Task 01: Delivering a New Feature
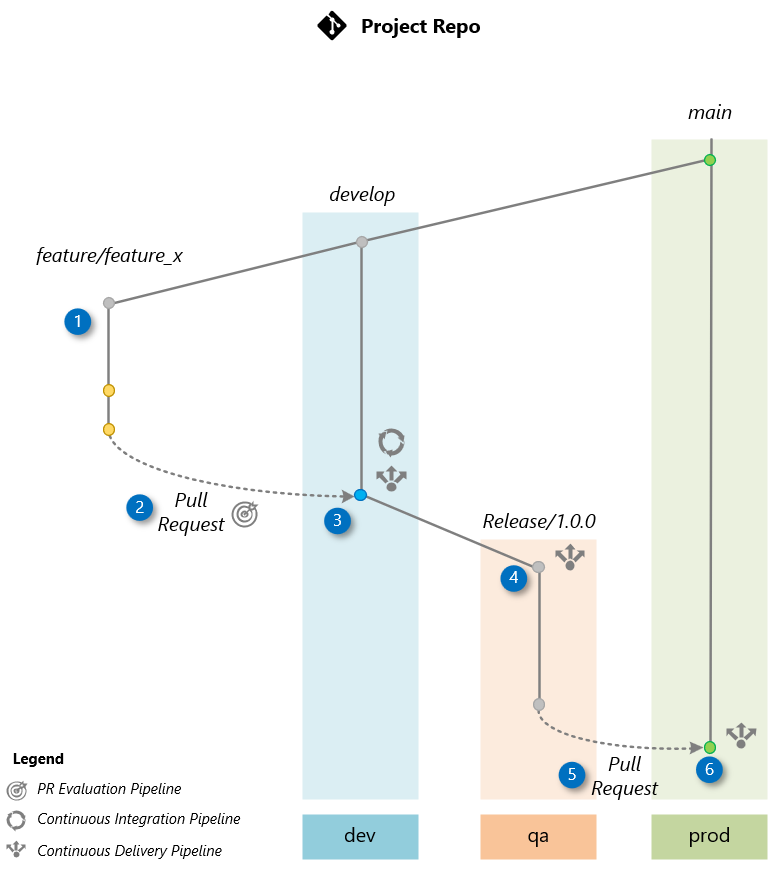
Once the project bootstrapping is complete, the team can begin developing new features. This section provides a detailed guide on delivering a new feature, covering every step from initial development to production deployment. To illustrate the procedure, we will develop a new feature called “Feature X,” which will be included in the project’s release 1.0.0. The process can be summarized in six steps, represented in the following diagram, making it easier to understand and follow along.
Solution
Follow the steps below to deliver this feature from the beginning of development to deployment in production. You will need access to your project repository that has been bootstrapped, a terminal (bash or PowerShell) with Git, and the GitHub page of your repository.
For the correct execution of all github action Pipelines we need to do a few fixes on the github actions workflows For All yaml files (pr_pipelines.yml, continuous_integration.yml, continuous_delivery_qa.yml, continuous_delivery_prod.yml, continuous_delivery_dev.yml) > Change the azd setup version from Azure/setup-azd@v1.0.0 to Azure/setup-azd@v2.1.0 > Change the python version from python-version: 3.8 to python-version: 3.11
On the file ./.github/actions/config-env/action.yml on the Provision environment step, on the Previous deployment exists section (line 231) before the azd provision line, add a line azd env set AZURE_PRINCIPAL_TYPE ‘ServicePrincipal’
On the file ./infra/main.bicep comment out all roles provisioning, from line 144 to 275
On the file ./evaluations/qa_quality_eval.py add a check if the file exist for data, and a try/except block for the base run, response and convert to jsonl
On the file ./evaluations/safety_eval.py add a try/except block for simulator, adversarial_eval_result, and adversarial_eval_w_jailbreak_result
If a deployment fails, the next time we retry the deployment azd wont be able to refresh the env variables correctly, to fix this go to the Azure Portal>Subscription>Deployments and remove the failed deployment for the environment
01: Create a feature branch
If you completed Exercise 02: Building LLMs Orchestration Flows, you can skip to the next section.
The workflow starts by creating a feature branch named feature/feature_x from the develop branch. This is where the development team will work on the new feature x.
Expand this section to view the solution
-
Switch to the develop branch and pull the latest changes:
git checkout develop git pullIf you do not have a develop branch you can use Git commands to create one. Ensure that you have created all the Environment variables in Prod, QA, Dev within your GitHub repo. Also ensure that you have added the SP secrets to each.
-
Create the feature branch:
git checkout -b feature/feature_x -
Make non-disruptive changes to the repository. For instance, create a file FEATUREX.md in the project root:
Using Bash:
touch FEATUREX.mdUsing PowerShell:
New-Item -ItemType File -Name "FEATUREX.md"
This ensures the new feature is developed in isolation, maintaining the integrity of the project’s develop branch and promptflow.
02: Pull Request (PR) to develop
Upon completing the feature, create a Pull Request (PR) to merge changes from the feature branch feature/feature_x to the develop branch, which is the default branch where the team integrates changes.
Expand this section to view the solution
-
Add changes, commit, and push to the feature branch:
git add . git commit -m "Feature X complete" git push origin feature/feature_x -
Create the PR:
gh pr create --base develop --head feature/feature_x --title "Feature X" --body "Description of the changes and the impact."If needed, install gh using sudo apt install gh, then login with gh auth login.
You can also use the GitHub website to create the pull request. Remember to select develop as the base branch and feature/feature_x as the compare branch.
The creation of the PR triggers a PR Evaluation Pipeline to ensure that the code adheres to standards, passes unit tests, and the orchestration flow is evaluated by AI to ensure it meets quality metrics.
03: Merge to develop
Approve the Pull Request, merging it into the develop branch. This merge triggers the Continuous Integration (CI) Pipeline, which builds the orchestration flow and conducts AI-assisted evaluations using a comprehensive test dataset based on the Golden Dataset. Upon successful completion, the Continuous Deployment (CD) Pipeline is executed to deploy the flow to the dev environment.
Expand this section to view the solution
- Merge the PR using GitHub by going to the Pull Requests tab in your repository, select the recently created PR, and select Merge pull request.
Optional Steps
The following steps are optional and can be skipped if you prefer to conclude the exercise after merging to develop. These steps are recommended for additional testing and quality assurance before deploying to production.
04. Release Branch (release/1.0.0) (Optional)
Creating a release branch is not mandatory but recommended for additional testing and quality assurance before deploying to production. Proceed with this step if your workflow benefits from a dedicated release phase.
After confirming the stability of the develop`branch through testing in dev, create a release branch release/1.0.0 from develop. This triggers a Continuous Deployment (CD) pipeline to deploy the application to the qa environment. Before deployment, an AI-based evaluation assesses quality, risk, and safety evaluations. The application in qa is then used for User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and red-teaming or LLM App.
Expand this section to view the solution
-
Create the release branch:
git checkout develop git pull origin develop git checkout -b release/1.0.0 git push origin release/1.0.0
05: Pull Request to main
After UAT tests in the qa environment confirm that the application is ready for production, create a Pull Request (PR) to merge the changes into the main branch from the release/1.0.0 branch.
Expand this section to view the solution
-
Create the PR:
Below is an example utilizing the GitHub CLI:
gh pr create --base main --head release/1.0.0 --title "Release 1.0.0" --body "Merging release/1.0.0 into main after successful UAT in QA environment"
You can also use the GitHub website to create the pull request. Remember to select main as the base branch and release/1.0.0 as the compare branch.
06: Merge to main
Expand this section to view the solution
-
Once the Pull Request (PR) to the main branch is approved on GitHub, go to the Pull Requests tab of your project repository on GitHub.
-
Select the PR created for merging into production, and select Merge pull request to manually approve the merge of release/1.0.0 into the main branch. This action triggers the Continuous Deployment (CD) pipeline, which deploys the code to the prod environment.