Reliability review
When reviewing the Reliability pillar you typically start with the business requirements of the application. Try to ask the questions:
- How critical is the application?
- What would happen if the application went down?
- Is it a custom solution or provided by a software vendor?
- What are the SLAs targets?
- Does the customer have a risk analysis?
Level 1 - Composite SLA, SPOF and HA
The first thing is to identify the type of architecture you are looking at, for example:
- Is it a hybrid solution?
- Does it support/implement global distribution?
- Is the database deployed with distributed availability?
- What is the main workload of the application for (IoT, Data Analytics, Web)?
With the Architecture Diagram at hand, you need to identify the Single Point Of Failure this architecture may suffer, and then calculate the composite SLA for the whole solution.
To audit SPOF, see how the architecture can respond to failures by using load-balancing, scalesets, stateless services, etc. Check if application resiliency is tested using any Chaos Engineering techniques.
Discuss about the High Availability requirements and see how is the application prepared for HA.
Calculate the cost implications of adding HA, but also the potential cost of application downtime and data loss.
Level 2 - BCDR, Detection & Response
Review the backup strategy and disaster recovery plan, and check if these are tested regularly.
Check what are the RPO and RTO constraints for this solution:
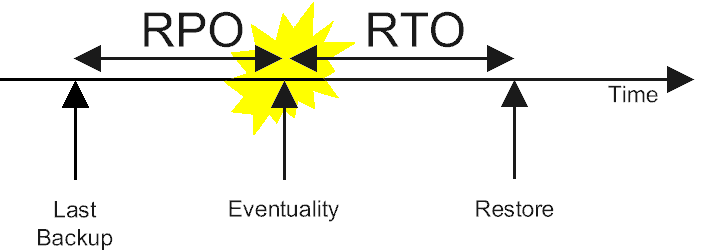
Discuss what are the Disaster Recovery plan triggers, what health checks are in place, how the system is monitored and what alerts are configured. Is there any traffic routing in place in the case of a general failure?
Level 3 - Design Patterns
There are several design patterns that can be used to improve reliability of the workload. Check with the development team if they are used in the architecture:
- Retry pattern and Fallback
- Timeout
- Circuit Breaker
- Rate Limiting
- Bulkhead or Shared-nothing architecture
Resources
- BCDR
- Composite SLA
- Single Point of Failure
- Reliability checklist
Checkpoint
- Most important SPOF identified.
- Composite SLA calculated.
- Disaster recovery plan.
Now you can move to the next pillar: Performance