Web Application Manual
Lockbox WebApp Role and Components
The WebApp deployed as part of the Lockbox is the main interface used to create and manage tasks performed by the solution. It allows users to:
-
Create and manage tasks
-
Create and manage schedules
-
Monitor activities
The WebApp orchestrates activities taking place in the solution (Mainly in Azure Data Factory and Synapse). To do so, the following concepts are used:
-
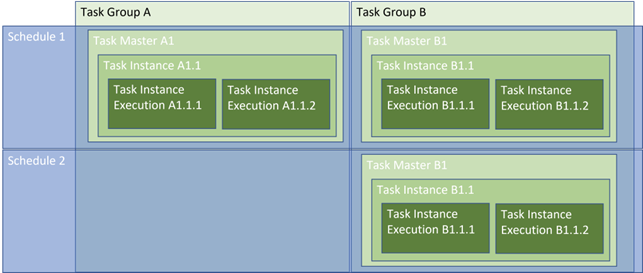
Task Masters: These define a specific task. As part of a task master, users can define a task type, a source and a destination in which the task will interact with. This can range from a data copy type activity to executing a synapse notebook. The user can also assign the task to a specific schedule
-
Task Instances: These are every instance a task master has been used to execute that specific task. A new instance will be created each time a schedule triggers a specific task master.
- Task Instance Execution: Each time a task instance executes, a new Task Instance Execution will be created. There should be normally be only one execution per task instance but in some cases there will be more. This is usually in the case of an error or time out; the user is then able to look at the logs of each execution to diagnose the reason for multiple execution attempts.
-
Task Groups: Tasks can be assigned to different task groups. This allows for easier management of tasks when wanting to generalise certain aspects of tasks.
-
Schedules: Schedules are defined as time triggers that will kick-off activities that have been assigned to those triggers. The solution comes with default schedules to be used as examples but users can add/modify as required.
- Schedule Instance: Each time a Schedule is executed, a new Schedule instance will be created. The Schedule Instance will contain all of the Task Instances associated with it that have been created due to the Schedule being executed.
-
Logs: Logs are created for every action the function app takes. Any errors or warnings will be listed in the Logs under their corresponding Function / Task Instance Execution.
Below is a representation of how these concepts interact with each other.