Embedding Text with local (per node) NVIDIA TensorRT accelerator and GPU based Aproximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN)
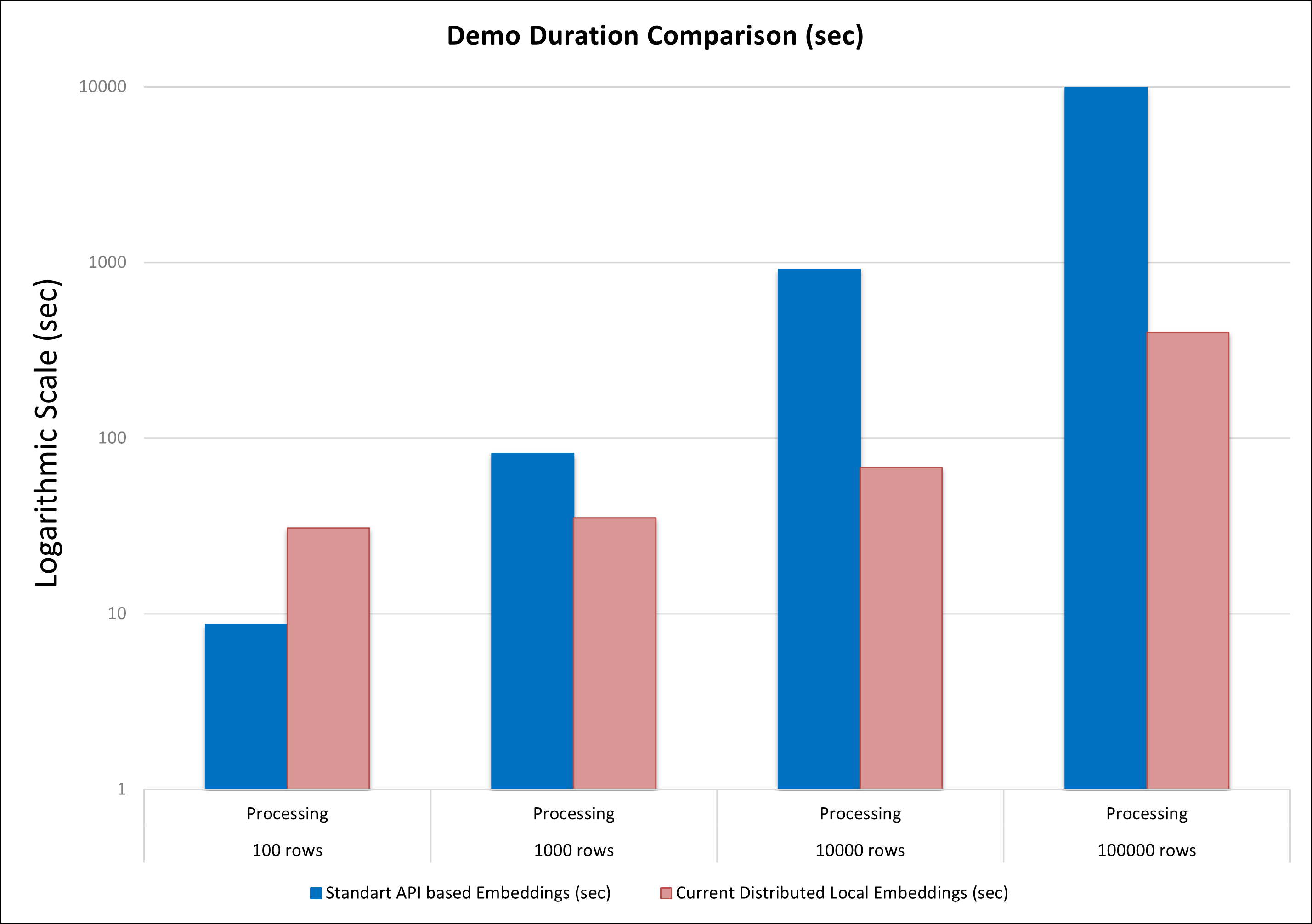
The demo extending existing Azure OpenAI based demo when encoding is processed by OpenAI requests and KNN was using GPU based brute force search. This tutorial shows how to perform fast local embeddings using multilingual E5 text embeddings and fast aproximate Nearest Neighbor search using IVFFlat alcorithm. All tutorial stages accelerated by NVIDIA GPU using NVIDIA TensorRT and Spark Rapids ML. The tutorial folder contains two benchmark notebooks to demonstrate advantages of the presented GPU based approach compare to previos CPU based demo
The key prerequisites for this quickstart include a working Azure OpenAI resource, and an Apache Spark cluster with SynapseML installed. We suggest creating a Synapse workspace, but currently the notebook was running on Databricks GPU based cluster using Standard_NC24ads_A100_v4 with 6 workers. Databricks Runtime was 13.3 LTS ML (includes Apache Spark 3.4.1, GPU, Scala 2.12) with related init_script to install all required packages.
Step 1: Prepare Environment
It will imports required libraries and get initial settings
import torch
import sys
import pyspark.sql.functions as F
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, IntegerType, StringType
from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors
from pyspark.ml.linalg import VectorUDT
from spark_rapids_ml.knn import (
ApproximateNearestNeighbors,
ApproximateNearestNeighborsModel,
)
from synapse.ml.hf import HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder
from synapse.ml.nn import KNN
Step 2: Load Input Data
It will load public dataset and generate extra syntetic rows if set by size parameter
The loaded dataset has 1000 rows. If you specify number_of_input_rows in [1..1000] it will cut extra rows if needed
If number_of_input_rows in [1000..1000000] it will generate extra rows using cross join of original data
file_path = "wasbs://publicwasb@mmlspark.blob.core.windows.net/fine_food_reviews_1k.csv"
df = spark.read.options(inferSchema="True", delimiter=",", header=True).csv(file_path)
df = df.withColumn(
"data",
F.format_string("Title: %s; Content: %s", F.trim(df.Summary), F.trim(df.Text)),
)
# Size of DF
number_of_input_rows = 100
# Check if the row count is less than 10
if number_of_input_rows <= 0 or number_of_input_rows >= 1000000:
raise ValueError(f"Limit is {number_of_input_rows}, which should be less than 1M.")
if number_of_input_rows > 1000:
# Cross-join the DataFrame with itself to create n x n pairs for string concatenation (synthetic data)
cross_joined_df = df.crossJoin(df.withColumnRenamed("data", "data_"))
# Create a new column 'result_vector' by concatenating the two source vectors
tmp_df = cross_joined_df.withColumn(
"result_vector",
F.concat(F.col("data"), F.lit(". \n"), F.col("data_")),
)
# Select only the necessary columns and show the result
tmp_df = tmp_df.select("result_vector")
# Shuffle the DataFrame with a fixed seed to have close strings spreaded
seed = 42
df = (
tmp_df.withColumnRenamed("result_vector", "data")
.withColumn("id", F.monotonically_increasing_id())
.orderBy(F.rand(seed))
)
df = df.limit(number_of_input_rows).repartition(10).cache()
print(f"Loaded: {number_of_input_rows} rows")
Step 3: Generate Embeddings
We will first generate embeddings using NVIDIA TensorRT optimized SentenceTransformer. In the demo you can use two fifferent HF models: intfloat/e5-large-v2 or sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
# To create embedder with different models, uncomment the following line
# embedder = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(modelName="intfloat/e5-large-v2", inputCol="data", outputCol="embeddings", runtime="tensorrt")
embedder = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(
modelName="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
inputCol="data",
outputCol="embeddings",
runtime="tensorrt",
)
embeddings = embedder.transform(df).select("id", "embeddings").cache()
Step 4: Build the query against embeddings
Get query embeddings running standard SentenceTransformer just on the driver. Convert embedding results to a data frame
# Sample query
queries = ["desserts", "disgusting"]
ids = [1, 2]
# Create DataFrame directly from the data and schema
query_df = spark.createDataFrame(
list(zip(ids, queries)),
StructType(
[
StructField("id", IntegerType(), nullable=False),
StructField("data", StringType(), nullable=False),
]
),
)
query_embeddings = embedder.transform(query_df).select("id", "embeddings").cache()
Step 5: Build a fast vector index to over review embeddings
We will use fast NVIDIA Rapids indexer. This KNN implementation will work only on GPU. If you want to use CPU then switch to synapse.ml.nn CPU based KNN implementation
RUN_ON_GPU = torch.cuda.is_available()
if RUN_ON_GPU:
rapids_knn_model = (
ApproximateNearestNeighbors(k=5)
.setInputCol("embeddings")
.setIdCol("id")
.fit(embeddings)
)
else:
array_to_vector_udf = udf(lambda array: Vectors.dense(array), VectorUDT())
df_with_vectors = embeddings.withColumn(
"features", array_to_vector_udf(embeddings["embeddings"])
)
knn = (
KNN()
.setFeaturesCol("features")
.setValuesCol("id")
.setOutputCol("output")
.setK(10)
)
knn_model = knn.fit(df_with_vectors)
Step 6: Find top k Nearest Neighbors ON GPU
We will use fast ANN IVFFlat algorithm from Rapids
if RUN_ON_GPU:
(_, _, knn_df) = rapids_knn_model.kneighbors(query_embeddings)
else:
array_to_vector_udf = udf(lambda array: Vectors.dense(array), VectorUDT())
df_with_vectors = query_embeddings.withColumn(
"features", array_to_vector_udf(query_embeddings["embeddings"])
)
knn_df = knn_model.transform(df_with_vectors)
Step 7: Collect and display results
if RUN_ON_GPU:
result_df = (
knn_df.withColumn(
"zipped", F.explode(F.arrays_zip(F.col("indices"), F.col("distances")))
)
.select(
F.col("query_id"),
F.col("zipped.indices").alias("id"),
F.col("zipped.distances").alias("distance"),
)
.join(df, on="id", how="inner")
.select("query_id", "id", "data", "distance")
)
else:
knn_df = knn_df.withColumnRenamed("data", "original_data")
result_df = (
knn_df.withColumn("match", F.explode("output"))
.join(df, df["id"] == F.col("match.value"))
.select("original_data", F.col("data"), "match.distance")
)
display(result_df)
Results
The goal of this demo is to showcase two acceleration techniques: local (per node) embedding generation and approximate KNN. Compared to the original method, which relies on HTTP requests to the OpenAI model and CPU-based KNN. The new approach is significantly more scalable and provides substantial acceleration, especially for large input datasets.
This is the comparison dureation results on 10 T4 GPU nodes for both approaches: