Named Entity Recognition with HuggingFace models
We designed this plugin to allow for out-of-the-box training and evaluation of HuggingFace models for NER tasks. We provide a golden config file (config.yaml) which you can adapt to your task. This config will make experimentations easier to schedule and track. All the source code and notebooks to submit jobs can be found here
Step by step with GermEval dataset#
We will go through how to adapt any dataset/task for PyMarlin and how to setup the plugin. For this purpose we will use the GermEval dataset - this is a dataset with German Named Entity annotation , with data sampled from German Wikipedia and News Corpora. For more granular information and raw dataset please refer here
Following HuggingFace documentation for preliminary data clean up we use their preprocess script to clean up the original dataset. These can be run in jupyter Notebook.
Dataset format#
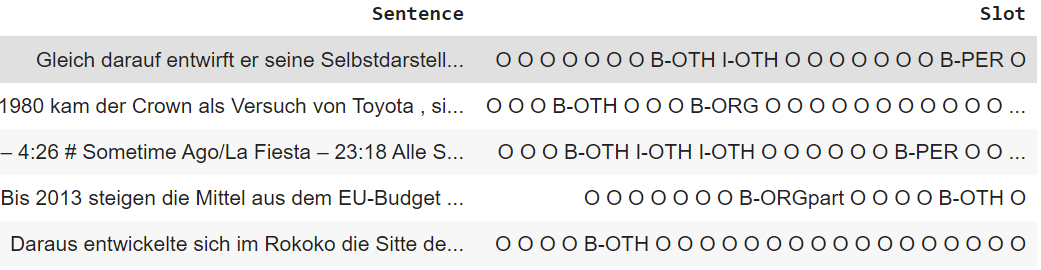
NER plugin expects the input to be a TSV or CSV with 2 columns. A column with the text sentences followed by a column with the labels for the tokens in the sentence. For example: 'Sentence': 'who is harry', 'Slot': 'O O B-contact_name'
For GermEval dataset below we show how to modify to format expected by plugin.
The dataset would now look like this:
Golden yaml config#
Marlin leverages yaml files for maintaining experiment parameters. For this German Evaluation dataset we provide a golden config config_germ.yaml.
Training#
Next we need a orchestrating script to initialize the plugin and start training. Assume the script test.py. It will contain the following.
We can now schedule a run locally using CLI , modify to point to the train and validation directory appropriately :
Evaluation#
We specify the path to store the model checkpoints in our config.yaml
The checkpoint consists of all the different components of your scenario like 'module_interface_state', 'trainer_state' and 'trainer_backend_state'. We need to save the model from within the 'module_interface_state' separately. Follow the below steps included in the notebook 'GermEvalAML.ipynb' here
Alternatively you could directly load only the model checkpoint as stored in the path specified by model_save_dir. In this case you would have the model weights directly in state_dict without needing to go through module_interface_state
Now you can use the model file stored as marlin_model.bin. You can specify this new model as the checkpoint to start from in config.yaml
You can use NER Plugin to evaluate: