
Spark Serving
An Engine for Deploying Spark Jobs as Distributed Web Services
- Distributed: Takes full advantage of Node, JVM, and thread level parallelism that Spark is famous for.
- Fast: No single node bottlenecks, no round trips to Python. Requests can be routed directly to and from worker JVMs through network switches. Spin up a web service in a matter of seconds.
- Low Latency: When using continuous serving, you can achieve latencies as low as 1 millisecond.
- Deployable Anywhere: Works anywhere that runs Spark such as Databricks, HDInsight, AZTK, DSVMs, local, or on your own cluster. Usable from Spark, PySpark, and SparklyR.
- Lightweight: No dependence on costly Kafka or Kubernetes clusters.
- Idiomatic: Uses the same API as batch and structured streaming.
- Flexible: Spin up and manage several services on a single Spark cluster. Synchronous and Asynchronous service management and extensibility. Deploy any spark job that is expressible as a structured streaming query. Use serving sources/sinks with other Spark data sources/sinks for more complex deployments.
Usage
Jupyter Notebook Examples
- Deploy a classifier trained on the Adult Census Dataset
- More coming soon!
Spark Serving Hello World
import synapse.ml
import pyspark
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf, col, length
from pyspark.sql.types import *
df = spark.readStream.server() \
.address("localhost", 8888, "my_api") \
.load() \
.parseRequest(StructType().add("foo", StringType()).add("bar", IntegerType()))
replies = df.withColumn("fooLength", length(col("foo")))\
.makeReply("fooLength")
server = replies\
.writeStream \
.server() \
.replyTo("my_api") \
.queryName("my_query") \
.option("checkpointLocation", "file:///path/to/checkpoints") \
.start()
Deploying a Deep Network with the CNTKModel
import synapse.ml
from synapse.ml.cntk import CNTKModel
import pyspark
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf, col
df = spark.readStream.server() \
.address("localhost", 8888, "my_api")
.load()
.parseRequest(<Insert your models input schema here>)
# See notebook examples for how to create and save several
# examples of CNTK models
network = CNTKModel.load("file:///path/to/my_cntkmodel.mml")
transformed_df = network.transform(df).makeReply(<Whatever column you wish to send back>)
server = transformed_df \
.writeStream \
.server() \
.replyTo("my_api") \
.queryName("my_query") \
.option("checkpointLocation", "file:///path/to/checkpoints") \
.start()
Architecture
Spark Serving adds special streaming sources and sinks to turn any structured streaming job into a web service. Spark Serving comes with two deployment options that vary based on what form of load balancing is being used.
In brief you can use:
spark.readStream.server(): For head node load balanced services
spark.readStream.distributedServer(): For custom load balanced services
spark.readStream.continuousServer(): For a custom load balanced, submillisecond-latency continuous server
to create the various different serving dataframes and use the equivalent statements after df.writeStream
for replying to the web requests.
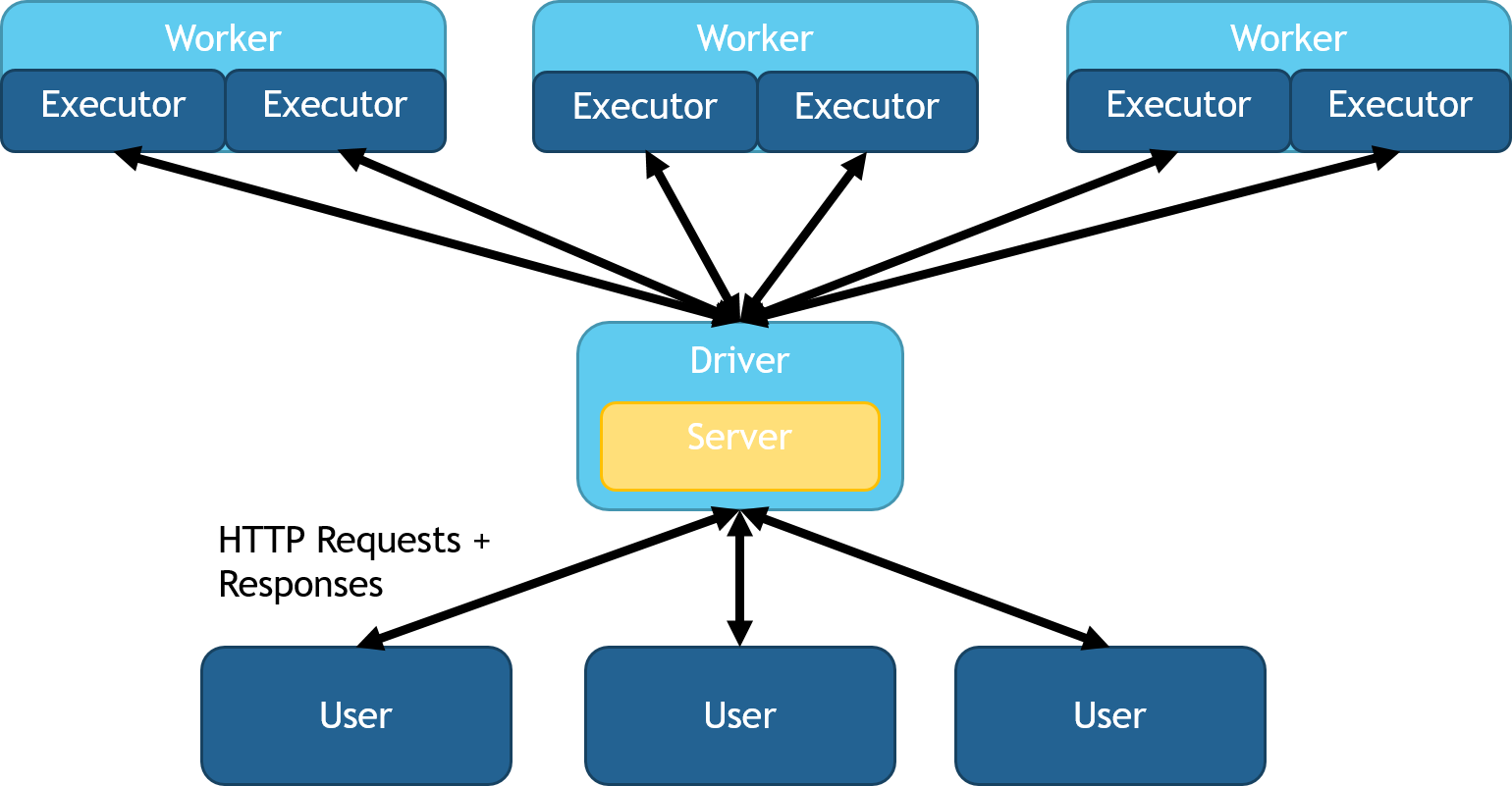
Head Node Load Balanced
You can deploy head node load balancing with the HTTPSource and
HTTPSink classes. This mode spins up a queue on the head node,
distributes work across partitions, then collects response data back to
the head node. All HTTP requests are kept and replied to on the head
node. In both python and Scala these classes can be access by using
spark.readStream.server() after importing SynapseML.
This mode allows for more complex windowing, repartitioning, and
SQL operations. This option is also idea for rapid setup and testing,
as it doesn't require any further load balancing or network
switches. A diagram of this configuration can be seen in this image:
Fully Distributed (Custom Load Balancer)
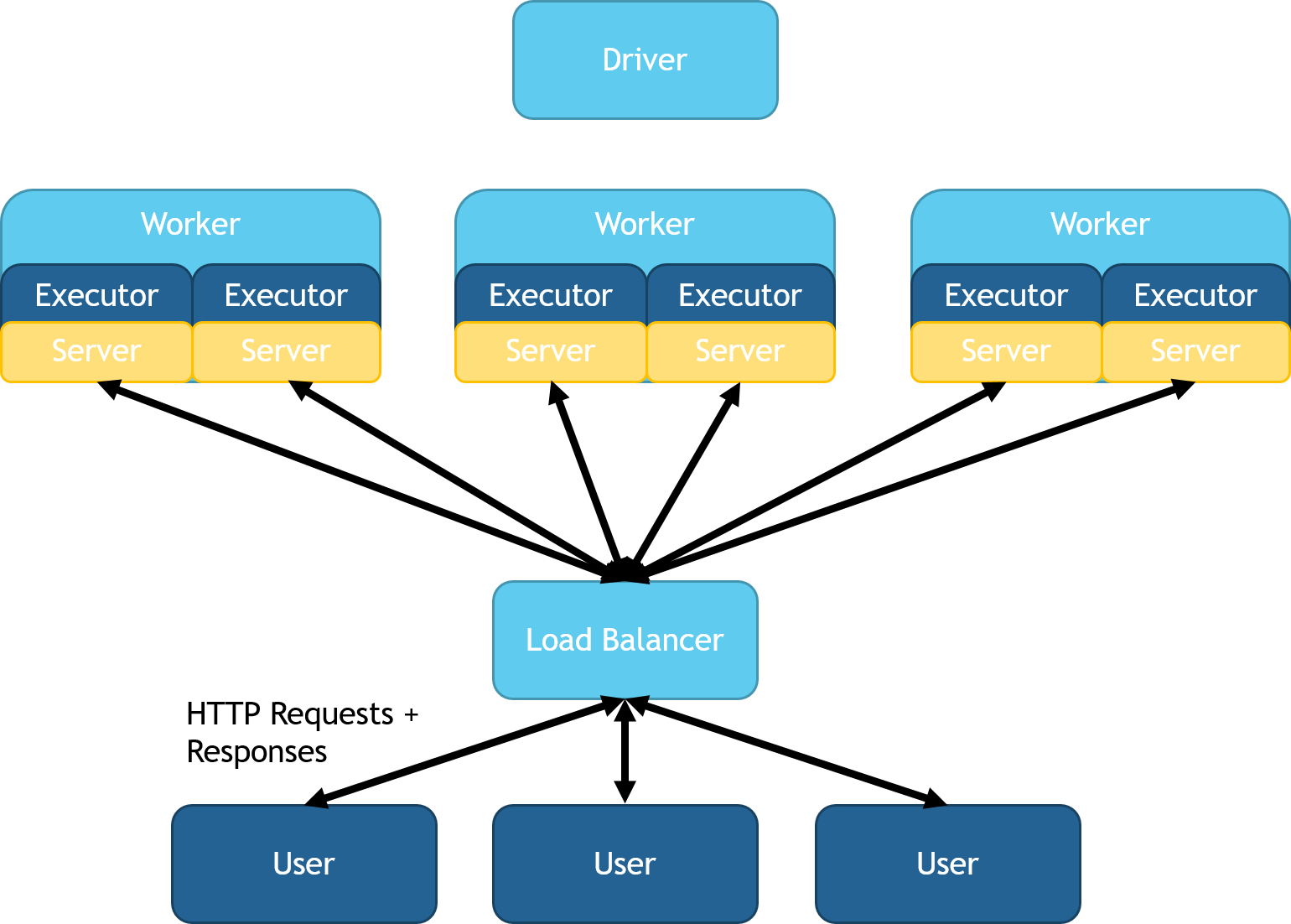
You can configure Spark Serving for a custom load balancer using the
DistributedHTTPSource and DistributedHTTPSink classes. This mode
spins up servers on each executor JVM.
In both python and Scala these classes can be access by using
spark.readStream.distributedServer() after importing SynapseML.
Each server will feed its
executor's partitions in parallel. This mode is key for high throughput
and low latency as data doesn't need to be transferred to and from the
head node. This deployment results in several web services that all
route into the same spark computation. You can deploy an external load
balancer to unify the executor's services under a single IP address.
Support for automatic load balancer management and deployment is
targeted for the next release of SynapseML. A diagram of this
configuration can be seen here:
Queries that involve data movement across workers, such as a nontrivial SQL join, need special consideration. The user must ensure that the right machine replies to each request. One can route data back to the originating partition with a broadcast join. In the future, request routing will be automatically handled by the sink.
Sub-Millisecond Latency with Continuous Processing
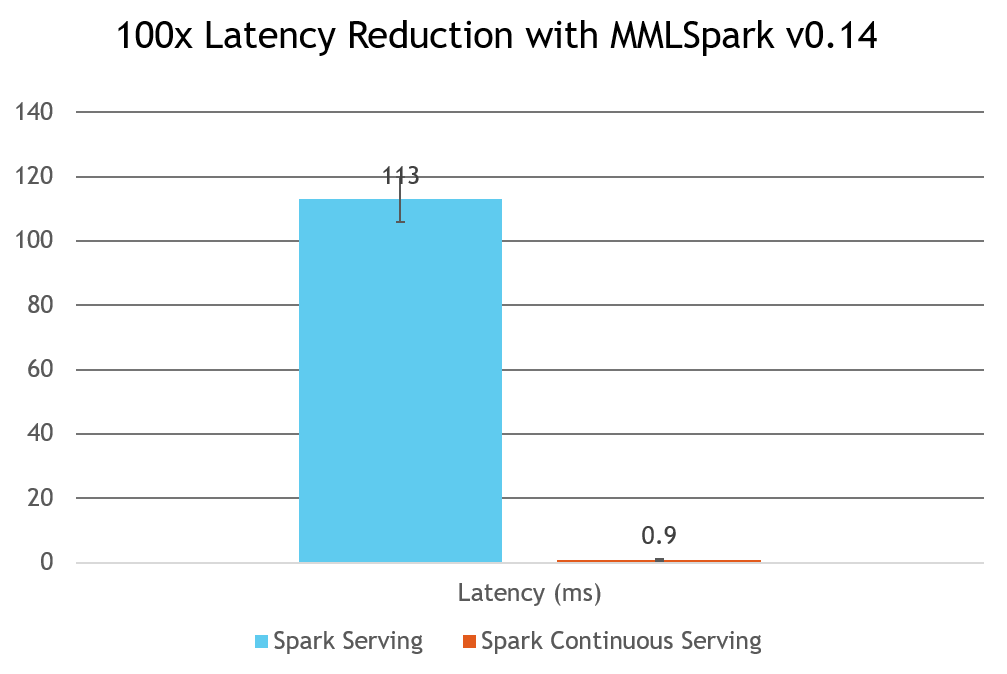
Continuous processing can be enabled by hooking into the HTTPSourceV2 class using:
spark.readStream.continuousServer()
...
In continuous serving, much like continuous streaming you need to add a trigger to your write statement:
df.writeStream
.continuousServer()
.trigger(continuous="1 second")
...
The architecture is similar to the custom load balancer setup described earlier. More specifically, Spark will manage a web service on each partition. These webservices can be unified together using an Azure Load Balancer, Kubernetes Service Endpoint, Azure Application gateway or any other way to load balance a distributed service. It's currently the user's responsibility to optionally unify these services as they see fit. In the future, we'll include options to dynamically spin up and manage a load balancer.
Databricks Setup
Databricks is a managed architecture and they've restricted all incoming traffic to the nodes of the cluster. If you create a web service in your databricks cluster (head or worker nodes), your cluster can communicate with the service, but the outside world can't. However, in the future, Databricks will support Virtual Network Injection, so problem will not arise. In the meantime, you must use SSH tunneling to forward the services to another machine(s) to act as a networking gateway. This machine can be any machine that accepts SSH traffic and requests. We have included settings to automatically configure this SSH tunneling for convenience.
Linux Gateway Setup - Azure
- Create a Linux VM using SSH
- Open ports 8000-9999 from the Azure portal
- Open the port on the firewall on the VM
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8000-10000/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
echo "GatewayPorts yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
service ssh --full-restart - Add your private key to a private container in Azure Storage Blob.
- Generate a SAS link for your key and save it.
- Include the following parameters on your reader to configure the SSH tunneling: serving_inputs = (spark.readStream.continuousServer() .option("numPartitions", 1) .option("forwarding.enabled", True) # enable ssh forwarding to a gateway machine .option("forwarding.username", "username") .option("forwarding.sshHost", "ip or dns") .option("forwarding.keySas", "SAS url from the previous step") .address("localhost", 8904, "my_api") .load()
This setup will make your service require an extra jump and affect latency. It's important to pick a gateway that has good connectivity to your spark cluster. For best performance and ease of configuration, we suggest using Spark Serving on an open cluster environment such as Kubernetes, Mesos, or Azure Batch.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Necessary | Default Value | Applicable When |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| host | The host to spin up a server on | Yes | ||
| port | The starting port when creating the web services. Web services will increment this port several times to find an open port. In the future, the flexibility of this param will be expanded | yes | ||
| name | The Path of the api a user would call. The format is hostname:port/name | yes | ||
| forwarding.enabled | Whether to forward the services to a gateway machine | no | false | When you need to forward services out of a protected network. Only Supported for Continuous Serving. |
| forwarding.username | the username to connect to on the remote host | no | ||
| forwarding.sshport | the port to ssh connect to | no | 22 | |
| forwarding.sshHost | the host of the gateway machine | no | ||
| forwarding.keySas | A Secure access link that can be used to automatically download the required ssh private key | no | Sometimes more convenient than a directory | |
| forwarding.keyDir | A directory on the machines holding the private key | no | "~/.ssh" | Useful if you can't send keys over the wire securely |