For the Business Manager
Fraud detection is one of the earliest industrial applications of data mining and machine learning. This solution shows how to build and deploy a machine learning model for online retailers to detect fraudulent purchase transactions.
The PowerBI dashboard allows you to visualize and use these predicted scores to aid in understanding the model you will deploy.
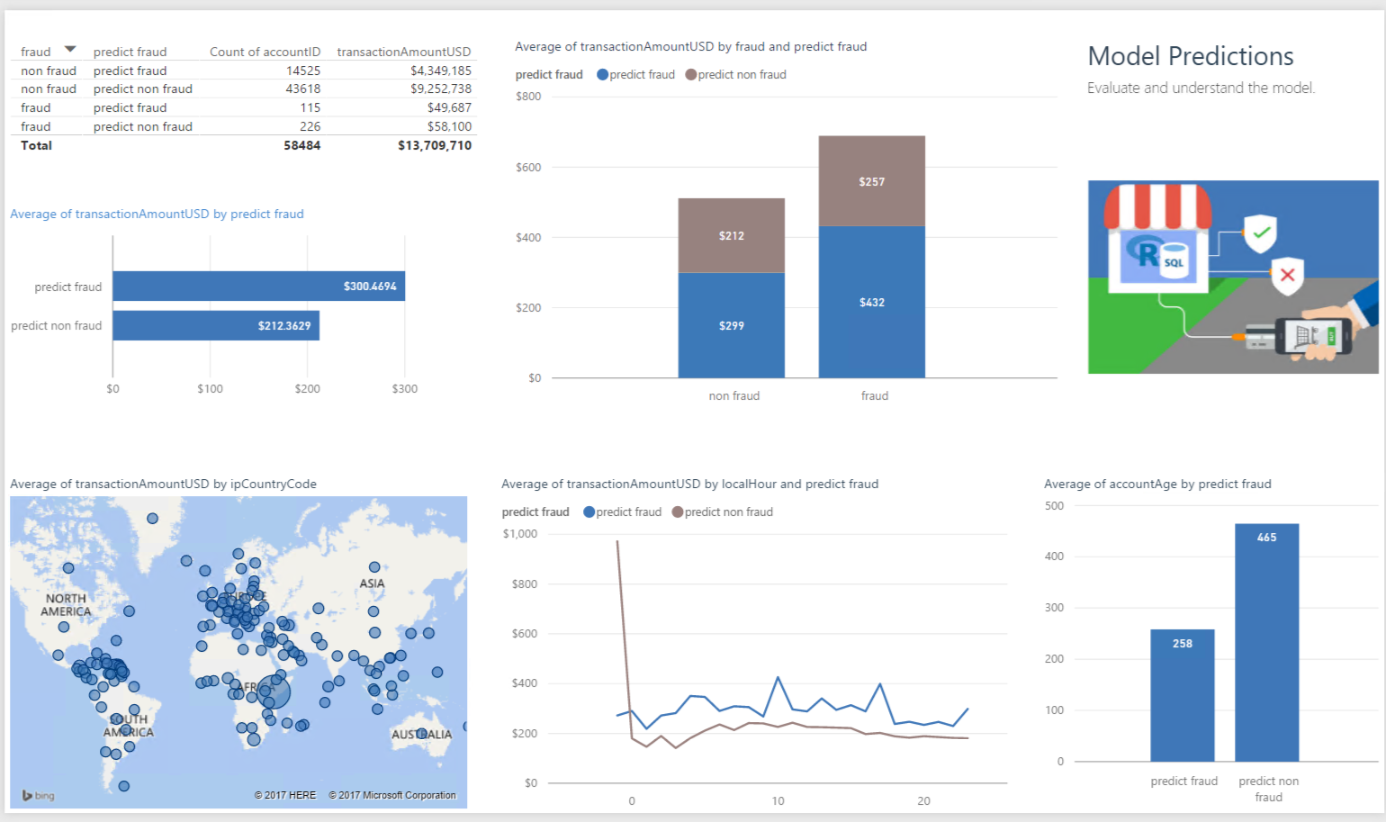
This dashboard shows the predicted scores of the data in the Test set - this is data for which we know whether the transaction was fraudulent, but was not used to build the model itself.
Note in the top table that we predicted fraud in 14,525 cases which were not fraudulent. This is something to keep in mind when deploying the model. Rather than reject a transaction that is predicted to be fraud, we might instead want to add a step to the purchase that would discourage an actual fraudulent transaction while still allowing a valid transaction to occur.
You can access this dashboard in any of the following ways:
-
Open the PowerBI file from the Fraud directory on the deployed VM desktop.
-
Install PowerBI Desktop on your computer and download and open the onlinefraud.pbix file.
-
Install PowerBI Desktop on your computer and download and open the onlinefraudHDI.pbix file.
To understand more about the entire end-to-end process of modeling and deploying this example, see Typical Workflow.