Task 01 - Deploy a Bicep script
Introduction
Before you can start building your AI shopping assistant, you need to deploy the necessary Azure resources. This includes setting up a resource group, deploying a Bicep script to create the required infrastructure, and configuring environment variables for your application.
Description
In this task, you will deploy a Bicep script that sets up the necessary Azure resources for your AI shopping assistant. This includes creating a resource group and deploying the required infrastructure. In addition, you will install any software prerequisites needed for the application to run.
Success Criteria
- You have installed software necessary for the application to run.
- You have created a resource group in Azure.
- You have deployed a Bicep script to create the necessary Azure resources.
Learning Resources
- Cloning a repository via the command line or GitHub Desktop
- az group (Azure Resource Group)
- Create Bicep files by using Visual Studio Code
- Azure Developer CLI (azd)
Key Tasks
01: Fork the repository
Fork this GitHub repository to your account. You will need to fork the repo in order to modify and use GitHub Actions workflows in later tasks.
Expand this section to view the solution
In order to fork this repository, make sure that you are signed in to GitHub with the account you would like to use. Then, select the Fork button.
On the next page, select your account as the Owner and leave the repository name alone. Then, select Create fork to complete the process.
02: Run Codespace or install necessary software
To work through this training, you can either use a GitHub Codespace or install the necessary software on your local machine.
To use a GitHub Codespace, navigate to your forked repository and select the Code button. Then, select the Codespaces tab and choose Create codespace on main.
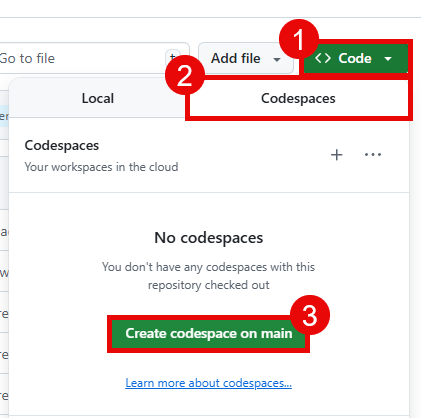
This Codespace is pre-configured with all the necessary software to complete this training.
Alternatively, you can install the necessary software on your local machine. This includes:
- Azure CLI
- Azure Developer CLI (azd)
- A Git client. An alternative option is to install GitHub Desktop.
- Python 3.10 or later
- Visual Studio Code
- The Bicep tools Visual Studio Code extension
- Docker Desktop (optional, but recommended)
If you do not use a Codespace, you will also need to clone the repository to your local machine.
You can do this using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/<your-username>/TechWorkshop-L300-AI-Apps-and-Agents.git
Make sure to replace <your-username> with your actual GitHub username.
03: Create a resource group in Azure
After you have set up your development environment, the next step is to create a resource group in Azure.
Expand this section to view the solution
You can do this using the following command in the Azure CLI, assuming you are logged in and have selected the correct subscription:
az group create --name techworkshop-l300-ai-agents --location eastus2
Alternatively, you may choose to do this from the Azure portal. In the search bar at the top, search for and select Resource groups. Then, select the + Create button to create a new resource group. Choose your subscription and give the resource group a name such as techworkshop-l300-ai-agents.
Make sure to choose from one of the following regions for the resource group location (in alphabetical order rather than order of preference):
- East US 2
- France Central
- Sweden Central
- Switzerland West
The reason for this is that certain Azure services used in this training are currently only available in these regions.
04: Deploy the Bicep script
You will use either the Azure CLI or the Bicep extension in Visual Studio Code to deploy the Bicep script that sets up the necessary Azure resources for this training.
Expand this section to view the solution
Before you can deploy the Bicep script, you need to ensure that you are logged into the Azure CLI. You can do so using az login on a local machine or az login --use-device-code in a Codespace VM.
If you receive an error message reading, “Your sign-in was successful but does not meet the criteria to access this resource,” you are likely using a Microsoft EMU account or some other account that has stringent restrictions on machine access. You will need to use an external MCAPS subscription or some other paid subscription to continue. A Visual Studio subscription will not be sufficient, as these accounts will likely not have access to Microsoft Foundry and the language models we will use.
If you receive an error message indicating that you do not have sufficient VM quota in the given region, try a different region from the four listed in the step above:
eastus2,swedencentral,francecentral,switzerlandwest. If your account does not have sufficient quota in any of those four regions, you may create resources in another region but you will not be able to run the Red Teaming agent in Exercise 06.
The next step is to deploy the Bicep stack. You can do this either via CLI, or you can use the Visual Studio Code Bicep extension.
To deploy via CLI in Linux or macOS, issue the following command:
az deployment group create \
--resource-group techworkshop-l300-ai-agents \
--template-file src/infra/DeployAzureResources.bicep
To deploy via CLI in PowerShell on Windows, issue the following command:
az deployment group create `
--resource-group techworkshop-l300-ai-agents `
--template-file src/infra/DeployAzureResources.bicep
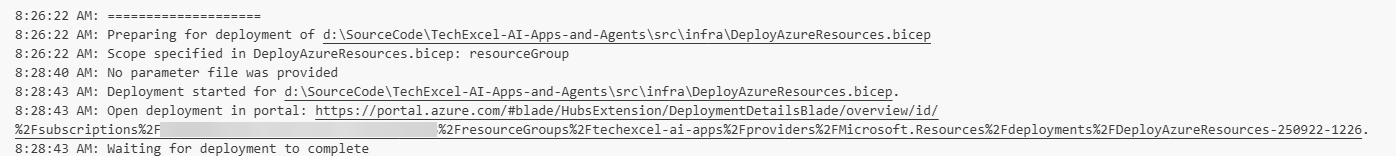
To deploy the Bicep stack using the Visual Studio Code Bicep extension, open Visual Studio Code and select File > Open Folder. Then, navigate to the location where you cloned the repository and open that folder. Then, strike Ctrl+Shift+P (or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS) to open the command palette. In the command palette, type Bicep: Deploy Bicep File and select that option.
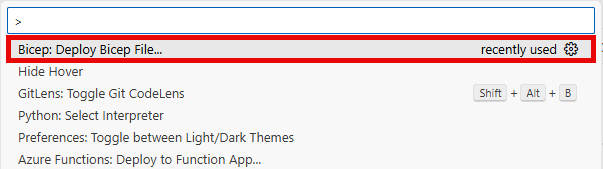
Choose the file src/infra/DeployAzureResources.bicep from the file dialog.
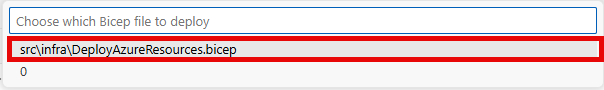
You may be prompted to sign into your Azure account. If so, follow the prompts to complete the sign-in process. Then, strike Enter to accept the default deployment name.
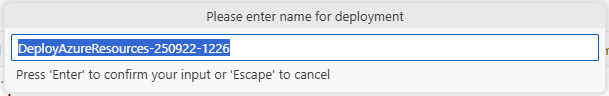
After that, you will need to select the subscription and resource group where you would like to deploy the resources. Choose the same resource group that you created in the previous step.
Finally, you will be prompted for a parameter file. Select None to continue.
In the console window, you will find a link to the deployment in the Azure portal. You can select this link to monitor the progress of the deployment.
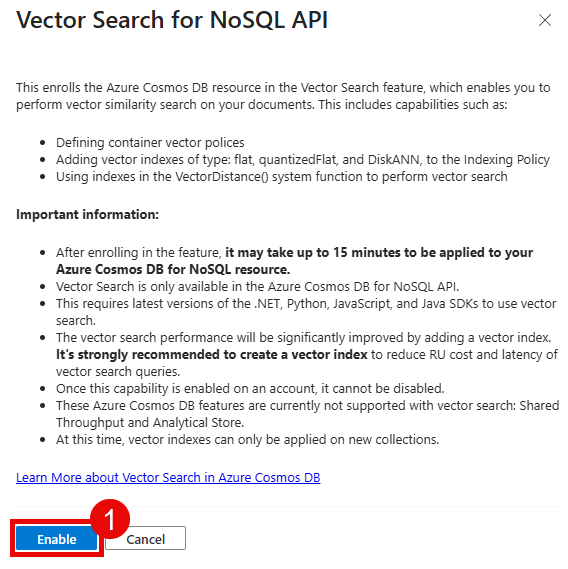
05: Enable Cosmos DB Vector Search
The final key task is to enable Vector Search for NoSQL API in your Cosmos DB account. This may take 15 or more minutes to become active, so enabling this now will ensure that the setting is enabled when you need it in Exercise 1 Task 3.
The Bicep script you have run already includes a command to enable Vector Search for the Comsos DB NoSQL API, but this command does not always work as expected (or in a timely fashion). If you see that vector search is already enabled, you do not need to re-enable it–you are already good to continue.
Expand this section to view the solution
Navigate to the Azure portal and open the Cosmos DB account that you created.
Before you can create the container that you will use for this training, you will need to enable vector search for the Cosmos DB NoSQL API. To do so, navigate to the Settings section of your Cosmos DB account and select Features. Then, select the Vector Search for NoSQL API option.
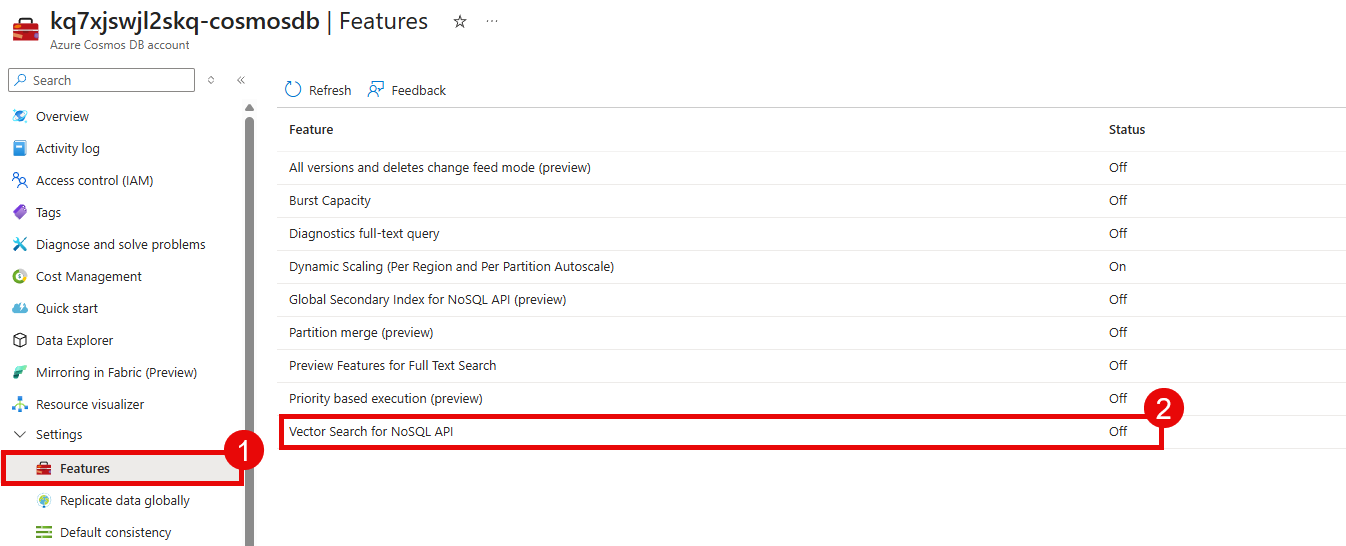
Select the Enable button to enable vector search. This may take up to 15 minutes for the policy to become active.