Local and Remote Workspaces
In a local workspace, DeviceScript opens a native serial connection to communicate with hardware devices.
In a remote workspace, DeviceScript uses a separate browser window using WebSerial that communicates with the localhost developer tools server.
In general, web editor is not supported.
| Feature | Local (Windows, MacOS, Linux) | Remote (WSL, Docker, Codespaces, ...) | Web |
|---|---|---|---|
| TypeScript completion, syntax | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Compiler | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Device Simulator | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Debugger | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Simulator Dashboard | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Devices/Watch views | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Flash Firmware | ✓ | ✓ (1) | |
| Serial connection to hardware | ✓ | ✓ (2) | |
| USB connection to hardware | (3) |
- (1) Using manual download of .UF2 files for RP2040 or the Adafruit WebSerial ESPTool
- (2) Through a seperate browser window using WebSerial
- (3) No board with USB connection supported yet
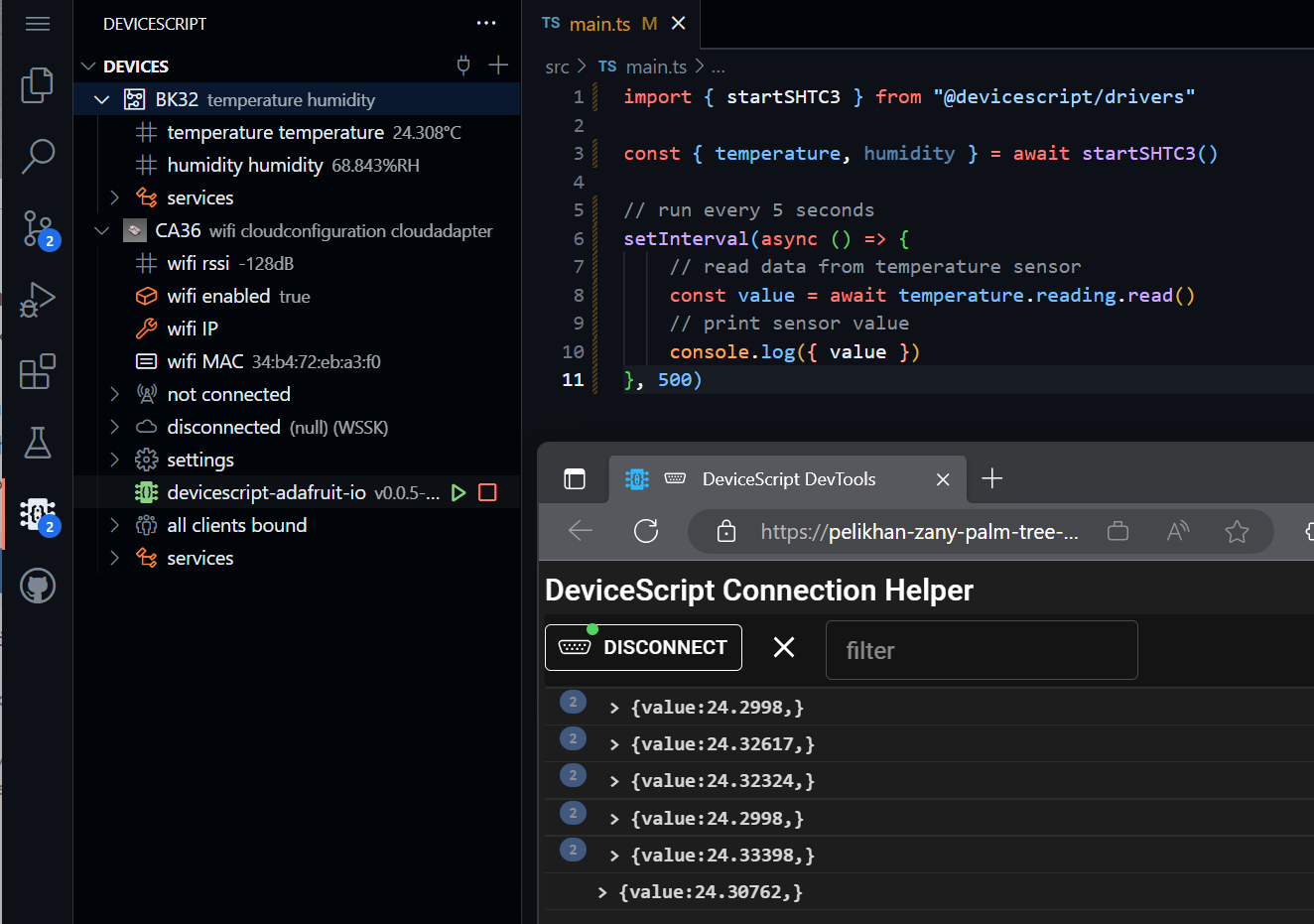
Remote workspace
When using a remote workspace, the developer tool command line (that gets spawned by the Visual Studio extension) cannot access physical devices.
To work around this issue, the extension launches a web page that uses WebSerial/WebUSB to connect to the physical device and proxy the packets back to the local web server hosted by the developer tools.
The key difference between local and remote are:
- the connection is done through a separate web page that needs to stay opened and in the foreground (browser aggressively throttle background pages)
- the console output is displayed in the connection page rather than in the VS Code terminal
The remote feature was tested for the following remote solutions:
Virtual Workspaces
Virtual Workspaces, not to be confused with remote workspaces, are not supported: