Conversation Patterns
In the previous chapter we used two-agent conversation, which can be
started by the initiate_chat method. Two-agent chat is a useful
conversation pattern but AutoGen offers more. In this chapter, we will
first dig a little bit more into the two-agent chat pattern and chat
result, then we will show you several conversation patterns that involve
more than two agents.
An Overview
- Two-agent chat: the simplest form of conversation pattern where two agents chat with each other.
- Sequential chat: a sequence of chats between two agents, chained together by a carryover mechanism, which brings the summary of the previous chat to the context of the next chat.
- Group Chat: a single chat involving more than two agents. An
important question in group chat is: What agent should be next to
speak? To support different scenarios, we provide different ways to
organize agents in a group chat:
- We support several strategies to select the next agent:
round_robin,random,manual(human selection), andauto(Default, using an LLM to decide). - We provide a way to constrain the selection of the next speaker (See examples below).
- We allow you to pass in a function to customize the selection of the next speaker. With this feature, you can build a StateFlow model which allows a deterministic workflow among your agents. Please refer to this guide and this blog post on StateFlow for more details.
- We support several strategies to select the next agent:
- Nested Chat: package a workflow into a single agent for reuse in a larger workflow.
Two-Agent Chat and Chat Result
Two-agent chat is the simplest form of conversation pattern. We start a
two-agent chat using the initiate_chat method of every
ConversableAgent agent. We have already seen multiple examples of
two-agent chats in previous chapters but we haven’t covered the details.
The following figure illustrates how two-agent chat works.
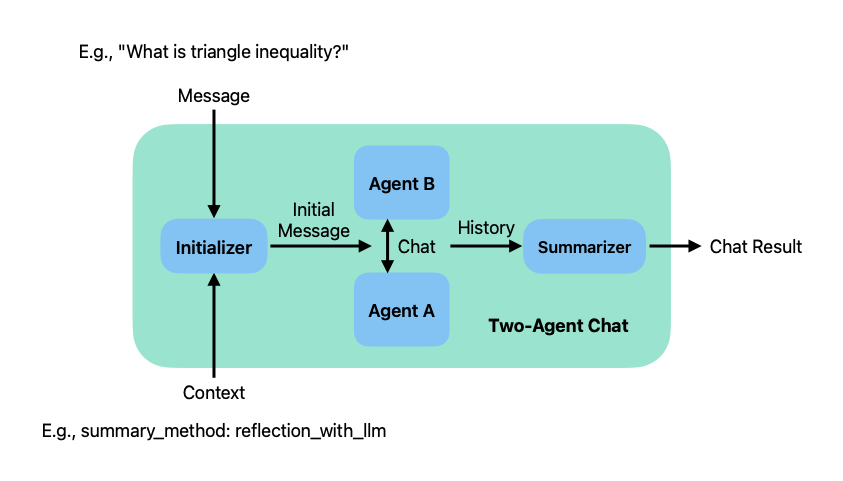
A two-agent chats takes two inputs: a message, which is a string
provided by the caller; a context, which specifies various parameters of
the chat. The sender agent uses its chat initializer method (i.e.,
generate_init_message method of ConversableAgent) to generate an
initial message from the inputs, and sends it to the recipient agent to
start the chat. The sender agent is the agent whose initiate_chat
method is called, and the recipient agent is the other agent.
Once the chat terminates, the history of the chat is processed by a chat
summarizer. The summarizer summarizes the chat history and calculates
the token usage of the chat. You can configure the type of summary using
the summary_method parameter of the initiate_chat method. By
default, it is the last message of the chat (i.e.,
summary_method='last_msg').
The example below is a two-agent chat between a student agent and a teacher agent. Its summarizer uses an LLM-based summary.
import os
from autogen import ConversableAgent
student_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Student_Agent",
system_message="You are a student willing to learn.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
)
teacher_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Teacher_Agent",
system_message="You are a math teacher.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
)
chat_result = student_agent.initiate_chat(
teacher_agent,
message="What is triangle inequality?",
summary_method="reflection_with_llm",
max_turns=2,
)
What is triangle inequality?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY...
Triangle inequality theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must always be greater than the length of the third side. In a triangle with sides of lengths a, b, and c, the theorem can be written as:
a + b > c
a + c > b
b + c > a
Each of these represents the condition for one specific side (a, b, or c). All must be true for a triangle to exist.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY...
Thank you for the explanation. This theorem helps in understanding the basic properties of a triangle. It can also be useful when solving geometric problems or proving other mathematical theorems. Can you give me an example of how we can use the triangle inequality theorem?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY...
Absolutely! Here's an example:
Suppose you're given three line segments with lengths 10, 7, and 3 units. The question is: "Can these three line segments form a triangle?"
To answer this, you would use the triangle inequality theorem. Adding any two side lengths together should be greater than the third:
- For sides 10 and 7: 10 + 7 = 17, which is larger than 3.
- For sides 10 and 3: 10 + 3 = 13, which is larger than 7.
- For sides 7 and 3: 7 + 3 = 10, which is equal to the length of the third side (10), but not greater.
So, these three lines cannot form a triangle, because not all pairs of sides satisfy the triangle inequality theorem.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Let’s see what the summary looks like. The summary is stored in the
chat_result object of the type ChatResult that was returned by the
initiate_chat method.
print(chat_result.summary)
The triangle inequality theorem states that in a triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must always be greater than the length of the third side. This principle is significant in geometry and is used in solving problems or proving theorems. For instance, if given three line segments, you can determine if they can form a triangle using this theorem.
In the above example, the summary method is set to reflection_with_llm
which takes a list of messages from the conversation and summarize them
using a call to an LLM. The summary method first tries to use the
recipient’s LLM, if it is not available then it uses the sender’s LLM.
In this case the recipient is “Teacher_Agent” and the sender is
“Student_Agent”. The input prompt for the LLM is the following default
prompt:
print(ConversableAgent.DEFAULT_SUMMARY_PROMPT)
Summarize the takeaway from the conversation. Do not add any introductory phrases.
You can also use a custom prompt by setting the summary_prompt
argument of initiate_chat.
There are some other useful information in the ChatResult object,
including the conversation history, human input, and token cost.
# Get the chat history.
import pprint
pprint.pprint(chat_result.chat_history)
[{'content': 'What is triangle inequality?', 'role': 'assistant'},
{'content': 'Triangle inequality theorem is a fundamental principle in '
'geometry that states that the sum of the lengths of any two '
'sides of a triangle must always be greater than the length of '
'the third side. In a triangle with sides of lengths a, b, and c, '
'the theorem can be written as:\n'
'\n'
'a + b > c\n'
'a + c > b\n'
'b + c > a\n'
'\n'
'Each of these represents the condition for one specific side (a, '
'b, or c). All must be true for a triangle to exist.',
'role': 'user'},
{'content': 'Thank you for the explanation. This theorem helps in '
'understanding the basic properties of a triangle. It can also be '
'useful when solving geometric problems or proving other '
'mathematical theorems. Can you give me an example of how we can '
'use the triangle inequality theorem?',
'role': 'assistant'},
{'content': "Absolutely! Here's an example:\n"
'\n'
"Suppose you're given three line segments with lengths 10, 7, and "
'3 units. The question is: "Can these three line segments form a '
'triangle?"\n'
'\n'
'To answer this, you would use the triangle inequality theorem. '
'Adding any two side lengths together should be greater than the '
'third:\n'
'\n'
'- For sides 10 and 7: 10 + 7 = 17, which is larger than 3.\n'
'- For sides 10 and 3: 10 + 3 = 13, which is larger than 7.\n'
'- For sides 7 and 3: 7 + 3 = 10, which is equal to the length of '
'the third side (10), but not greater.\n'
'\n'
'So, these three lines cannot form a triangle, because not all '
'pairs of sides satisfy the triangle inequality theorem.',
'role': 'user'}]
That chat messages in the chat result are from the recipient agent’s perspective – the sender is the “assistant” and the recipient is the “user”.
# Get the cost of the chat.
pprint.pprint(chat_result.cost)
({'gpt-4-0613': {'completion_tokens': 399,
'cost': 0.04521,
'prompt_tokens': 709,
'total_tokens': 1108},
'total_cost': 0.04521},
{'total_cost': 0})
Sequential Chats
The name of this pattern is self-explanatory – it is a sequence of chats between two agents, chained together by a mechanism called carryover, which brings the summary of the previous chat to the context of the next chat.
This pattern is useful for complex task that can be broken down into interdependent sub-tasks. The figure below illustrate how this pattern works.
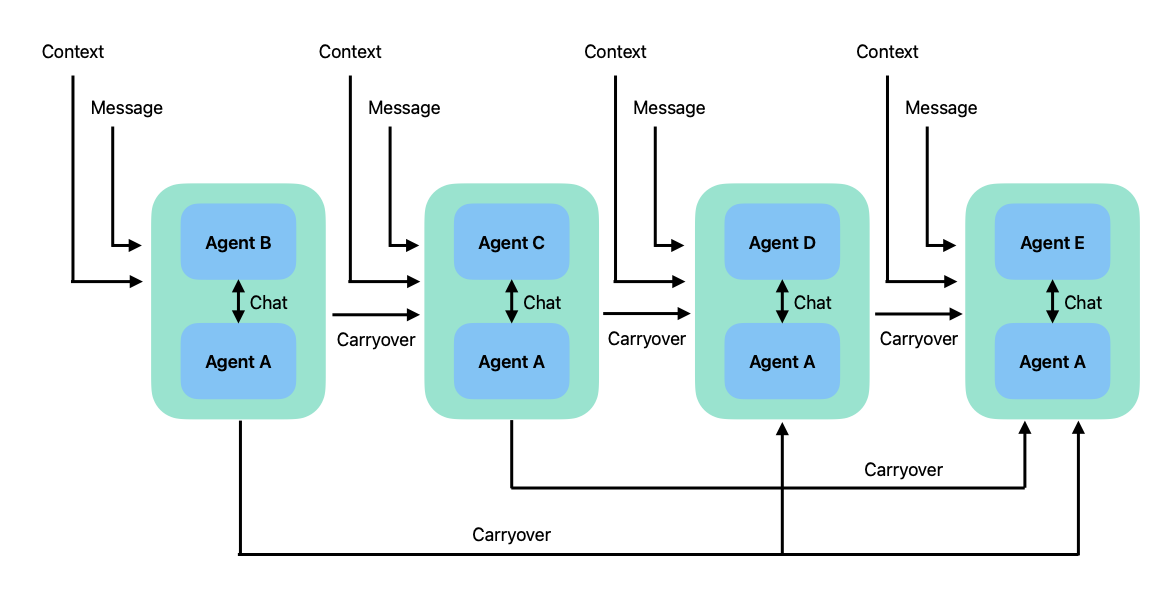
In this pattern, the a pair of agents first start a two-agent chat, then
the summary of the conversation becomes a carryover for the next
two-agent chat. The next chat passes the carryover to the carryover
parameter of the context to generate its initial message.
Carryover accumulates as the conversation moves forward, so each subsequent chat starts with all the carryovers from previous chats.
The figure above shows distinct recipient agents for all the chats, however, the recipient agents in the sequence are allowed to repeat.
To illustrate this pattern, let’s consider a simple example of arithmetic operator agents. One agent (called the “Number_Agent”) is responsible for coming up with a number, and other agents are responsible for performing a specific arithmetic operation on the number, e.g., add 1, multiply by 2, etc..
# The Number Agent always returns the same numbers.
number_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Number_Agent",
system_message="You return me the numbers I give you, one number each line.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
# The Adder Agent adds 1 to each number it receives.
adder_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Adder_Agent",
system_message="You add 1 to each number I give you and return me the new numbers, one number each line.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
# The Multiplier Agent multiplies each number it receives by 2.
multiplier_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Multiplier_Agent",
system_message="You multiply each number I give you by 2 and return me the new numbers, one number each line.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
# The Subtracter Agent subtracts 1 from each number it receives.
subtracter_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Subtracter_Agent",
system_message="You subtract 1 from each number I give you and return me the new numbers, one number each line.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
# The Divider Agent divides each number it receives by 2.
divider_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Divider_Agent",
system_message="You divide each number I give you by 2 and return me the new numbers, one number each line.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
The Number Agent chats with the first operator agent, then the second
operator agent, and so on. After each chat, the last message in the
conversation (i.e., the result of the arithmetic operation from the
operator agent) is used as the summary of the chat. This is specified by
the summary_method parameter. In the end we will have the result of
the arithmetic operations.
# Start a sequence of two-agent chats.
# Each element in the list is a dictionary that specifies the arguments
# for the initiate_chat method.
chat_results = number_agent.initiate_chats(
[
{
"recipient": adder_agent,
"message": "14",
"max_turns": 2,
"summary_method": "last_msg",
},
{
"recipient": multiplier_agent,
"message": "These are my numbers",
"max_turns": 2,
"summary_method": "last_msg",
},
{
"recipient": subtracter_agent,
"message": "These are my numbers",
"max_turns": 2,
"summary_method": "last_msg",
},
{
"recipient": divider_agent,
"message": "These are my numbers",
"max_turns": 2,
"summary_method": "last_msg",
},
]
)
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
14
With the following carryover:
********************************************************************************
14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
16
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
These are my numbers
With the following carryover:
16
********************************************************************************
These are my numbers
Context:
16
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
32
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
32
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
64
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
These are my numbers
With the following carryover:
16
64
********************************************************************************
These are my numbers
Context:
16
64
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
15
63
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
15
63
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14
62
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
These are my numbers
With the following carryover:
16
64
14
62
********************************************************************************
These are my numbers
Context:
16
64
14
62
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8
32
7
31
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8
32
7
31
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
16
3.5
15.5
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
First thing to note is that the initiate_chats method takes a list of
dictionaries, each dictionary contains the arguments for the
initiate_chat method.
Second, each chat in the sequence has a maximum round of 2, as specified
with the setting max_turns=2, which means each arithmetic operation is
performed twice. So you can see in the first chat the number 14 becomes
15 and then 16, in the second chat the number 16 becomes 32 and then 64,
and so on.
Third, the carryover accumulates as the chats go on. In the second chat, the carryover is the summary of the first chat “16”. In the third chat, the carryover is the summary of the first and second chat, which is the list “16” and “64”, and both numbers are operated upon. In the forth and last chat, the carryover is the summary of all previous chats, which is the list “16”, “64”, “14” and “62”, and all of these numbers are operated upon.
The final note is that the initiate_chats method returns a list of
ChatResult objects, one for each chat in the sequence.
print("First Chat Summary: ", chat_results[0].summary)
print("Second Chat Summary: ", chat_results[1].summary)
print("Third Chat Summary: ", chat_results[2].summary)
print("Fourth Chat Summary: ", chat_results[3].summary)
First Chat Summary: 16
Second Chat Summary: 64
Third Chat Summary: 14
62
Fourth Chat Summary: 4
16
3.5
15.5
Besides calling initiate_chats from the same sender agent, you can
also call a high-level function autogen.agentchat.initiate_chats to
start a sequence of two-agent chats with different sender agents. This
function allows you to specify the sender agent for each chat in the
sequence.
Group Chat
So far we have only seen conversation patterns that involve two agents or a sequence of two-agent chats. AutoGen provides a more general conversation pattern called group chat, which involves more than two agents. The core idea of group chat is that all agents contribute to a single conversation thread and share the same context. This is useful for tasks that require collaboration among multiple agents.
The figure below illustrates how group chat works.
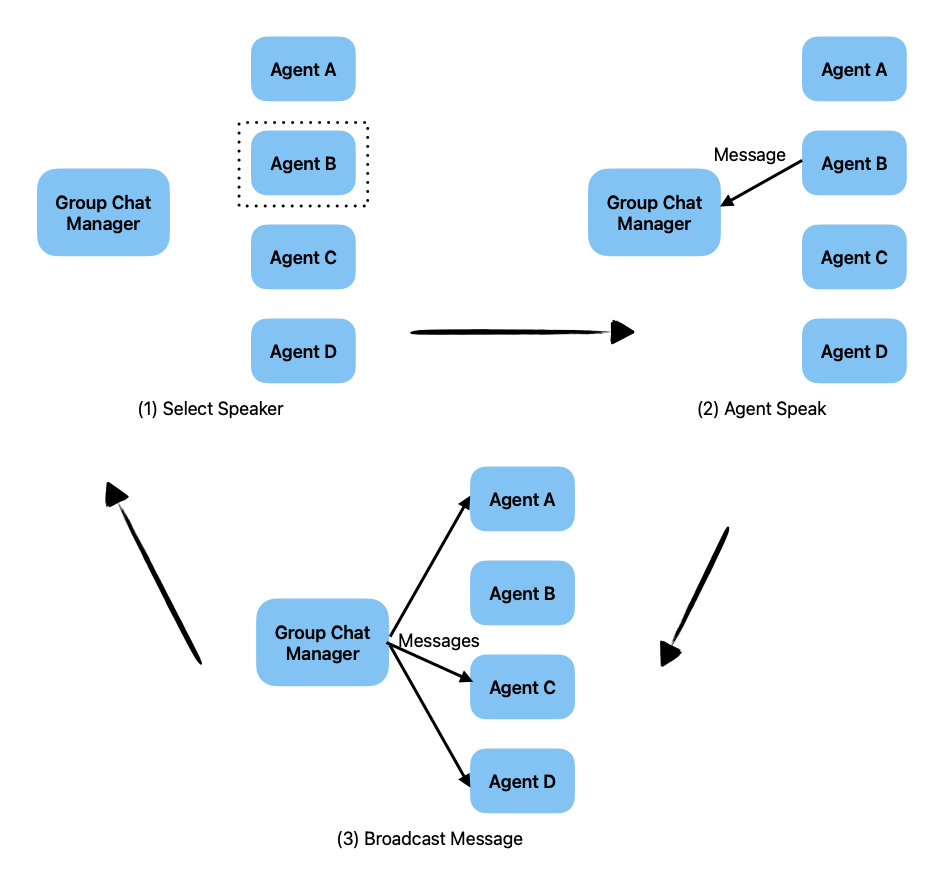
A group chat is orchestrated by a special agent type GroupChatManager.
In the first step of the group chat, the Group Chat Manager selects an
agent to speak. Then, the selected agent speaks and the message is sent
back to the Group Chat Manager, who broadcasts the message to all
other agents in the group. This process repeats until the conversation
stops.
The Group Chat Manager can use several strategies to select the next agent. Currently, the following strategies are supported:
round_robin: The Group Chat Manager selects agents in a round-robin fashion based on the order of the agents provided.random: The Group Chat Manager selects agents randomly.manual: The Group Chat Manager selects agents by asking for human input.auto: The default strategy, which selects agents using the Group Chat Manager’s LLM.
To illustrate this pattern, let’s consider a simple example of a group chat among the same arithmetic operator agents as in the previous example, with the objective of turning a number into a specific target number using a sequence of arithmetic operations powered by the agents.
In this example, we use the auto strategy to select the next agent. To
help the Group Chat Manager select the next agent, we also set the
description of the agents. Without the description, the Group Chat
Manager will use the agents’ system_message, which may be not be the
best choice.
# The `description` attribute is a string that describes the agent.
# It can also be set in `ConversableAgent` constructor.
adder_agent.description = "Add 1 to each input number."
multiplier_agent.description = "Multiply each input number by 2."
subtracter_agent.description = "Subtract 1 from each input number."
divider_agent.description = "Divide each input number by 2."
number_agent.description = "Return the numbers given."
We first create a GroupChat object and provide the list of agents. If
we were to use the round_robin strategy, this list would specify the
order of the agents to be selected. We also initialize the group chat
with an empty message list and a maximum round of 6, which means there
will be at most 6 iterations of selecting a speaker, agent speaks and
broadcasting message.
from autogen import GroupChat
group_chat = GroupChat(
agents=[adder_agent, multiplier_agent, subtracter_agent, divider_agent, number_agent],
messages=[],
max_round=6,
)
Now we create a GroupChatManager object and provide the GroupChat
object as input. We also need to specify the llm_config of the Group
Chat Manager so it can use the LLM to select the next agent (the auto
strategy).
from autogen import GroupChatManager
group_chat_manager = GroupChatManager(
groupchat=group_chat,
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
)
Finally, we have the Number Agent from before to start a two-agent chat with the Group Chat Manager, which runs the group chat internally and terminates the two-agent chat when the internal group chat is done. Because the Number Agent is selected to speak by us, it counts as the first round of the group chat.
chat_result = number_agent.initiate_chat(
group_chat_manager,
message="My number is 3, I want to turn it into 13.",
summary_method="reflection_with_llm",
)
My number is 3, I want to turn it into 13.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
13
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
13
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can see that the Number Agent is selected to speak first, then the Group Chat Manager selects the Multiplier Agent to speak, then the Adder Agent, and so on. The number is operated upon by each agent in the group chat, and the final result is 13.
We can take a look at the summary of the group chat, provided by the
ChatResult object returned by the initiate_chat method.
print(chat_result.summary)
The agents cooperatively manipulated the initial number (3) through multipliying, adding, and subtracting operations to reach the target number (13).
Send Introductions
In the previous example, we set the description of the agents to help
the Group Chat Manager select the next agent. This only helps the Group
Chat Manager, however, does not help the participating agents to know
about each other. Sometimes it is useful have each agent introduce
themselves to other agents in the group chat. This can be done by
setting the send_introductions=True.
group_chat_with_introductions = GroupChat(
agents=[adder_agent, multiplier_agent, subtracter_agent, divider_agent, number_agent],
messages=[],
max_round=6,
send_introductions=True,
)
Under the hood, the Group Chat Manager sends a message containing the agents’ names and descriptions to all agents in the group chat before the group chat starts.
Group Chat in a Sequential Chat
Group chat can also be used as a part of a sequential chat. In this case, the Group Chat Manager is treated as a regular agent in the sequence of two-agent chats.
# Let's use the group chat with introduction messages created above.
group_chat_manager_with_intros = GroupChatManager(
groupchat=group_chat_with_introductions,
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
)
# Start a sequence of two-agent chats between the number agent and
# the group chat manager.
chat_result = number_agent.initiate_chats(
[
{
"recipient": group_chat_manager_with_intros,
"message": "My number is 3, I want to turn it into 13.",
},
{
"recipient": group_chat_manager_with_intros,
"message": "Turn this number to 32.",
},
]
)
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
My number is 3, I want to turn it into 13.
With the following carryover:
********************************************************************************
My number is 3, I want to turn it into 13.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
13
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Your number is 13.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
Turn this number to 32.
With the following carryover:
Your number is 13.
********************************************************************************
Turn this number to 32.
Context:
Your number is 13.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
26
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
28
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
15
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
30
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Users/ekzhu/autogen/autogen/agentchat/chat.py:46: UserWarning: Repetitive recipients detected: The chat history will be cleared by default if a recipient appears more than once. To retain the chat history, please set 'clear_history=False' in the configuration of the repeating agent.
warnings.warn(
In the above example, the Group Chat Manager runs the group chat two times. In the first time the number 3 becomes 13, and the last message of this group chat is being used as the carryover for the next group chat, which starts from 13.
You can also see from the warning message that the Group Chat Manager’s
history is being cleared after the first group chat, which is the
default. To keep the history of the Group Chat Manager, you can set the
clear_history=False for the first chat.
Constrained Speaker Selection
Group chat is a powerful conversation pattern, but it can be hard to
control if the number of participating agents is large. AutoGen provides
a way to constrain the selection of the next speaker by using the
allowed_or_disallowed_speaker_transitions argument of the GroupChat
class.
The allowed_or_disallowed_speaker_transitions argument is a dictionary
that maps a given agent to a list of agents that can (or cannot) be
selected to speak next. The speaker_transitions_type argument
specifies whether the transitions are allowed or disallowed.
Here is an example:
allowed_transitions = {
number_agent: [adder_agent, number_agent],
adder_agent: [multiplier_agent, number_agent],
subtracter_agent: [divider_agent, number_agent],
multiplier_agent: [subtracter_agent, number_agent],
divider_agent: [adder_agent, number_agent],
}
In this example, the allowed transitions are specified for each agent.
The Number Agent can be followed by the Adder Agent and the Number
Agent, the Adder Agent can be followed by the Multiplier Agent and the
Number Agent, and so on. Let’s put this into the group chat and see how
it works. The speaker_transitions_type is set to allowed so the
transitions are positive constraints.
constrained_graph_chat = GroupChat(
agents=[adder_agent, multiplier_agent, subtracter_agent, divider_agent, number_agent],
allowed_or_disallowed_speaker_transitions=allowed_transitions,
speaker_transitions_type="allowed",
messages=[],
max_round=12,
send_introductions=True,
)
constrained_group_chat_manager = GroupChatManager(
groupchat=constrained_graph_chat,
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
)
chat_result = number_agent.initiate_chat(
constrained_group_chat_manager,
message="My number is 3, I want to turn it into 10. Once I get to 10, keep it there.",
summary_method="reflection_with_llm",
)
My number is 3, I want to turn it into 10. Once I get to 10, keep it there.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.5
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4.5
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
9
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This time, the agents are selected following the constraints we have specified.
Changing the select speaker role name
As part of the Group chat process, when the select_speaker_method is set to ‘auto’ (the default value), a select speaker message is sent to the LLM to determine the next speaker.
Each message in the chat sequence has a role attribute that is
typically user, assistant, or system. The select speaker message
is the last in the chat sequence when used and, by default, has a role
of system.
When using some models, such as Mistral through Mistral.AI’s API, the
role on the last message in the chat sequence has to be user.
To change the default behaviour, Autogen provides a way to set the value
of the select speaker message’s role to any string value by setting the
role_for_select_speaker_messages parameter in the GroupChat’s
constructor. The default value is system and by setting it to user
you can accommodate the last message role requirement of Mistral.AI’s
API.
Nested Chats
The previous conversations patterns (two-agent chat, sequential chat, and group chat) are useful for building complex workflows, however, they do not expose a single conversational interface, which is often needed for scenarios like question-answering bots and personal assistants. In some other cases, it is also useful to package a workflow into a single agent for reuse in a larger workflow. AutoGen provides a way to achieve this by using nested chats.
Nested chats is powered by the nested chats handler, which is a
pluggable component of ConversableAgent. The figure below illustrates
how the nested chats handler triggers a sequence of nested chats when a
message is received.
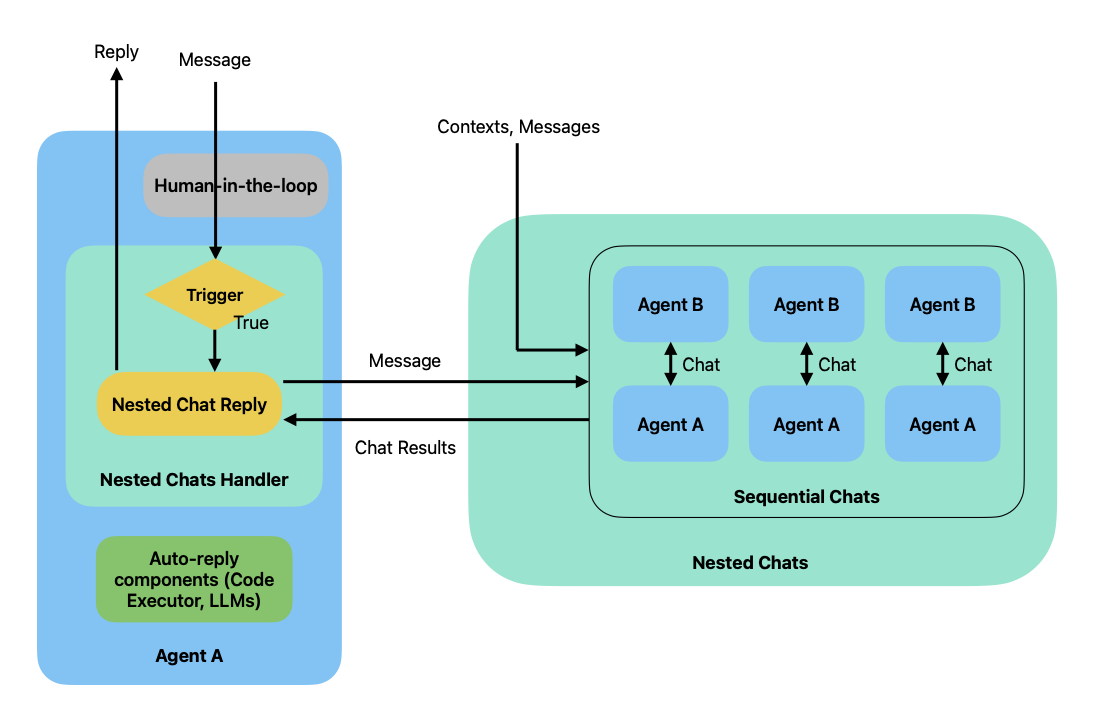
When a message comes in and passes the human-in-the-loop component, the nested chats handler checks if the message should trigger a nested chat based on conditions specified by the user. If the conditions are met, the nested chats handler starts a sequence of nested chats specified using the sequential chats pattern. In each of the nested chats, the sender agent is always the same agent that triggered the nested chats. In the end, the nested chat handler uses the results of the nested chats to produce a response to the original message. By default, the nested chat handler uses the summary of the last chat as the response.
Here is an example of using nested chats to build an arithmetic agent that packages arithmetic operations, code-based validation, and poetry into a single agent. This arithmetic agent takes a number transformation request like “turn number 3 into 13” and returns a poem that describes a transformation attempt.
First we define the agents. We reuse the
group_chat_manager_with_intros from previous example to orchestrate
the arithmetic operations.
import tempfile
temp_dir = tempfile.gettempdir()
arithmetic_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Arithmetic_Agent",
llm_config=False,
human_input_mode="ALWAYS",
# This agent will always require human input to make sure the code is
# safe to execute.
code_execution_config={"use_docker": False, "work_dir": temp_dir},
)
code_writer_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Code_Writer_Agent",
system_message="You are a code writer. You write Python script in Markdown code blocks.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
poetry_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="Poetry_Agent",
system_message="You are an AI poet.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4", "api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]}]},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
Now we define the nested chats using the sequential chat pattern. All
the senders are always artihmetic_agent.
nested_chats = [
{
"recipient": group_chat_manager_with_intros,
"summary_method": "reflection_with_llm",
"summary_prompt": "Summarize the sequence of operations used to turn " "the source number into target number.",
},
{
"recipient": code_writer_agent,
"message": "Write a Python script to verify the arithmetic operations is correct.",
"summary_method": "reflection_with_llm",
},
{
"recipient": poetry_agent,
"message": "Write a poem about it.",
"max_turns": 1,
"summary_method": "last_msg",
},
]
Now we register the nested chats handler to the arithmetic_agent and
set the conditions for triggering the nested chats.
arithmetic_agent.register_nested_chats(
nested_chats,
# The trigger function is used to determine if the agent should start the nested chat
# given the sender agent.
# In this case, the arithmetic agent will not start the nested chats if the sender is
# from the nested chats' recipient to avoid recursive calls.
trigger=lambda sender: sender not in [group_chat_manager_with_intros, code_writer_agent, poetry_agent],
)
Finally, we call generate_reply to get a response from the
arithmetic_agent – this will trigger a sequence of nested chats and
return the summary of the last nested chat as the response.
# Instead of using `initiate_chat` method to start another conversation,
# we can use the `generate_reply` method to get single reply to a message directly.
reply = arithmetic_agent.generate_reply(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "I have a number 3 and I want to turn it into 7."}]
)
>>>>>>>> NO HUMAN INPUT RECEIVED.
>>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY...
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
I have a number 3 and I want to turn it into 7.
With the following carryover:
********************************************************************************
I have a number 3 and I want to turn it into 7.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To give you the result, I'll add 1 to the number you gave me. So your new number is 4.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
Write a Python script to verify the arithmetic operations is correct.
With the following carryover:
First, 1 was added to the initial number 3 to make it 4. Then it was multiplied by 2 which resulted in 8. Finally, 1 was subtracted from 8 to reach the target number 7.
********************************************************************************
Write a Python script to verify the arithmetic operations is correct.
Context:
First, 1 was added to the initial number 3 to make it 4. Then it was multiplied by 2 which resulted in 8. Finally, 1 was subtracted from 8 to reach the target number 7.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Here is a Python script to verify the aforementioned arithmetic operations:
```python
# defining the initial value
initial_number = 3
# Adding 1 to initial number
initial_number += 1
assert initial_number == 4, "The first operation failed!"
# Multiplying the result by 2
initial_number *= 2
assert initial_number == 8, "The second operation failed!"
# Subtracting 1 from the result
initial_number -= 1
assert initial_number == 7, "The final operation failed!"
print("All operations were carried out successfully!")
```
In the script, the entire process is broken down into steps. The `assert` function is used to verify the result at every step. If any of the operations doesn't yield the expected result, an `AssertionError` exception will be raised. If all operations pass, the message "All operations were carried out successfully!" will be printed.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>>>>>> NO HUMAN INPUT RECEIVED.
>>>>>>>> USING AUTO REPLY...
>>>>>>>> EXECUTING CODE BLOCK 0 (inferred language is python)...
exitcode: 0 (execution succeeded)
Code output:
All operations were carried out successfully!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Certainly, that means the python script was successful and every arithmetic operation performed correctly given the initial input and the steps performed.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
********************************************************************************
Start a new chat with the following message:
Write a poem about it.
With the following carryover:
First, 1 was added to the initial number 3 to make it 4. Then it was multiplied by 2 which resulted in 8. Finally, 1 was subtracted from 8 to reach the target number 7.
The Python script successfully performed and verified the arithmetic operations on the initial number provided. The steps included adding 1 to the initial number, multiplying the result by 2, and finally subtracting 1. The assert function was used to check the result at each step, and confirmed that all operations were carried out correctly.
********************************************************************************
Write a poem about it.
Context:
First, 1 was added to the initial number 3 to make it 4. Then it was multiplied by 2 which resulted in 8. Finally, 1 was subtracted from 8 to reach the target number 7.
The Python script successfully performed and verified the arithmetic operations on the initial number provided. The steps included adding 1 to the initial number, multiplying the result by 2, and finally subtracting 1. The assert function was used to check the result at each step, and confirmed that all operations were carried out correctly.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
From numbers, logic, pure mathematical creation,
Ponder this tale of numeric manipulation.
In the universe of Python where operations exist,
A story of integers and functions persist.
Three was the number from where we began,
Oblivious to the journey and its grandiosely plan.
Added with 1, the sum it adorned,
A sweet quadruple in the dawn was formed.
The saga continued with a twist of the tale,
The four was multiplied, while the winds wail.
The duo of four unfolded its wings,
An octet presence in our midst it brings.
Then enters subtraction, sly and clever,
Removing one to alter the endeavor.
From eight, subtracted one in delight,
To finally bask in the glow of seven's light.
Each operation, together they conspired,
In this tale of integers, creatively inspired.
Through life's equation, the script ran so free,
Amidst the language of Python, a symphony, you see.
Tested with assert, cross-checked the chain,
Confirming accuracy in program's domain.
Each move calculated, each step so right,
In the maze of coding, found was the light.
Such is the tale, of numbers and operations,
A dance among digits, logical iterations,
Just another day, in this AI poet's life,
Cutting through ambiguity, like a razor-sharp knife.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A poem is returned as the response, which describes the transformation attempt from 3 to 7.
The implementation of the nested chats handler makes use of the
register_reply
method, which allows you to make extensive customization to
ConversableAgent. The GroupChatManager uses the same mechanism to
implement the group chat.
Nested chat is a powerful conversation pattern that allows you to package complex workflows into a single agent. You can hide tool usages within a single agent by having the tool-caller agent starts a nested chat with a tool-executor agent and then use the result of the nested chat to generate a response. See the nested chats for tool use notebook for an example.
Summary
In this chapter, we covered two-agent chat, sequential chat, group chat,
and nested chat patterns. You can compose these patterns like LEGO
blocks to create complex workflows. You can also use
register_reply
to create new patterns.
This is the last chapter on basic AutoGen concepts. In the next chatper, we will give you some tips on what to do next.
