceSettingManager;
const stationDef = settingManager.loadStationDefs.find(def => def.id === id);
if (!stationDef) {
return null;
}
return (
<WeightBalancePaneViewLoadStation
show={settingManager.getSetting(`weightBalanceLoadStationEnabled_${id}`)}
label={stationDef.name}
loadWeight={settingManager.getSetting(`weightBalanceLoadStationLoadWeight_${id}`)}
weightDisplayUnit={this.props.unitsSettingManager.weightUnits}
class={cssClass}
/>
);
}
}