Python#
Introduction#
Users are empowered by the Python Tool to offer customized code snippets as self-contained executable nodes in PromptFlow. Users can effortlessly create Python tools, edit code, and verify results with ease.
Inputs#
Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Code |
string |
Python code snippet |
Yes |
Inputs |
- |
List of tool function parameters and its assignments |
- |
Types#
Type |
Python example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
int |
param: int |
Integer type |
bool |
param: bool |
Boolean type |
string |
param: str |
String type |
double |
param: float |
Double type |
list |
param: list or param: List[T] |
List type |
object |
param: dict or param: Dict[K, V] |
Object type |
param: CustomConnection |
Connection type, will be handled specially |
Parameters with Connection type annotation will be treated as connection inputs, which means:
Promptflow extension will show a selector to select the connection.
During execution time, promptflow will try to find the connection with the name same from parameter value passed in.
Note that Union[...] type annotation is supported ONLY for connection type,
for example, param: Union[CustomConnection, OpenAIConnection].
Outputs#
The return of the python tool function.
How to write Python Tool?#
Guidelines#
Python Tool Code should consist of a complete Python code, including any necessary module imports.
Python Tool Code must contain a function decorated with @tool (tool function), serving as the entry point for execution. The @tool decorator should be applied only once within the snippet.
Below sample defines python tool “my_python_tool”, decorated with @tool
Python tool function parameters must be assigned in ‘Inputs’ section
Below sample defines inputs “message” and assign with “world”
Python tool function shall have return
Below sample returns a concatenated string
Code#
The snippet below shows the basic structure of a tool function. Promptflow will read the function and extract inputs from function parameters and type annotations.
from promptflow.core import tool
from promptflow.connections import CustomConnection
# The inputs section will change based on the arguments of the tool function, after you save the code
# Adding type to arguments and return value will help the system show the types properly
# Please update the function name/signature per need
@tool
def my_python_tool(message: str, my_conn: CustomConnection) -> str:
my_conn_dict = dict(my_conn)
# Do some function call with my_conn_dict...
return 'hello ' + message
Inputs#
Name |
Type |
Sample Value in Flow Yaml |
Value passed to function |
|---|---|---|---|
message |
string |
“world” |
“world” |
my_conn |
CustomConnection |
“my_conn” |
CustomConnection object |
Promptflow will try to find the connection named ‘my_conn’ during execution time.
outputs#
"hello world"
Keyword Arguments Support#
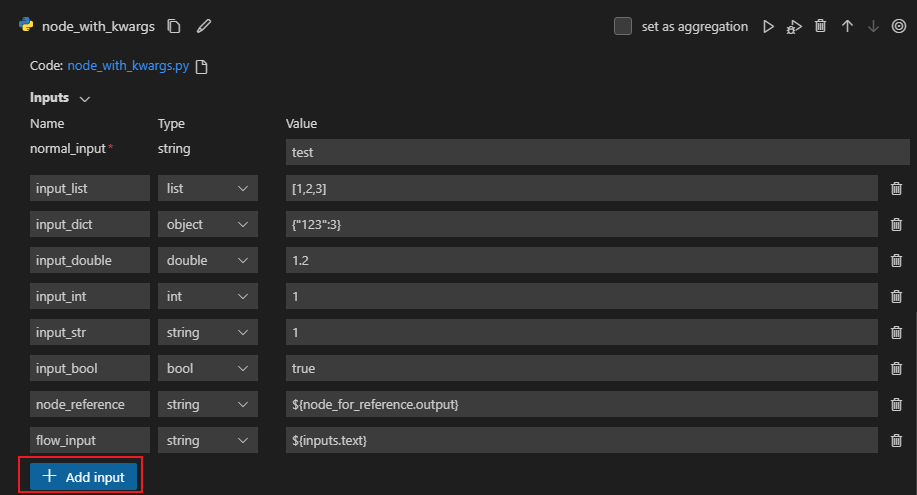
Starting from version 1.0.0 of PromptFlow and version 1.4.0 of Prompt flow for VS Code, we have introduced support for keyword arguments (kwargs) in the Python tool.
from promptflow.core import tool
@tool
def print_test(normal_input: str, **kwargs):
for key, value in kwargs.items():
print(f"Key {key}'s value is {value}")
return len(kwargs)
When you add kwargs in your python tool like above code, you can insert variable number of inputs by the +Add input button.