If you have the midi console installed, you can invoke it from any command prompt using midi. We recommend using Windows Terminal for the best experience.
The Windows MIDI Services console is delivered as part of the SDK Runtime and Tools installer available via the links at the top of this page.
MIDI Console commands are words with no symbol prefix. For example endpoint or send-message-file. Options are prefixed with two dashes if you use the full word, or a single dash if you use the single-letter abbreviation. For example --help or -h. There is no statement completion built in to the console, but there are some supported abbreviations for commands. These are not yet fully documented but are present in the Program.cs in the console source code.
In MIDI 1.0, specifically USB MIDI 1.0, a connected device would have a single input and single output stream. Inside that stream are packets of data with virtual cable numbers. Those numbers (16 total at most in typical implementations) identify the “port” the data is going to. Operating systems would then translate those into input and output ports. Those cable numbers were hidden from users by the concept of a port.
MIDI 2.0 does not have the concept of a port. Instead, you always work with the stream itself. The group number, which is in the MIDI message now, is the moral equivalent of that cable number. Like the virtual cable, it helps address where the message is being sent.
So where you may have seen a device with 5 input and 5 output ports in the past show up as 10 discrete ports, you will now see a single bidirectional UMP Endpoint stream with 5 input groups and 5 output groups. We know this can take some getting used to, but it enables us to use MIDI 1.0 devices as though they are MIDI 2.0 devices, and provide a unified API.
The Windows MIDI Services Console app has been developed using C#, .NET 8, the MIT-licensed open source Spectre.Console library, and the Microsoft-developed open source C#/WinRT toolkit.
The console uses the same Windows MIDI Services WinRT APIs available to other desktop applications. Its full source code is available on our Github repo. Pull-requests, feature requests, and bug reports welcome. The project is open source, but we request that instead of forking it to create your own version, you consider contributing to the project.
Not every command has its own page here in the documentation. To find out more, including what options are available for a command, simply add --help after the command name when using the MIDI Console.
Each of these commands follows midi enumerate at the command line. Aliases for enumerate include list and enum.
For additional information, type midi enumerate <command> --help at the command-line. For example midi enumerate active-sessions --help.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
midi-services-endpoints |
List MIDI UMP endpoints visible to Windows MIDI Services-aware applications. Aliases include endpoints, ump-endpoints and ep |
legacy-winrt-api-endpoints |
List MIDI 1.0 endpoints as seen in apps using older MIDI APIs. Aliases include legacy-endpoints, bytestream-endpoints, and legacy |
active-sessions |
List all currently active Windows MIDI Services sessions on this PC. sessions is the alias. |
transport-plugins |
List all MIDI transport plugins installed on this PC. transports is the alias. |
endpoint-property-keys |
List the Windows MIDI Services-specific property keys. property-keys is the alias. |
Each of these commands follows midi endpoint at the command line. The alias for endpoint is ep. If a endpoint identifier is not supplied on the command line, the console will prompt you with a list of available endpoints.
For additional information, type midi endpoint <command> --help at the command-line. For example midi endpoint monitor --help.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
monitor |
Monitors a UMP endpoint for incoming messages and optionally displays them as they arrive. The alias is listen |
send-message |
Send a single message to a UMP endpoint as a list of up to four 32 bit MIDI words. The aliases include send-ump and send. |
send-message-file |
Sends a text file of UMP MIDI words to the specified endpoint. See arguments and options for format and delimiters. The aliases include send-ump-file and send-file. |
send-sysex-file |
(Experimental) Send a file of MIDI 1.0 or MIDI 2.0 SysEx messages (7 or 8 bit, binary or text) to a compatible endpoint. The alias is send-sysex |
play-notes |
Send MIDI 1.0 or 2.0 note on and off messages to the endpoint. The alias is play |
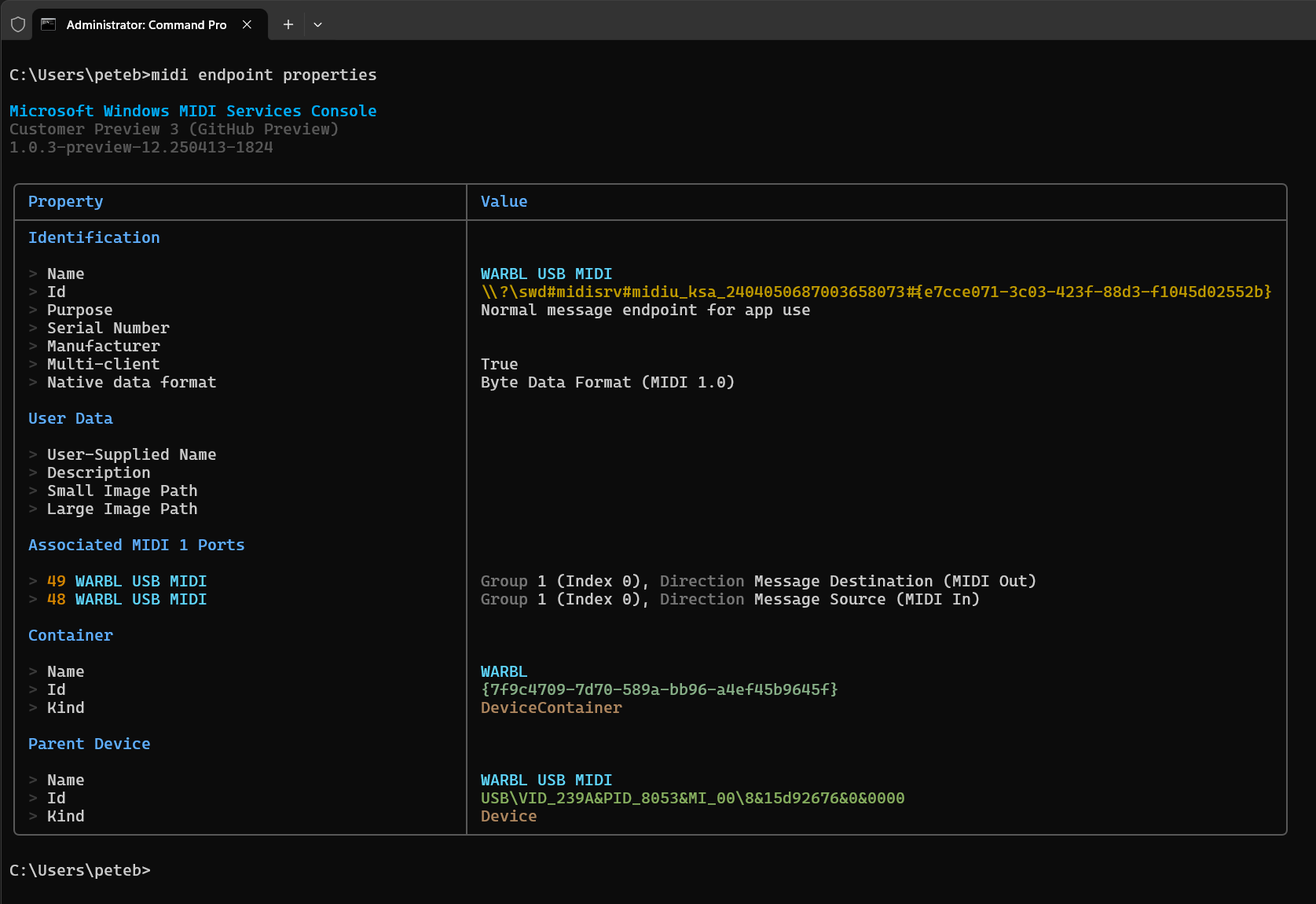
properties |
List out system-captured metadata properties for the specified endpoint. The alias include props, information, and info |
send-beat-clock |
(Experimental) Send MIDI beat clock to one or more groups on an endpoint. The alias is send-clock |
These commands are typically used for debugging MIDI 2.0 hardware. Each of these commands follows midi endpoint request at the command line. The alias for request is req.
For additional information, type midi endpoint request --help at the command-line.
function-blocks |
Send a request for one or more function blocks. Aliases include function-block, fb, functions, function |
endpoint-info |
Sends a MIDI 2.0 endpoint information request. Aliases include endpoint-metadata, endpoint-data, em, and metadata |
Most of these need to be run in an Administrator terminal session. Each of these commands follows midi service at the command line. The alias for service is svc
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
status |
Check to see if the Windows Service is running |
ping |
Ping the MIDI Windows Service |
restart |
Restart the MIDI service. This will close all open connections, remove any non-persistent configuration, and otherwise reset the MIDI system. Must be run as Administrator. |
start |
Start the MIDI Service if it is currently stopped. Must be run as Administrator. |
stop |
Stops the MIDI Service, freeing up all resources in use, closing all devices, and clearing any runtime configuration. Must be run as Administrator. |
set-auto-start |
Set the MIDI Service to start shortly after Windows starts, to avoid connection delays with the first connection made by an app |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
time |
Get the current MIDI clock timestamp value and information about the clock resolution. The alias for time is clock. |
watch-endpoints |
Watch endpoints for add/remove and PnP property change notifications. |