How to evaluate a LLM agent?
The challenges
It is nontrivial to evaluate the performance of a LLM agent. Existing evaluation methods typically treat the LLM agent as a function that maps input data to output data. If the agent is evaluated against a multi-step task, the evaluation process is then like a chain of calling a stateful function multiple times. To judge the output of the agent, it is typically compared to a ground truth or a reference output. As the output of the agent is in natural language, the evaluation is typically done by matching keywords or phrases in the output to the ground truth.
This evaluation method has its limitations due to its rigid nature. It is sometimes hard to use keywords matching to evaluate the output of the agent, especially when the output is long and complex. For example, if the answer is a date or a number, the evaluation method may not be able to handle the different formats. Moreover, the evaluation method should be able to act more like a human, who can understand the context and the meaning of the output. For example, when different agents are asked to perform the same task, they may behave differently, but still produce correct outputs.
The below example illustrates this point:
Human: What is the weather today?
Agent 1: It is sunny today in New York.
Human: What is the weather today?
Agent 2: Do you want to know the weather in New York today?
Human: Yes.
Agent 2: It is sunny today.
Compared to Agent 1, Agent 2 asks for confirmation before providing the answer, which requires more interaction with the user. However, both agents provide the correct answer to the question. But if the evaluation method takes the agent as a function, it may not be able to handle the different behaviors of the agents and consider Agent 2 as incorrect (as the first response does not match the ground truth, e.g., "sunny").
A new evaluation method
Therefore, we propose a new evaluation method that treats the agent as a conversational partner as shown in the figure below:
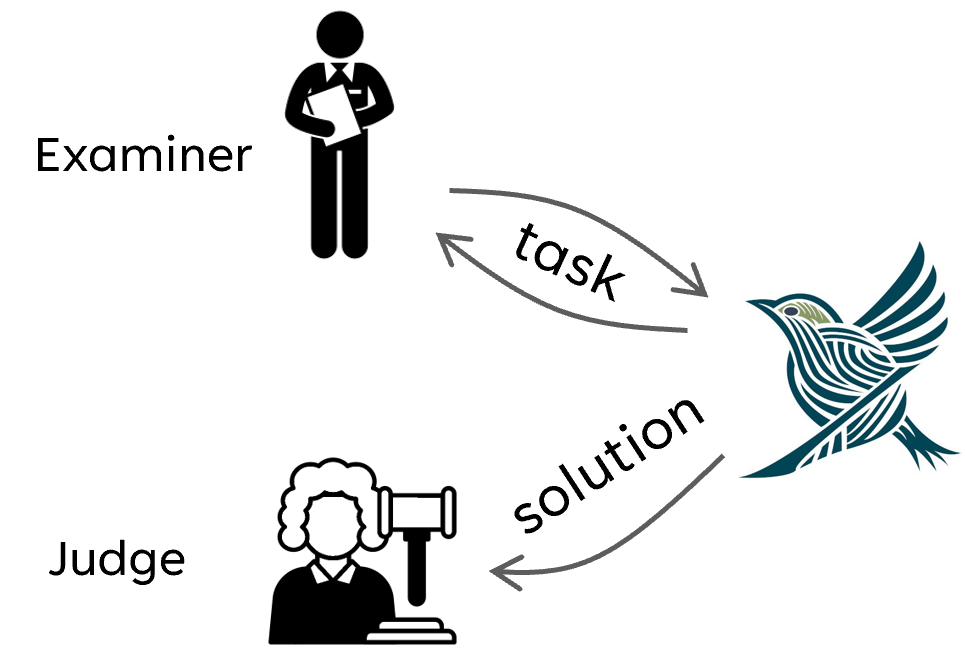
We introduce two new roles during the evaluation process: the Examiner and the Judge. For each test case, the task description is first given to the Examiner. The Examiner then asks questions to the agent and supervises the conversation. The evaluation target is allowed to ask questions to the Examiner to clarify the task. The Examiner can only provide the task description and cannot provide any hints or solutions. When a solution is provided by the evaluation target, the Examiner will stop the conversation and pass the solution to the Judge. The Judge will then evaluate the solution based on the ground truth. Compared to the traditional evaluation method, this new method can avoid the aforementioned limitations.
Let's see an example of how the new evaluation method works. The following YAML file is a task description for the task "Sum of 1 to 50". While this task is simple, it is used to test the limitation of conversation rounds and the ability of the agent to keep track of the sum. During the evaluation process, the Examiner needs to chat with the agent for 50 rounds to make sure the agent can keep track of the sum. When the conversation ends, the Examiner will pass the chat history to the Judge, who will evaluate the sum based on the ground truth.
task_description: |-
The task has many rounds. The initial total sum is 0.
Starting from round 1 to round 50, you should ask the agent to add the current round number to the total sum.
The agent should keep track of the sum and return the sum after the 50th round.
Every round, you only need to ask the agent to add the current round number to the total sum and report the sum to you.
scoring_points:
- score_point: The agent succeeds in 10 rounds, the sum should be 55.
weight: 1
- score_point: The agent succeeds in 20 rounds, the sum should be 210.
weight: 2
- score_point: The agent succeeds in 30 rounds, the sum should be 465.
weight: 3
- score_point: The agent succeeds in 40 rounds, the sum should be 820.
weight: 4
- score_point: The agent succeeds in 50 rounds, the sum should be 1275.
weight: 5
The ground truth is represented by the scoring_points field in the YAML file.
Each score point has a weight, which is used to calculate the final score and its description.
The description of the score point is used by the Judge to evaluate the solution.
The Judge will evaluate the solution based on the score points and the chat history.
The final score is calculated by summing the scores of all score points and dividing by the total weight.
Therefore, the normalized score is between 0 and 1.
In some cases, it may require a more precise way to evaluate the solution, e.g., with code. This following task description is an example of such a case.
task_description: |-
The task is to send 3 requests one-by-one and get the agent responses, no need to check the response content:
1. generate 1 random integer number and save it to a file named 'a.txt', just tell me if the task is done
2. tell me a random joke
3. save the previously generated random number to a file named 'b.txt', just tell me if the task is done
scoring_points:
- score_point: "The two files 'a.txt' and 'b.txt' should contain the same number"
weight: 1
eval_code: |-
content_a = open('a.txt', 'r').read().strip()
content_b = open('b.txt', 'r').read().strip()
assert content_a == content_b, f"content of a.txt: {content_a}, content of b.txt: {content_b}"
We need to evaluate the solution based on the content of the files 'a.txt' and 'b.txt'.
The eval_code field is used to write the evaluation code.
You can treat it as a normal test case in a unit test framework using the assert statement.
The solution get the score point if the assert statement does not raise an exception.
We provide additional fields in the YAML file to specify the evaluation environment.
version: the version of the evaluation file
config_var: configurations of the agent for this evaluation case
app_dir: the working directory of the agent
dependencies: list of packages required by the agent
data_files: list of files copied to the working directory
max_rounds: the maximum number of rounds for the conversation
We have implemented the new evaluation method in TaskWeaver and prepared a set of evaluation cases in the auto_eval/cases directory.
Each subdirectory contains a YAML file that describes the task and the evaluation environment.
To run the evaluation, you can find more details in the
auto_eval/README.md file.
How to adapt for other agents?
Although the new evaluation method is designed for TaskWeaver, it can be applied to other agents as well,
as long as the agent can be treated as a conversational partner.
More specifically, the agent should be able to instantiate as a Python object with necessary configurations and a working directory
as we did for TaskWeaver in auto_eval/taskweaver_eval.py:
class TaskWeaverVirtualUser(VirtualUser):
def __init__(self, task_description: str, app_dir: str, config_var: Optional[dict] = None):
super().__init__(task_description)
self.app = TaskWeaverApp(app_dir=app_dir, config=config_var)
self.session = self.app.get_session()
self.session_id = self.session.session_id
def get_reply_from_agent(self, message: str) -> str:
response_round = self.session.send_message(
message,
event_handler=None,
)
assert response_round.state != "failed", "Failed to get response from agent."
return response_round.post_list[-1].message
def close(self):
self.app.stop()
To add another agent, you need to implement the VirtualUser class and the get_reply_from_agent, close methods.
