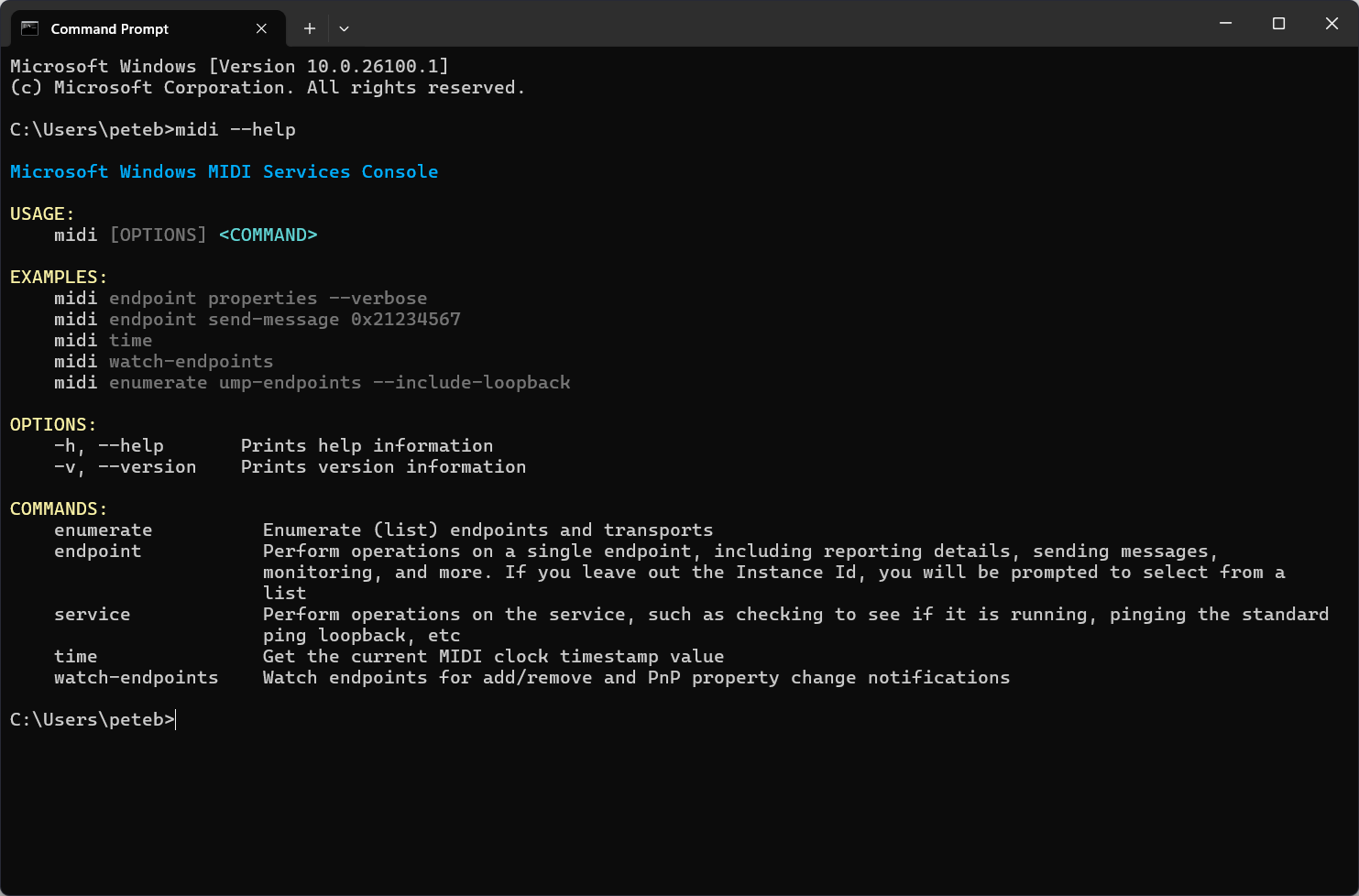
Add the option --help or its short version -h to any command to get information and examples for that command.
midi --help
midi service --help
midi enumerate --help
midi enumerate endpoints --help
The --help option will always provide the most up-to-date list of commands and options supported by the MIDI Services Console.
The heart of Windows MIDI Services is the Windows Service which processes and routes messages, creates endpoints, and more. The MIDI Services Console app includes a few commands to check the status and health of the service.
If you want to verify that the MIDI Service is running, you can check its status using the Service Control Manager, or through the MIDI Console.
midi service status
midi svc status
If you uset the --verbose or -v option, the console will display more information about the service.
midi service status
midi svc status
If you want to verify that the service is transmitting and receiving messages, you can use the ping command, much like you would
midi service ping
midi svc ping
This command also supports the --verbose or -v option to display the full results of the ping. It also supports a --count or -c parameter for the number of messages you want to send. Finally, the call supports a --timeout or -t parameter to set the timeout in milliseconds before the ping is considered to have failed.
Here are examples of the command with various parameters.
midi service ping --verbose
midi service ping --verbose --count 20 --timeout 20000
The MIDI console has three commands for managing the Windows service. These can be useful when developing or debugging service-side plugins. Note that these must be run from an Administrator console session.
midi service stop
midi service start
midi service restart
Tip: You can use the new Windows
sudocommand if you are a developer and you have enabled it in the Windows 11 developer settings.
sudo midi service restart