ONNX model inferencing on Spark
ONNX
ONNX is an open format to represent both deep learning and traditional machine learning models. With ONNX, AI developers can more easily move models between state-of-the-art tools and choose the combination that is best for them.
SynapseML now includes a Spark transformer to bring a trained ONNX model to Apache Spark, so you can run inference on your data with Spark's large-scale data processing power.
ONNXHub
Although you can use your own local model, many popular existing models are provided through the ONNXHub. You can use a model's ONNXHub name (for example "MNIST") and download the bytes of the model, and some metadata about the model. You can also list available models, optionally filtering by name or tags.
// List models
val hub = new ONNXHub()
val models = hub.listModels(model = Some("mnist"), tags = Some(Seq("vision")))
// Retrieve and transform with a model
val info = hub.getModelInfo("resnet50")
val bytes = hub.load(name)
val model = new ONNXModel()
.setModelPayload(bytes)
.setFeedDict(Map("data" -> "features"))
.setFetchDict(Map("rawPrediction" -> "resnetv24_dense0_fwd"))
.setSoftMaxDict(Map("rawPrediction" -> "probability"))
.setArgMaxDict(Map("rawPrediction" -> "prediction"))
.setMiniBatchSize(1)
val (probability, _) = model.transform({YOUR_DATAFRAME})
.select("probability", "prediction")
.as[(Vector, Double)]
.head
Usage
Create a
com.microsoft.azure.synapse.ml.onnx.ONNXModelobject and usesetModelLocationorsetModelPayloadto load the ONNX model.For example:
val onnx = new ONNXModel().setModelLocation("/path/to/model.onnx")Optionally, create the model from the ONNXHub.
val onnx = new ONNXModel().setModelPayload(hub.load("MNIST"))Use ONNX visualization tool (for example, Netron) to inspect the ONNX model's input and output nodes.
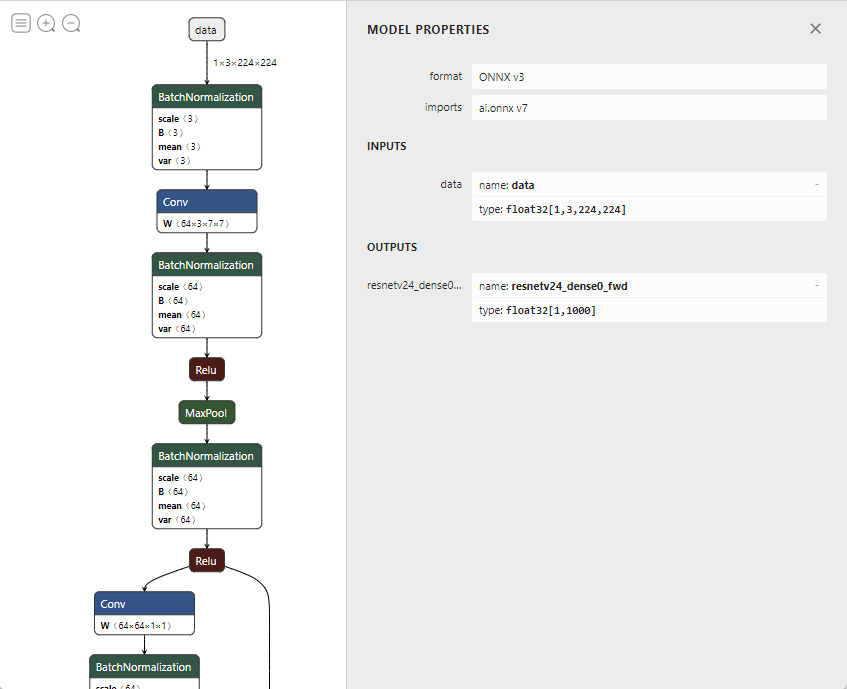
Set the parameters properly to the
ONNXModelobject.The
com.microsoft.azure.synapse.ml.onnx.ONNXModelclass provides a set of parameters to control the behavior of the inference.Parameter Description Default Value feedDict Map the ONNX model's expected input node names to the input DataFrame's column names. Make sure the input DataFrame's column schema matches with the corresponding input's shape of the ONNX model. For example, an image classification model may have an input node of shape [1, 3, 224, 224]with type Float. It's assumed that the first dimension (1) is the batch size. Then the input DataFrame's corresponding column's type should beArrayType(ArrayType(ArrayType(FloatType))).None fetchDict Map the output DataFrame's column names to the ONNX model's output node names. NOTE: If you put outputs that are intermediate in the model, transform will automatically slice at those outputs. See the section on Slicing. None miniBatcher Specify the MiniBatcher to use. FixedMiniBatchTransformerwith batch size 10softMaxDict A map between output DataFrame columns, where the value column will be computed from taking the softmax of the key column. If the 'rawPrediction' column contains logits outputs, then one can set softMaxDict to Map("rawPrediction" -> "probability")to obtain the probability outputs.None argMaxDict A map between output DataFrame columns, where the value column will be computed from taking the argmax of the key column. This parameter can be used to convert probability or logits output to the predicted label. None deviceType Specify a device type the model inference runs on. Supported types are: CPU or CUDA. If not specified, auto detection will be used. None optimizationLevel Specify the optimization level for the ONNX graph optimizations. Supported values are: NO_OPT,BASIC_OPT,EXTENDED_OPT,ALL_OPT.ALL_OPTCall
transformmethod to run inference on the input DataFrame.
Model Slicing
By default, an ONNX model is treated as a black box with inputs and outputs. If you want to use intermediate nodes of a model, you can slice the model at particular nodes. Slicing will create a new model, keeping only parts of the model that are needed for those nodes. This new model's outputs will be the outputs from the intermediate nodes. You can save the sliced model and use it to transform just like any other ONNXModel.
This slicing feature is used implicitly by the ImageFeaturizer, which uses ONNX models. The OnnxHub manifest entry for each model includes which intermediate node outputs should be used for featurization, so the ImageFeaturizer will automatically slice at the correct nodes.
The below example shows how to perform the slicing manually with a direct ONNXModel.
// create a df: Dataframe with image data
val hub = new ONNXHub()
val info = hub.getModelInfo("resnet50")
val bytes = hub.load(name)
val intermediateOutputName = "resnetv24_pool1_fwd"
val slicedModel = new ONNXModel()
.setModelPayload(bytes)
.setFeedDict(Map("data" -> "features"))
.setFetchDict(Map("rawFeatures" -> intermediateOutputName)) // automatic slicing based on fetch dictionary
// -- or --
// .sliceAtOutput(intermediateOutputName) // manual slicing
val slicedModelDf = slicedModel.transform(df)