Task 01 - Create a customer account information API endpoint (20 minutes)
Introduction
Azure OpenAI has the capacity to parse natural language and facilitate generating API calls through a mechanism known as function calling. Throughout the course of this exercise, you will create an API endpoint and then build the capacity to call this API endpoint based on user prompts.
Description
In this task, you will load data that Contoso Suites staff has provided to you into Cosmos DB. This data contains a sample of customer account details from their Customer Information System (CIS). From there, they would like you to implement a .NET Web API endpoint exposing this customer information.
The key tasks are as follows:
-
Import the data in Customers.json into a Cosmos DB database named ContosoSuites and a collection named Customers.
The value for DateOfMostRecentStay is in the format yyyy-mm-dd. JSON does not include a native DateTime type, so Cosmos DB stores dates as strings. For date operators like
>or<to work, we need to ensure date values are stored in lexicographic order, so common formats such as mm/dd/yyyy or dd/mm/yyyy would not work. -
Create a new environment variable on your machine called
AZURE_COSMOS_DB_CONNECTION_STRING. This should host the connection string for the Cosmos DB resource you have created.After creating an environment variable, you will need to close and re-open your terminal to refresh the list of environment variables. If you are using Visual Studio Code to run this code base, you may need to close and re-open all open instances of VS Code, as instantiating a new terminal might not refresh the list of environment variables.
- Using the Web API project ContosoSuitesWebAPI, update the stub
app.MapGet()endpoint to retrieve customer information based on two inputs. The first is a string calledsearchCriterionand may be one of the three following values: CustomerName, LoyaltyTier, DateOfMostRecentStay. The second is a string calledsearchValueand will be what we use to determine relevant documents. There are stub methods inCosmosService.csthat will help you implement this customer account lookup endpoint. -
Run the Web API service on your machine using
dotnet runif you are in Visual Studio Code or running the project locally in Visual Studio. Once it is running, should be able to make a web request in your browser by navigating tohttp://{your_url}/Customer/?searchCriterion={search_criterion}&searchValue={search_value}, filling in appropriate values for{your_url},{search_criterion}, and{search_value}.When you run the Web API service in debug mode, keep track of the port it runs on. You will need this information in the next task.
- Perform a lookup against the Customers collection based on the search criterion and search value, returning all relevant documents. Sample queries include:
- searchCriterion =
CustomerNameand searchValue =Amber Rodriguez - searchCriterion =
LoyaltyTierand searchValue =Platinum - searchCriterion =
DateOfMostRecentStayand searchValue =2023-10-06
- searchCriterion =
Success Criteria
- You have created a Cosmos DB collection named Customers.
- You have updated the .NET Web API endpoint to allow querying against the Customers collection.
Tips
- If your .NET application build is failing when you try to run
dotnet runand you receive an error that the build cannot load the required packages from NuGet, you may be missing a link to the Microsoft NuGet repository. Run the commanddotnet nuget list sourceand see if you have an entry enabled for nuget.org. If not, you can add it with the following command:dotnet nuget add source https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json -n nuget.org. If you have one but it is currently disabled, you can enable it with the commanddotnet nuget enable source nuget.org.
Learning Resources
- Quickstart: Create an Azure Cosmos DB account, database, container, and items from the Azure portal
- Tutorial: Create a web API with ASP.NET Core
- Configuration in ASP.NET Core
- Query items in Cosmos DB from .NET
- cosmos-db-nosql-dotnet-sample-web
- Tutorial: Develop an ASP.NET web application with Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL
Solution
Expand this section to view the solution
- To create the Cosmos DB container, perform the following steps:
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Cosmos DB service associated with your resource group.
- Select the Data Explorer option from the top menu.
- In the Data Explorer, select the New Container button in the middle of the screen.
- Create a new database and give it a name of
ContosoSuites. You may safely set the database throughput either toAutoscalewith a Database Max RU/s of1000, orManualwith a Database RU/s of400. -
The new Container id should be called
Customers. Choose a partition key, such as/FullNameand select OK to create the database and container.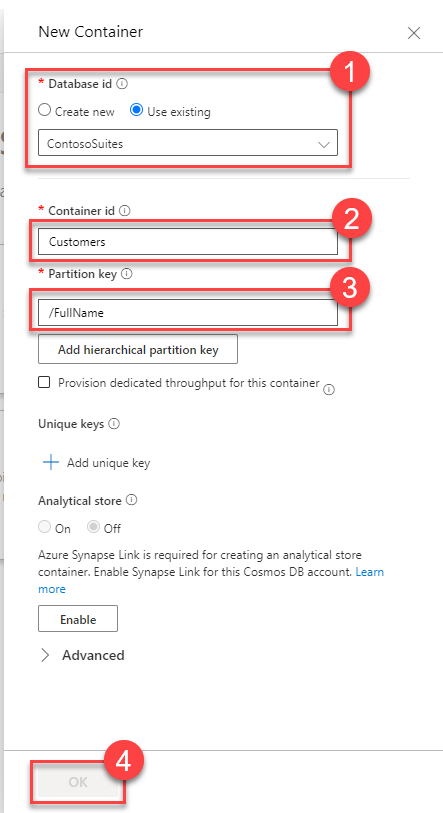
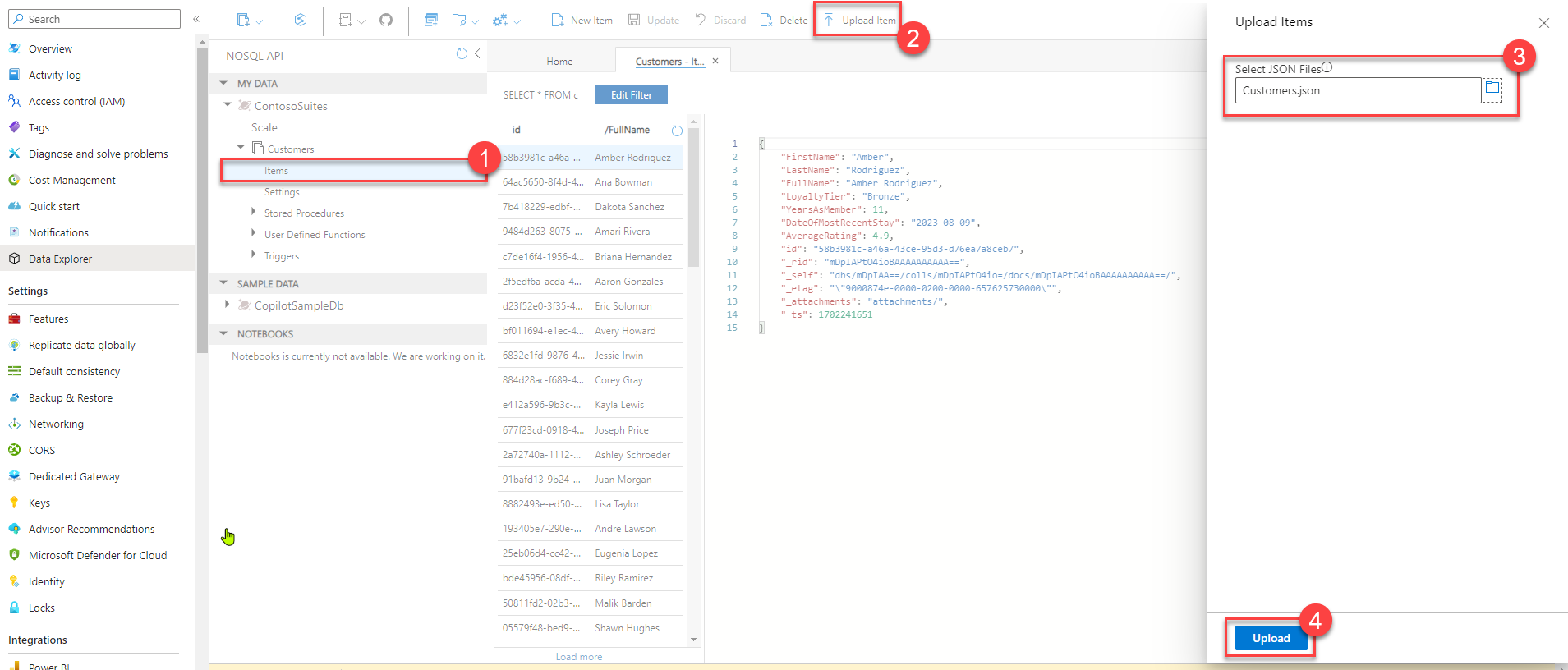
- After container creation finishes, import customer data using the Data Explorer:
- In the Data menu tree for the NoSQL API left-hand menu, drill into ContosoSuites, then Customer, and finally select the Items menu option.
- Choose the Upload Item menu option. Navigate to where you have saved the file “Customer.json” and upload it.
-
Uploading will succeed and import 77 entries.
-
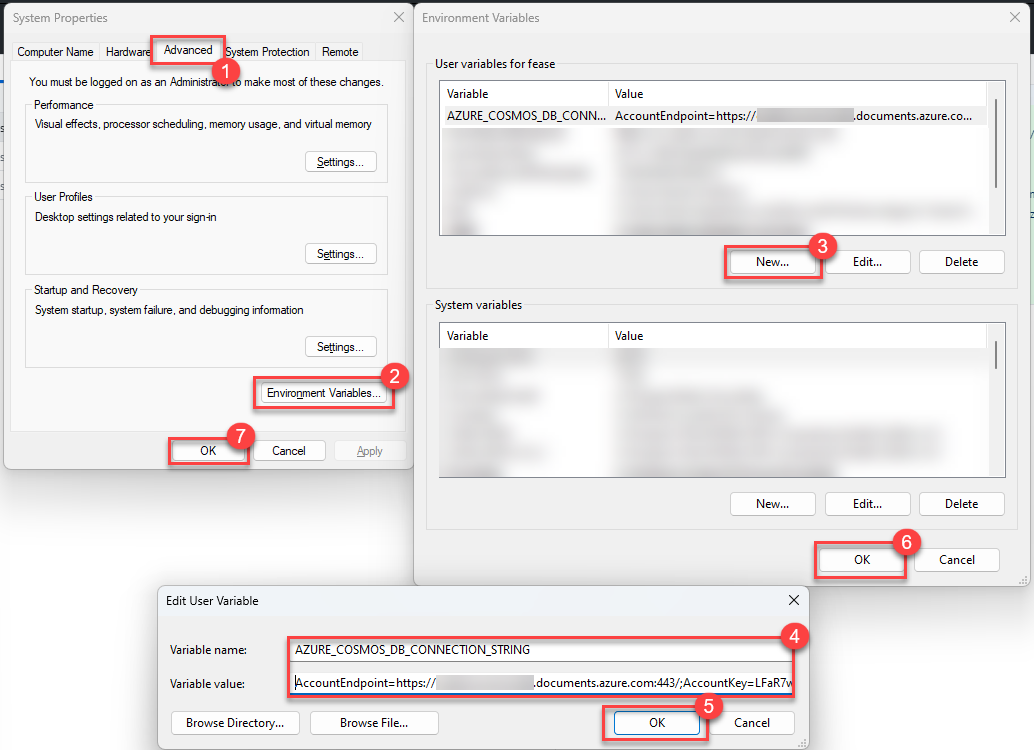
Create an environment variable locally, giving it the name
AZURE_COSMOS_DB_CONNECTION_STRING. There are several ways to create an environment variable, includingsetxin the Windows command shell, the$envvariable in PowerShell, and the Environment Variables option in the Advanced tab of System Properties.To perform this in PowerShell, you can run the following command:
$env:AZURE_COSMOS_DB_CONNECTION_STRING = 'AccountEndpoint=https://{your_endpoint}.documents.azure.com:443/;AccountKey={your_key};'Should you wish to create an environment variable using the System Properties user interface, it is possible to do this as well.
- The final code to support customer lookup should look something like this.
- Here is the code for the four functions in
CosmosService.cs:
public async Task<IEnumerable<Customer>> GetCustomersByName(string name) { var queryable = container.GetItemLinqQueryable<Customer>(); using FeedIterator<Customer> feed = queryable .Where(c => c.FullName == name) .ToFeedIterator<Customer>(); return await ExecuteQuery(feed); } public async Task<IEnumerable<Customer>> GetCustomersByLoyaltyTier(string loyaltyTier) { LoyaltyTier lt = Enum.Parse<LoyaltyTier>(loyaltyTier); var queryable = container.GetItemLinqQueryable<Customer>(); using FeedIterator<Customer> feed = queryable .Where(c => c.LoyaltyTier.ToString() == loyaltyTier) .ToFeedIterator<Customer>(); return await ExecuteQuery(feed); } public async Task<IEnumerable<Customer>> GetCustomersWithStaysAfterDate(DateTime dt) { var queryable = container.GetItemLinqQueryable<Customer>(); using FeedIterator<Customer> feed = queryable .Where(c => c.DateOfMostRecentStay > dt) .ToFeedIterator<Customer>(); return await ExecuteQuery(feed); } private async Task<IEnumerable<Customer>> ExecuteQuery(FeedIterator<Customer> feed) { List<Customer> results = new(); while (feed.HasMoreResults) { var response = await feed.ReadNextAsync(); foreach (Customer c in response) { results.Add(c); } } return results; }- Here is the code for Program.cs:
app.MapGet("/Customer", async (string searchCriterion, string searchValue) => { switch (searchCriterion) { case "CustomerName": return await app.Services.GetService<ICosmosService>()!.GetCustomersByName(searchValue); case "LoyaltyTier": return await app.Services.GetService<ICosmosService>()!.GetCustomersByLoyaltyTier(searchValue); case "DateOfMostRecentStay": return await app.Services.GetService<ICosmosService>()!.GetCustomersWithStaysAfterDate(DateTime.Parse(searchValue)); default: throw new Exception("Invalid search criterion. Valid search criteria include 'CustomerName', 'LoyaltyTier', and 'DateOfMostRecentStay'."); } }) - Here is the code for the four functions in