This page was generated from
docs/examples/DataSet/Offline plotting with categorical data.ipynb.
Interactive online version:
.
Offline plotting with categorical data¶
This notebook is a collection of plotting examples using the plot_dataset function and caterogical (string-valued) data. The notebook should cover all possible permutations of categorical versus numerical data.
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from qcodes.dataset import (
Measurement,
initialise_or_create_database_at,
load_or_create_experiment,
plot_dataset,
)
from qcodes.parameters import Parameter
[2]:
initialise_or_create_database_at(
Path.cwd().parent / "example_output" / "offline_plotting_example_categorical.db"
)
exp = load_or_create_experiment("offline_plotting_experiment", "nosample")
1D plotting¶
Category is the independent parameter¶
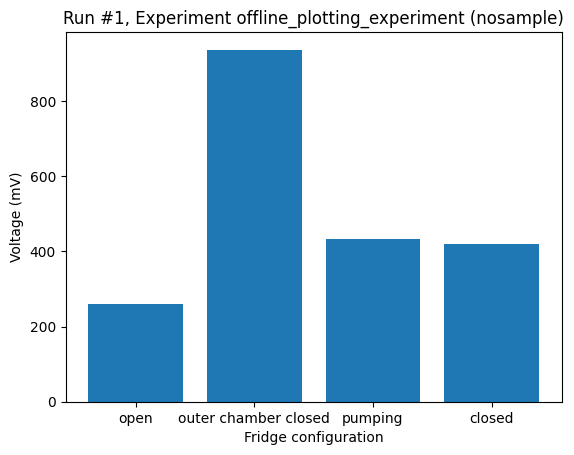
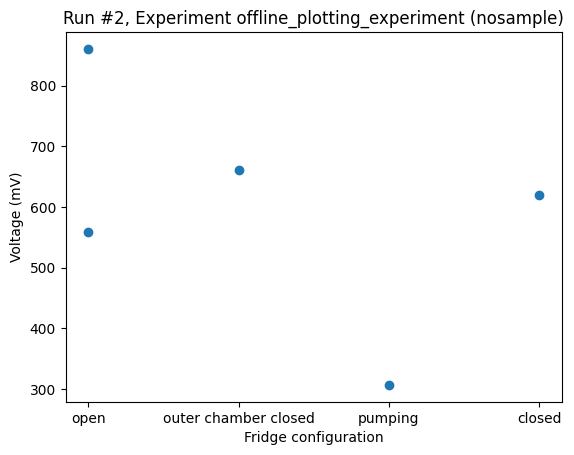
With the category as the independent parameter, plot_dataset will default to a bar plot as long as there is at most one value per category. If more than one value is found for any category a bar plot is not possible, and the plot_dataset falls back to a scatter plot.
[3]:
voltage = Parameter("voltage", label="Voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
fridge_config = Parameter(
"config", label="Fridge configuration", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(fridge_config, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(voltage, setpoints=(fridge_config,))
with meas.run() as datasaver:
configurations = ["open", "outer chamber closed", "pumping", "closed"]
for configuration in configurations:
datasaver.add_result(
(fridge_config, configuration), (voltage, np.random.rand())
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 1.
[4]:
_ = plot_dataset(dataset)
[5]:
with meas.run() as datasaver:
configurations = ["open", "outer chamber closed", "pumping", "closed"]
for configuration in configurations:
datasaver.add_result(
(fridge_config, configuration), (voltage, np.random.rand())
)
datasaver.add_result((fridge_config, "open"), (voltage, np.random.rand()))
dataset = datasaver.dataset
_ = plot_dataset(dataset)
Starting experimental run with id: 2.
Category is the dependent parameter¶
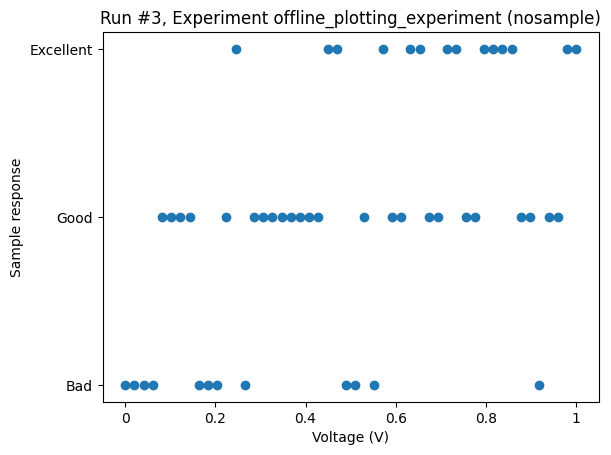
With the categories as the dependent variable, i.e., the outcome of a measurement, the plot_dataset defaults to a scatter plot.
Here is an example with made-up parameters and random values.
UNRESOLVED: How do we ensure the y-axis order?
[6]:
voltage = Parameter("voltage", label="Voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
response = Parameter("response", label="Sample response", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(voltage)
meas.register_parameter(response, paramtype="text", setpoints=(voltage,))
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for volt in np.linspace(0, 1, 50):
coinvalue = volt + 0.5 * np.random.randn()
if coinvalue < 0:
resp = "Bad"
elif coinvalue < 0.8:
resp = "Good"
else:
resp = "Excellent"
datasaver.add_result((voltage, volt), (response, resp))
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 3.
[7]:
_ = plot_dataset(dataset)
Both variables are categorical¶
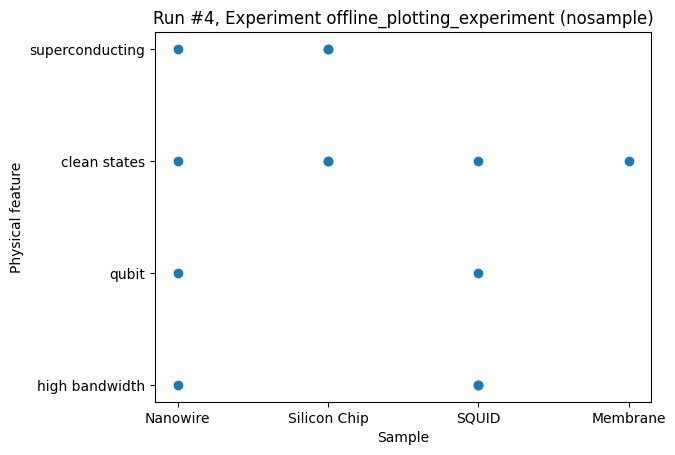
For both variables being categorical, the plot_dataset defaults to a scatter plot.
This case would typically be some summary of a large number of measurements.
[8]:
sample = Parameter("sample", label="Sample", unit="", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
feature = Parameter("feature", label="Physical feature", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(sample, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(feature, paramtype="text", setpoints=(sample,))
with meas.run() as datasaver:
features = ["superconducting", "qubit", "clean states", "high bandwidth"]
for samp in ["Nanowire", "Silicon Chip", "SQUID", "Membrane"]:
feats = np.random.randint(1, 5)
for _ in range(feats):
datasaver.add_result(
(sample, samp), (feature, features[np.random.randint(0, 4)])
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 4.
[9]:
_ = plot_dataset(dataset)
2D plotting¶
Naming convention: the x-axis is horizontal, the y-axis is vertical, and the z-axis is out-of-plane.
Categorical data on the x-axis¶
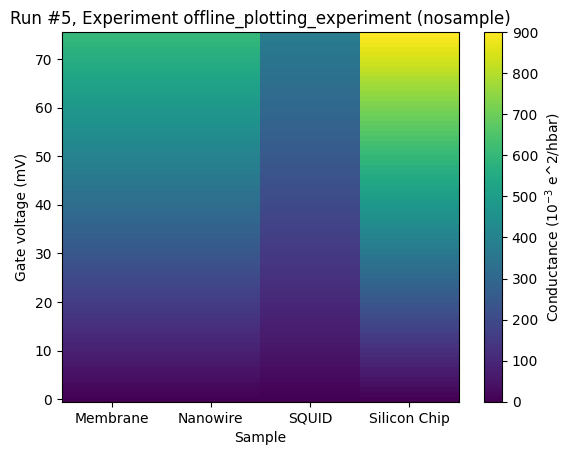
Here is an example where different samples are tested for conductivity. The longer the name of the sample, the higher the conductivity.
[10]:
sample = Parameter("sample", label="Sample", unit="", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
conductance = Parameter(
"conductance", label="Conductance", unit="e^2/hbar", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(sample, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(conductance, setpoints=(sample, gate_voltage))
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for samp in ["Nanowire", "Silicon Chip", "SQUID", "Membrane"]:
gate_vs = np.linspace(0, 0.075, 75)
for gate_v in gate_vs:
datasaver.add_result(
(sample, samp),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(conductance, len(samp) * gate_v),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 5.
[11]:
ax, _ = plot_dataset(dataset)
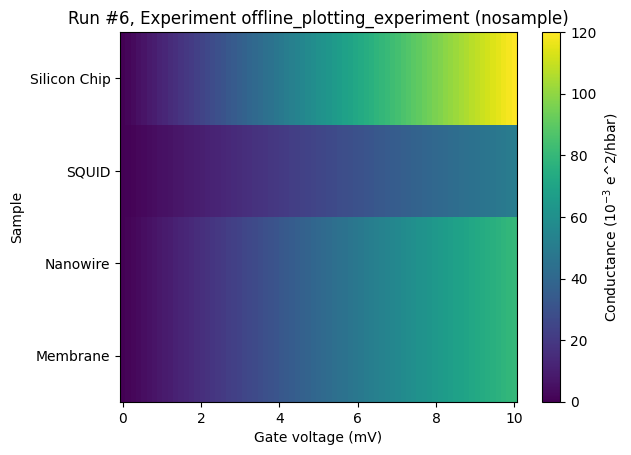
Categorical data on the y-axis¶
This situation is very similar to having categorical data on the x-axis. We reuse the same example.
[12]:
sample = Parameter("sample", label="Sample", unit="", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
conductance = Parameter(
"conductance", label="Conductance", unit="e^2/hbar", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(sample, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(conductance, setpoints=(gate_voltage, sample))
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for samp in ["Nanowire", "Silicon Chip", "SQUID", "Membrane"]:
gate_vs = np.linspace(0, 0.01, 75)
for gate_v in gate_vs:
datasaver.add_result(
(sample, samp),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(conductance, len(samp) * gate_v),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 6.
[13]:
ax, _ = plot_dataset(dataset)
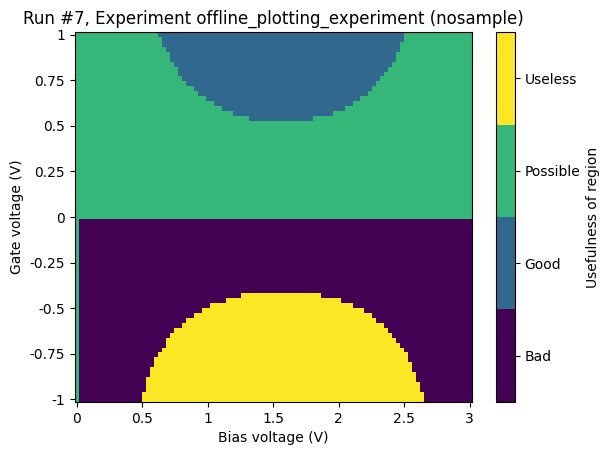
Categorical data on the z-axis¶
Categorical data on the z-axis behaves similarly to numerical data on the z-axis; what kind of plot we get depends on the structure of the setpoints (i.e. the x-axis and y-axis data). If the setpoints are on a grid, we get a heatmap. If not, we get a scatter plot.
Gridded setpoints¶
[14]:
bias_voltage = Parameter(
"bias_v", label="Bias voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
useful = Parameter(
"usefulness", label="Usefulness of region", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(bias_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(
useful, setpoints=(bias_voltage, gate_voltage), paramtype="text"
)
# a function to simulate the usefulness of a region
def get_usefulness(x, y):
val = np.sin(x) * np.sin(y)
if val < -0.4:
return "Useless"
if val < 0:
return "Bad"
if val < 0.5:
return "Possible"
return "Good"
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for bias_v in np.linspace(0, 3, 100):
for gate_v in np.linspace(-1, 1, 75):
datasaver.add_result(
(bias_voltage, bias_v),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(useful, get_usefulness(bias_v, gate_v)),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 7.
[15]:
ax, cax = plot_dataset(dataset)
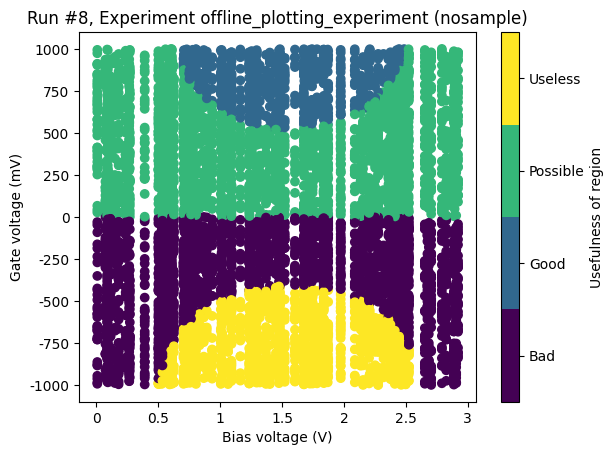
Scattered setpoints¶
The same example as above, but this time with setpoints not on a grid.
[16]:
bias_voltage = Parameter(
"bias_v", label="Bias voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
useful = Parameter(
"usefulness", label="Usefulness of region", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(bias_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(
useful, setpoints=(bias_voltage, gate_voltage), paramtype="text"
)
# a function to simulate the usefulness of a region
def get_usefulness(x, y):
val = np.sin(x) * np.sin(y)
if val < -0.4:
return "Useless"
if val < 0:
return "Bad"
if val < 0.5:
return "Possible"
return "Good"
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for bias_v in 3 * (np.random.rand(100)):
for gate_v in 2 * (np.random.rand(75) - 0.5):
datasaver.add_result(
(bias_voltage, bias_v),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(useful, get_usefulness(bias_v, gate_v)),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 8.
[17]:
ax, cax = plot_dataset(dataset)
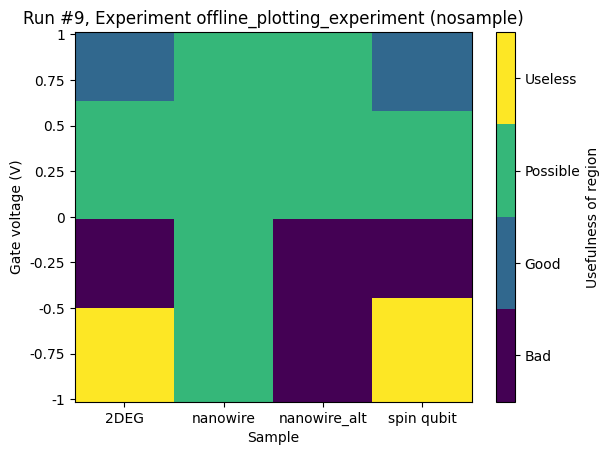
Categorical data on x-axis and z-axis¶
For completeness, we include two examples of this situation. One resulting in a grid and one resulting in a scatter plot. We reuse the example with the x- and y-axes having numerical data with just a slight modification.
[18]:
sample = Parameter("sample", label="Sample", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
useful = Parameter(
"usefulness", label="Usefulness of region", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(sample, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(useful, setpoints=(sample, gate_voltage), paramtype="text")
samples = ["nanowire", "2DEG", "spin qubit", "nanowire_alt"]
# a function to simulate the usefulness of a region
def get_usefulness(x, y):
x_num = samples.index(x) * 4 / len(samples)
val = np.sin(x_num) * np.sin(y)
if val < -0.4:
return "Useless"
if val < 0:
return "Bad"
if val < 0.5:
return "Possible"
return "Good"
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for samp in samples:
for gate_v in np.linspace(-1, 1, 75):
datasaver.add_result(
(sample, samp),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(useful, get_usefulness(samp, gate_v)),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 9.
[19]:
ax, cax = plot_dataset(dataset)
[20]:
sample = Parameter("sample", label="Sample", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None)
gate_voltage = Parameter(
"gate_v", label="Gate voltage", unit="V", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
useful = Parameter(
"usefulness", label="Usefulness of region", set_cmd=None, get_cmd=None
)
meas = Measurement(exp=exp)
meas.register_parameter(sample, paramtype="text")
meas.register_parameter(gate_voltage)
meas.register_parameter(useful, setpoints=(sample, gate_voltage), paramtype="text")
samples = ["nanowire", "2DEG", "spin qubit", "nanowire_alt"]
# a function to simulate the usefulness of a region
def get_usefulness(x, y):
x_num = samples.index(x) * 4 / len(samples)
val = np.sin(x_num) * np.sin(y)
if val < -0.4:
return "Useless"
if val < 0:
return "Bad"
if val < 0.5:
return "Possible"
return "Good"
with meas.run() as datasaver:
for samp in samples:
for gate_v in 2 * (np.random.rand(75) - 0.5):
datasaver.add_result(
(sample, samp),
(gate_voltage, gate_v),
(useful, get_usefulness(samp, gate_v)),
)
dataset = datasaver.dataset
Starting experimental run with id: 10.
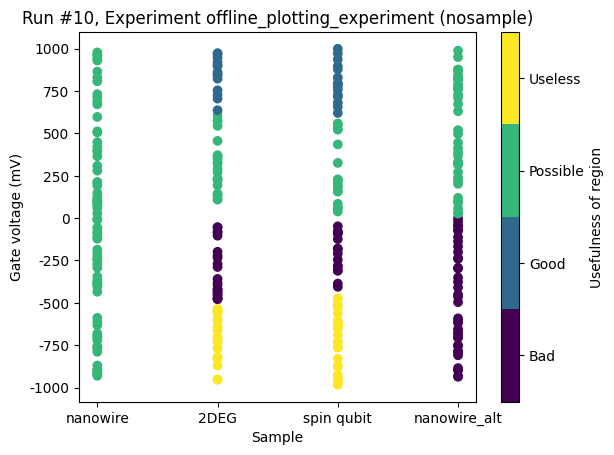
[21]:
ax, cax = plot_dataset(dataset)
[ ]: