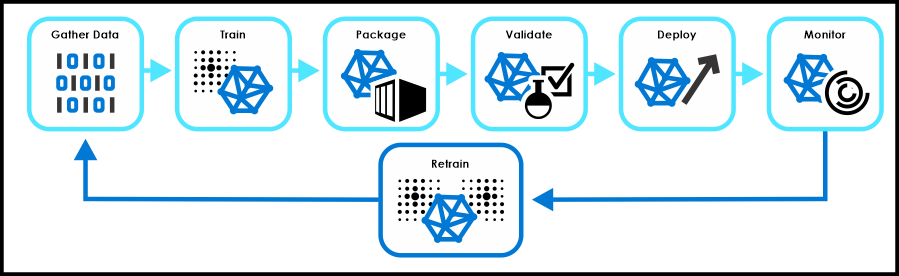
Machine learning training process
Get started with Machine learning
The process for creating a machine learning model varies based on the characteristics of the model, tools and other variables like where it will be run. Here is a high level example that gives an overview of the main steps included to the process.
Gathering and labeling data
AI models for vision and sound require data for training purposes. Production models may require thousands of samples. For vision, training data should be captured, if possible, from the actual location where the camera(s) will be used in production. Also, you should consider different lighting conditions and other variables with the target of being able to generate as comprehensive data set as possible as that is important. For getting started with machine learning, you can create basic image classification models with tens or hundreds of pictures using the Azure Custom Vision service.
Labeling refers to the process of assigning meaning to your data. In practice it’s indicating what data represent by labeling objects in a picture or label sound sample. With a basic image classification model, labeling can be as simple as maintaining folders with the name that corresponds to the images that you have for each label. Depending on the use case it’s recommended that part of the data set is preserved (unlabeled) for validating the model.
Train
The next step in the process is to train your model using a ML framework. There are many solutions for developing machine learning models that have the training part built into the workflow. A machine learning model can be trained locally or in a cloud. As the training is computationally intensive, we recommend leveraging Azure services for training which will save you time and integrate with supported frameworks.
Package, validate, deploy
The order of packaging, validating and deploying the model varies depending whether the target is to validate the model based on a pre-defined data sets and manual inputs or validate the model running it in a device. To be able to do validation in a device the model has to be packaged first. An AI model can be deployed to a device first for testing and then for production use using Azure IoT Hub. In the development phase most of the scripts used to train and convert machine learning models also include a build in functions for deployment making it faster to iterate and test the model in a device. A deployed IoT module is a container that includes your model and associated script or application and any additional dependencies.
Monitoring
When running the AI model in the production it should be monitored for accuracy and performance. There are several solutions like Azure Stream Analytics that can be run in the intelligent edge device to refine the data before actions are taken based on it. This allows you to reduce noise in your data before you it is fed into the business logic for your solution.
Retrain
Most of the AI models that run in production use are retrained and improved based on the data the model gets as an input. Vision is a great example of this – AI vision model can be retrained with the pictures a camera takes in a production use. This continuous loop ensures that the accuracy of the AI model keeps gradually improving.