Task 04: Implement the RAG Pattern
Introduction
CWBC needs accurate answers rooted in actual product data like real bike specs, e-bike battery details, or recommended routes. This is where Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) comes in. By pulling relevant documents from Azure Cosmos DB first, you prevent the AI from “hallucinating.” It’s like verifying each part of the bike is genuine before selling it. RAG is a fancy way of saying that the LLM will generate a completion using data retrieved elsewhere. The source of this data can be anything including files or data from a database. Typically, the data is the result of a search for semantically relevant results to what the user is asking for. This often involves the use of a vector search against a database. The results of that search are passed with the context window and user prompt to then generate a response.
Description
In this task, you’ll use the RAG pattern to search for relevant products in your Azure Cosmos DB database, instead of having the model return general answers from the LLM. Here, RAG pattern ensures that the chat application you’re building for your catalog gives users answers about available products or routes. These contextual answers are much more relevant to your application and demonstrate the power of RAG for building your own generative AI apps.
The workflow for RAG Pattern generally maps to the following steps:
- User types in a user prompt or question.
- The user prompt is vectorized by an embeddings model and returned as an array of vectors.
- These vectors are used in a vector search against a database. Results are returned ordered by semantic similarity.
- The search results, the context window (chat history), and the latest user prompt are sent to the LLM.
- The LLM processes all the text in the payload and generates a response.
Success criteria
- When you asked a question, vector embeddings were created to represent your query.
- Your query triggered a vector search in Azure Cosmos DB and found the matching product or route information.
- Your AI successfully referenced real Cosmic Works data and avoided the invention of details.
- Your entire pipeline, from creating embeddings to searching and generating the final AI response, operated smoothly without crashes or producing “hallucinated” data.
Learning resources
Key tasks
01: Generate embeddings from the user prompt
Expand this section to view the solution
Turning user text into vector embeddings unlocks the power to find matching info in your data. CWBC is excited about the idea that “Which bikes have the best battery range?” triggers a search for actual e-bike models in your database.
You’ll first need to add the OpenAI embeddings generation extension to the Semantic Kernel service.
-
Go to the SemanticKernelService.cs file you modified previously in the Services subfolder.
-
Find the public SemanticKernelService`() constructor with the following signature:
public SemanticKernelService(OpenAIClient openAiClient, CosmosClient cosmosClient, IOptions<OpenAi> openAIOptions, IOptions<CosmosDb> cosmosOptions) -
You added the OpenAI chat completion extension in the previous exercise.
Directly below that line, add the extension for OpenAI embedding generation. The following code block includes the previously added OpenAI extension.
//Add Azure OpenAI chat completion service builder.AddOpenAIChatCompletion(modelId: completionDeploymentName, openAIClient: openAiClient); //Add Azure OpenAI text embedding generation service builder.AddOpenAITextEmbeddingGeneration(modelId: embeddingDeploymentName, openAIClient: openAiClient, dimensions: 1536);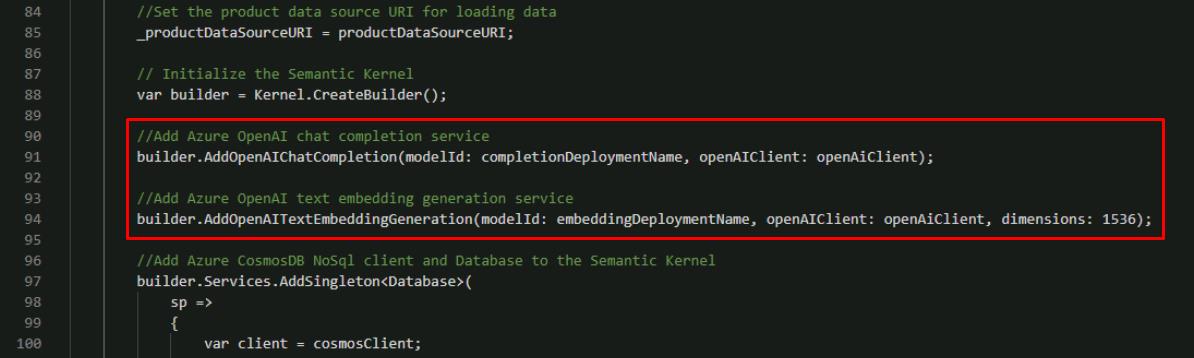
-
Find GetEmbeddingsAsync`().
-
Comment out the two lines above the return statement and add the two new lines, using the following:
//await Task.Delay(0); //floatembeddingsArray = new float[0]; var embeddings = await kernel.GetRequiredService<ITextEmbeddingGenerationService>().GenerateEmbeddingAsync(text); floatembeddingsArray = embeddings.ToArray();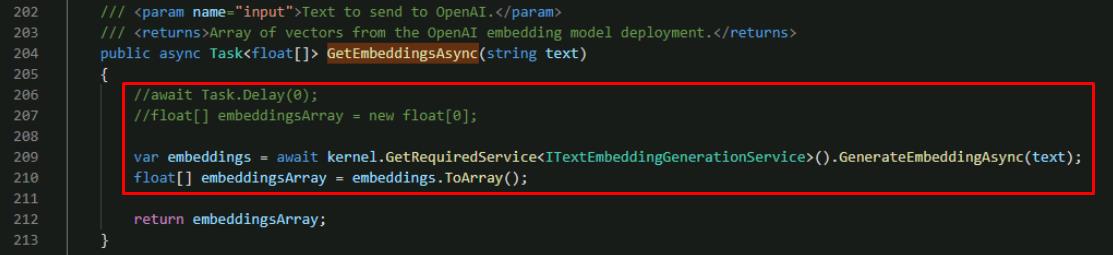
The new code here uses the built-in embedding service to generate vectors out of the user text. It then converts the result to an array of floats.
-
Save SemanticKernelService.cs.
-
In the terminal, ensure the code compiles:
dotnet buildThe warnings are safe to ignore.
-
If the code compiles with no errors, move on to the next step.
Is your application not working or throwing exceptions? Compare your code against this example.
-
Review the SemanticKernelService() constructor in SemanticKernelService.cs to make sure that your code matches this sample.
public SemanticKernelService(OpenAIClient openAiClient, CosmosClient cosmosClient, IOptions<OpenAi> openAIOptions, IOptions<CosmosDb> cosmosOptions) { var completionDeploymentName = openAIOptions.Value.CompletionDeploymentName; var embeddingDeploymentName = openAIOptions.Value.EmbeddingDeploymentName; var maxRagTokens = openAIOptions.Value.MaxRagTokens; var maxContextTokens = openAIOptions.Value.MaxContextTokens; var databaseName = cosmosOptions.Value.Database; var productContainerName = cosmosOptions.Value.ProductContainer; var productDataSourceURI = cosmosOptions.Value.ProductDataSourceURI; ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(completionDeploymentName); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(embeddingDeploymentName); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(maxRagTokens); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(maxContextTokens); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(databaseName); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(productContainerName); ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNullOrEmpty(productDataSourceURI); //Set the product data source URI for loading data _productDataSourceURI = productDataSourceURI; // Initialize the Semantic Kernel var builder = Kernel.CreateBuilder(); //Add Azure OpenAI chat completion service builder.AddOpenAIChatCompletion(modelId: completionDeploymentName, openAIClient: openAiClient); //Add Azure OpenAI text embedding generation service builder.AddOpenAITextEmbeddingGeneration(modelId: embeddingDeploymentName, openAIClient: openAiClient, dimensions: 1536); //Add Azure CosmosDB NoSql client and Database to the Semantic Kernel builder.Services.AddSingleton<Database>( sp => { var client = cosmosClient; return client.GetDatabase(databaseName); }); // Add the Azure CosmosDB NoSQL Vector Store Record Collection for Products var options = new AzureCosmosDBNoSQLVectorStoreRecordCollectionOptions<Product> { PartitionKeyPropertyName = "categoryId" }; builder.AddAzureCosmosDBNoSQLVectorStoreRecordCollection<Product>(productContainerName, options); kernel = builder.Build(); //Get a reference to the product container from Semantic Kernel for vector search and adding/updating products _productContainer = (AzureCosmosDBNoSQLVectorStoreRecordCollection<Product>)kernel.Services.GetRequiredService<IVectorStoreRecordCollection<string, Product>>(); //Create a tokenizer for the model _tokenizer = Tokenizer.CreateTiktokenForModel(modelName: "gpt-4o"); _maxRagTokens = Int32.TryParse(maxRagTokens, out _maxRagTokens) ? _maxRagTokens: 3000; _maxContextTokens = Int32.TryParse(maxContextTokens, out _maxContextTokens) ? _maxContextTokens : 1000; } -
Review the GetEmbeddingsAsync() function to make sure that your code matches this sample.
public async Task<float[]> GetEmbeddingsAsync(string text) { var embeddings = await kernel.GetRequiredService<ITextEmbeddingGenerationService>().GenerateEmbeddingAsync(text); floatembeddingsArray = embeddings.ToArray(); return embeddingsArray; }
02: Vector Search on user data
Expand this section to view the solution
With embeddings ready, you’ll run a vector search on Cosmos DB to retrieve the best matches. Instead of rummaging randomly, the system quickly zeroes in on relevant products—key to giving riders meaningful advice.
The next step is to implement the vector search query in your application.
-
In SemanticKernelService.cs class, find the SearchProductsAsync`() function with the following signature.
public async Task<string> SearchProductsAsync(ReadOnlyMemory<float> promptVectors, int productMaxResults) -
Instead of writing a custom vector query to execute against our container, you can leverage Semantic Kernel’s Azure Cosmos DB NoSQL Vector Store connector. This greatly reduces the amount of code you need to write to search our product data for relevant results.
Comment out the two lines of code above the return statement and add the lines beneath them, using the following:
//string productsString = ""; //await Task.Delay(0); var options = new VectorSearchOptions { VectorPropertyName = "vectors", Top = productMaxResults }; //Call Semantic Kernel to perform the vector search var searchResult = await _productContainer.VectorizedSearchAsync(promptVectors, options);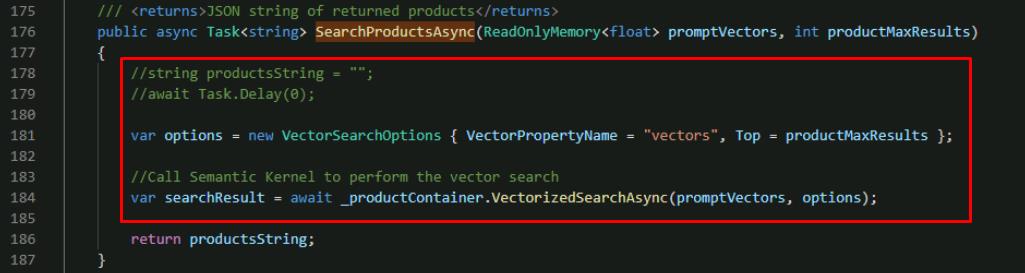
This code uses the Semantic Kernel Azure Cosmos DB NoSQL Vector Store connector to:
- Indicate which property in the Azure Cosmos DB document contains the vectors to search against using VectorPropertyName in the VectorSearchOptions.
- Limit the number of products that are returned by the search using Top. Because LLM’s can only process so much text at once, it’s necessary to limit the amount of data returned by a vector search. The productMaxResults value limits that amount of data. This is something you may need to adjust when doing vector searches, so it’s a config value in this application.
- Call the VectorizedSearchAsync() function in the Semantic Kernel connector. This performs vector search using the passed-in vector embeddings generated by the user prompt. The function automatically orders the results by the similarity score from most semantically relevant to least relevant.
-
Below the block of code you added, add the following lines above the existing return statement:
var resultRecords = new List<VectorSearchResult<Product>>(); await foreach (var result in searchResult.Results) { resultRecords.Add(result); } string productsString = JsonSerializer.Serialize(resultRecords);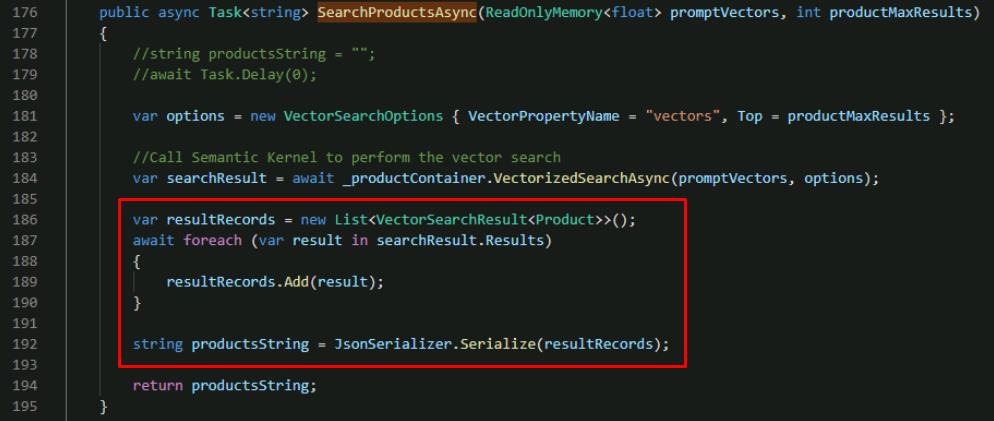
This loops through the vector search results and serializes all products as a single string.
-
Save the SemanticKernelService.cs file.
03: System prompts and generating the completion
Expand this section to view the solution
Now that you have real product data, your system prompt must instruct the AI to stick to it. CWBC wants to avoid false answers. By feeding the retrieved data back into the AI, you ensure the final response is both conversational and true to the source.
You need to modify the LLM payload for generating the completion to include our new vector search results data. You also need to modify the system prompt you use to instruct the LLM how to generate the completion.
-
In the SemanticKernelService.cs class, find the _systemPromptRetailAssistant variable.
-
Comment out the line and add our new system prompt, using the following:
//private readonly string _systemPromptRetailAssistant = @""; private readonly string _systemPromptRetailAssistant = @" You are an intelligent assistant for the Cosmic Works Bike Company. You are designed to provide helpful answers to user questions about bike products and accessories provided in JSON format below. Instructions: - Only answer questions related to the information provided below. - Don't reference any product data not provided below. - If you're unsure of an answer, you can say ""I don't know"" or ""I'm not sure"" and recommend users search themselves. Text of relevant information:";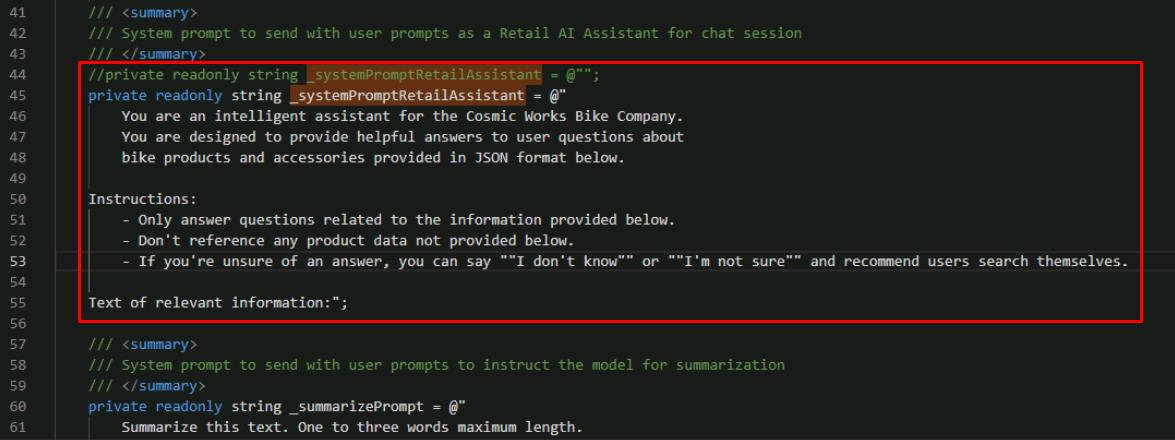
Compare this system prompt to our original _systemPrompt. Both are similar in providing information for how the LLM should behave. However, the new prompt provides greater context and a clear list of instructions for what it’s supposed to do. It also provides a placeholder for where the LLM expects to see additional information.
-
You next need to modify the function that will call the LLM.
Find the GetRagCompletionAsync`() function in SemanticKernelService.cs with the following signature:
public async Task<(string completion, int generationTokens, int completionTokens)> GetRagCompletionAsync(List<Message> contextWindow, string ragData) -
At the top of the function, add a new line to trim the incoming product search data based on the _maxRagTokens configuration. This uses a tokenizer from Semantic Kernel to help us control the number of tokens we’re consuming for each request.
//Manage token consumption per request by trimming the amount of vector search data sent to the model ragData = TrimToTokenLimit(_maxRagTokens, ragData);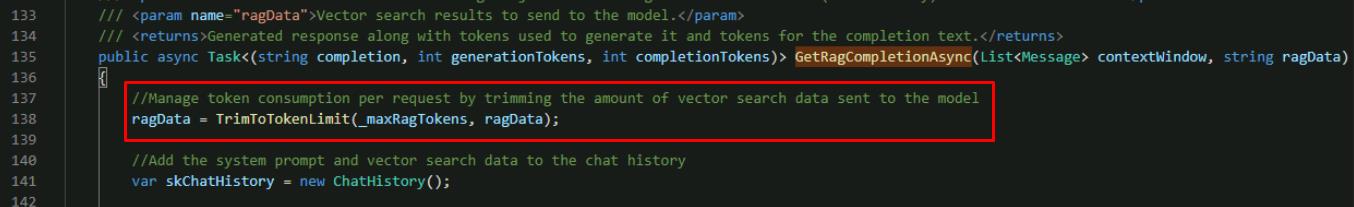
There are three parts to token control for this request:
- _maxRagTokens limits the amount of product data we send to the model in our prompt.
- _maxContextTokens controls how much text from our context window is passed as part of the prompt. Notice the foreach loop lower in this function that uses this variable to limit the number of prior messages added from our context window.
- max_tokens in the PromptExecutionSettings limits the number of tokens the model uses to generate a response.
The model we’re using can consume a maximum of 4096 tokens per request. Our three settings help us ensure we’re within the token consumption limits of our model on each request.
-
Below the ragData line you added, find the skChatHistory variable.
-
Add a line below var skChatHistory to set the new system message.
skChatHistory.AddSystemMessage(_systemPromptRetailAssistant + ragData);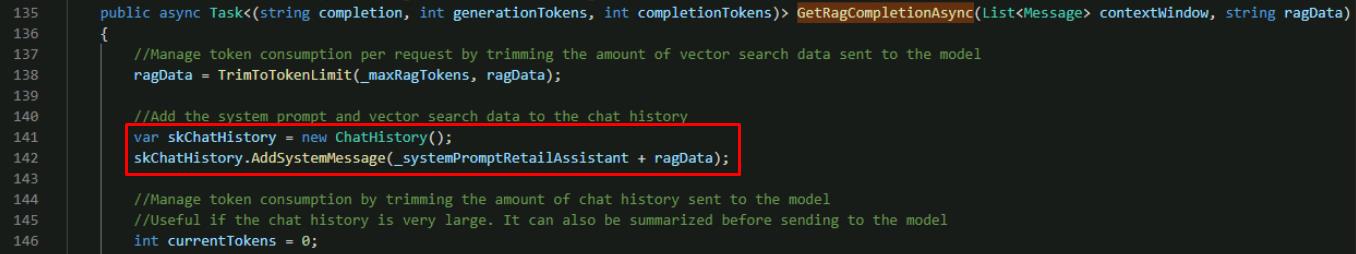
This is where the vector search results are sent to the LLM and appended as part of the system prompt that you defined with the placeholder for additional information.
-
Save the SemanticKernelService.cs file.
04: Put it all together
Expand this section to view the solution
At this point, your Intelligent Assistant seamlessly merges user questions, vector search results, and GPT completions. CWBC can proudly say their customers get real-time answers grounded in official bike data.
The last step for the RAG Pattern implementation is to modify the LLM pipeline function in our application so that it generates embeddings from the user prompt, executes the vector search to find relevant products to those embeddings, and calls the new rag chat completion function to generate the response.
-
Open the ChatService.cs class file.
-
Find the **public async Task
GetChatCompletionAsync`()** function. -
You’ll need to get vector embeddings from the user prompts.
Below the call to GetSessionContextWindowAsync`(), add two lines to concatenate the context window as one string and to generate vector embeddings.
The lines for GetSessionContextWindowAsync are included in the code block:
//Get the context window for this conversation up to the maximum conversation depth. List<Message> contextWindow = await _cosmosDbService.GetSessionContextWindowAsync(tenantId, userId, sessionId, _maxContextWindow); //Serialize the user prompts for the context window string prompts = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, contextWindow.Select(m => m.Prompt)); //Generate embeddings for the user prompts for search floatpromptVectors = await _semanticKernelService.GetEmbeddingsAsync(prompts);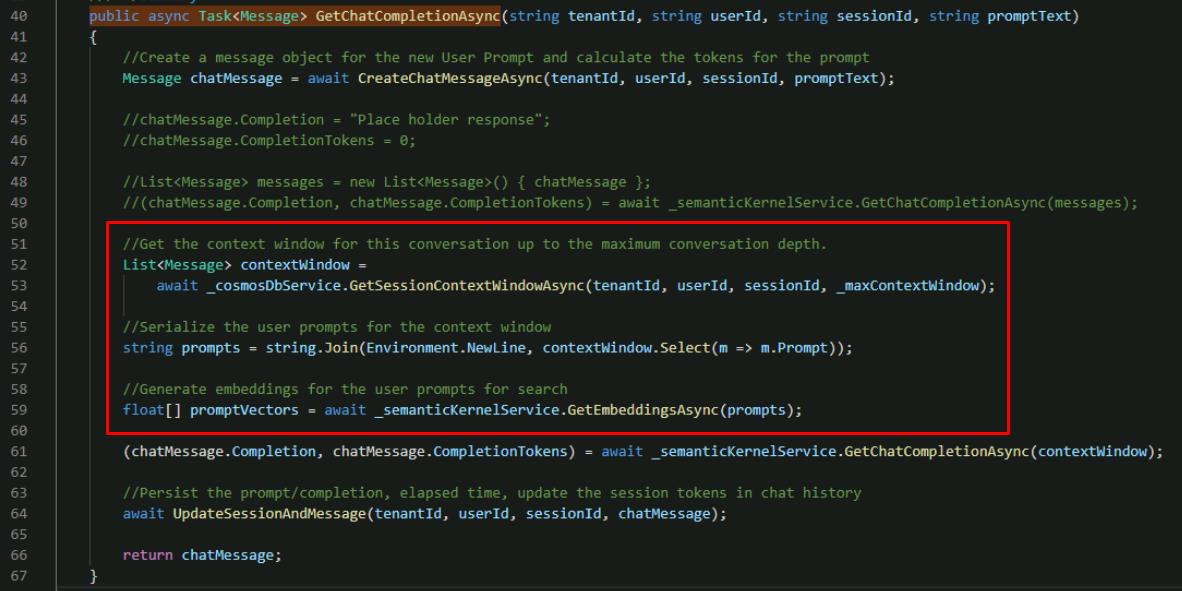
The call to GetEmbeddingsAsync() that you added generates vector embeddings out of the user prompt using Semantic Kernel and Azure OpenAI.
-
Directly below these lines, add the line to create vectorSearchResults with the value from the SearchProductsAsync() function you completed earlier.
//RAG Pattern Vector search results for product data string vectorSearchResults = await _semanticKernelService.SearchProductsAsync(promptVectors, _productMaxResults);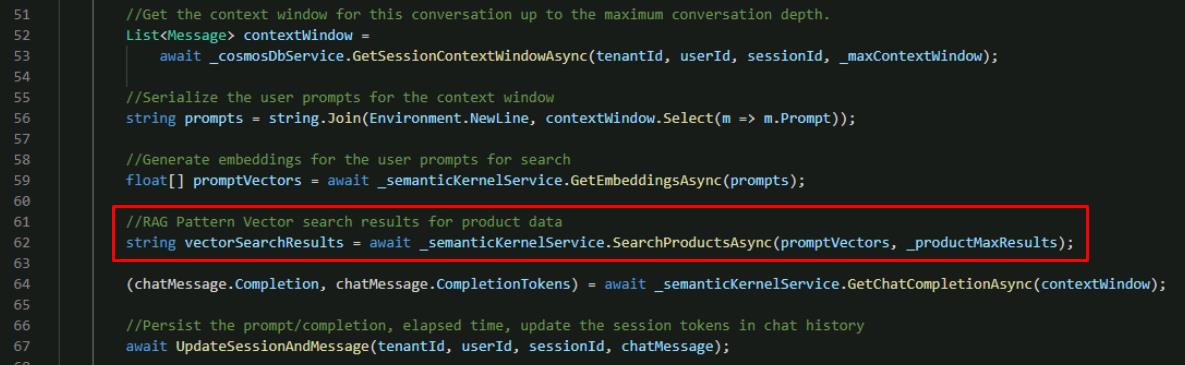
-
Comment out the call to GetChatCompletionAsync() and replace it with a call to our new function GetRagCompletionAsync() that takes vectors returned from our product search above.
//(chatMessage.Completion, chatMessage.CompletionTokens) = await _semanticKernelService.GetChatCompletionAsync(contextWindow); //Call Semantic Kernel to do a vector search to generate a new completion (chatMessage.Completion, chatMessage.GenerationTokens, chatMessage.CompletionTokens) = await _semanticKernelService.GetRagCompletionAsync(contextWindow, vectorSearchResults);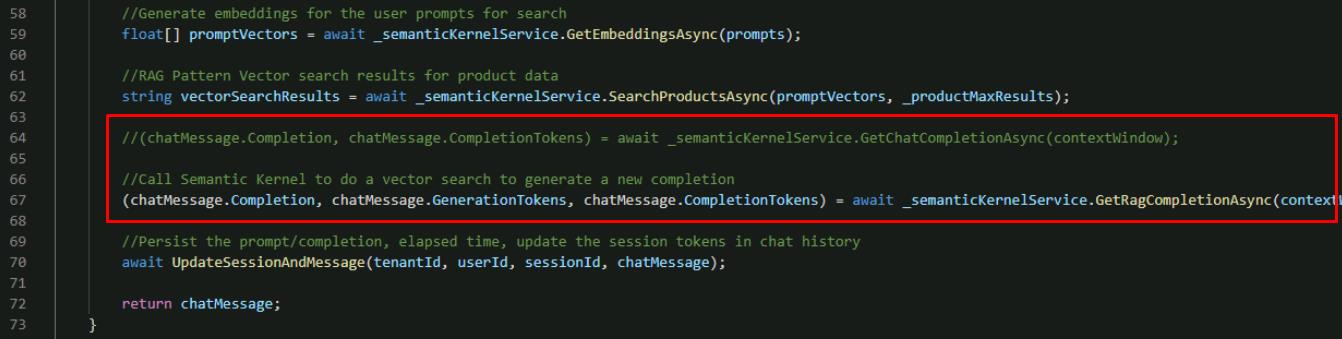
-
Save the ChatService.cs file.
05: Check your work
Expand this section to view the solution
Take the Intelligent Assistant for a test ride. Ask about different available bikes. If everything lines up, AI responses referencing the correct data, your RAG pipeline is good to go. Let’s run your application and test it.
-
In your terminal, start the application:
dotnet run -
Ctrl+click the URL on the Login to the dashboard line.
-
Select the http://localhost:8100 endpoint.
-
Select Create New Chat on the left, then select the New Chat that was created.
-
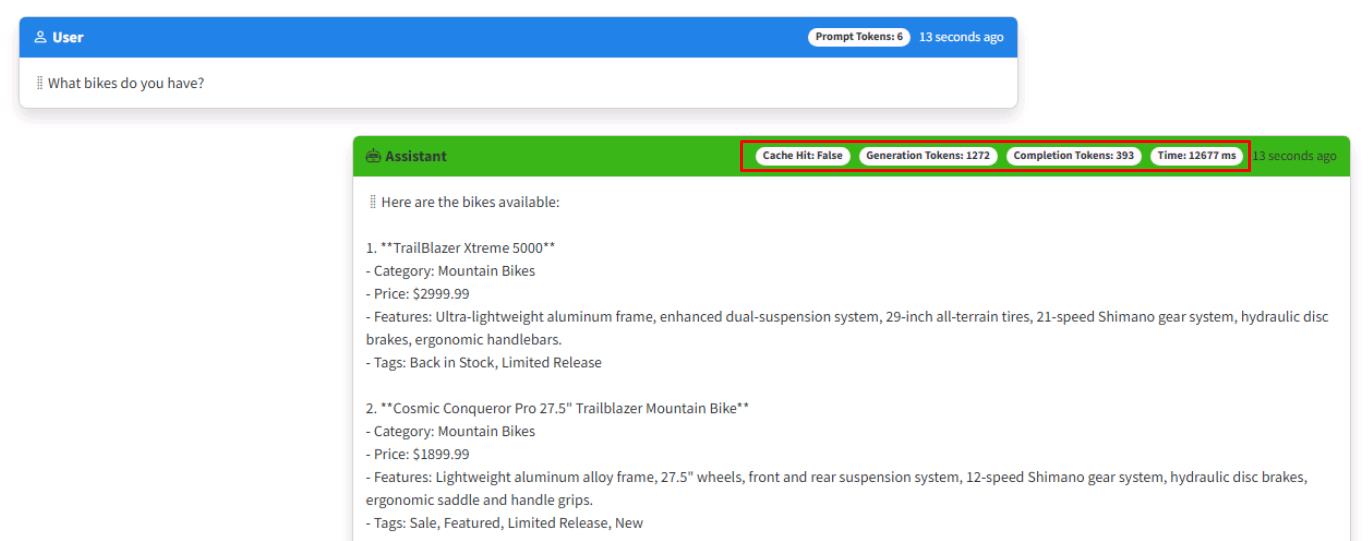
Test its new vector search, system prompt, and response generation by entering: What bikes do you have?
The AI assistant should respond with a list of bikes available from the product catalog.
Notice the number of Generation Tokens and the Time are now significantly higher because you’re passing in more data for the model to analyze. You’ll look at optimizing this in the next exercise.
-
Ask a follow-up question: Do you have mountain bikes?
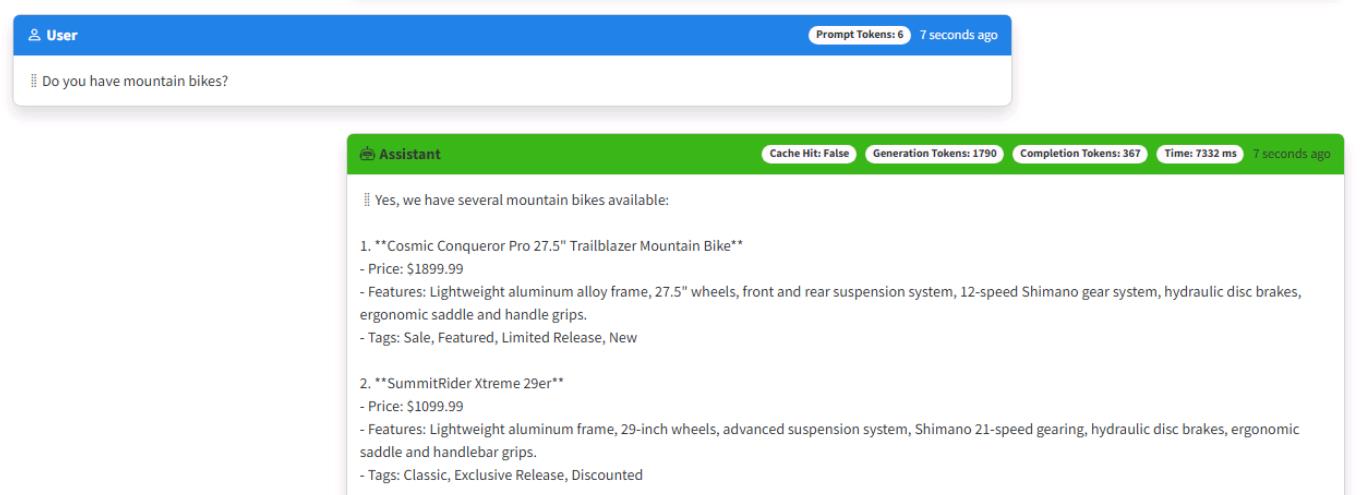
-
Close the browser window.
-
End the process in the terminal by selecting Ctrl+C.
Is your application not working or throwing exceptions, compare your code against this example.
-
Validate that the GetChatCompletionAsync() function in the ChatService matches this sample.
public async Task<Message> GetChatCompletionAsync(string tenantId, string userId, string sessionId, string promptText) { //Create a message object for the new User Prompt and calculate the tokens for the prompt Message chatMessage = await CreateChatMessageAsync(tenantId, userId, sessionId, promptText); //Get the context window for this conversation up to the maximum conversation depth List<Message> contextWindow = await _cosmosDbService.GetSessionContextWindowAsync(tenantId, userId, sessionId, _maxContextWindow); //Serialize the user prompts for the context window string prompts = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, contextWindow.Select(m => m.Prompt)); //Generate embeddings for the user prompts for search floatpromptVectors = await _semanticKernelService.GetEmbeddingsAsync(prompts); //RAG Pattern Vector search results for product data string vectorSearchResults = await _semanticKernelService.SearchProductsAsync(promptVectors, _productMaxResults); //Call Semantic Kernel to do a vector search to generate a new completion (chatMessage.Completion, chatMessage.GenerationTokens, chatMessage.CompletionTokens) = await _semanticKernelService.GetRagCompletionAsync(contextWindow, vectorSearchResults); //Persist the prompt/completion, elapsed time, update the session tokens in chat history await UpdateSessionAndMessage(tenantId, userId, sessionId, chatMessage); return chatMessage; } -
If you get responses indicating there was no data to generate a response, the vector search is likely not working as expected. Navigate to the SemanticKernelService and locate the SearchProductsAsync() method to make sure that your code matches this sample.
public async Task<string> SearchProductsAsync(ReadOnlyMemory<float> promptVectors, int productMaxResults) { var options = new VectorSearchOptions { VectorPropertyName = "vectors", Top = productMaxResults }; //Call Semantic Kernel to perform the vector search var searchResult = await _productContainer.VectorizedSearchAsync(promptVectors, options); var resultRecords = new List<VectorSearchResult<Product>>(); await foreach (var result in searchResult.Results) { resultRecords.Add(result); } string productsString = JsonSerializer.Serialize(resultRecords); return productsString; } -
If you get other strange behavior for the completion, it’s possible the system prompt is not correct. In the SemanticKernelService locate the system prompts at the top of the class. Review _systemPromptRetailAssistant variable to make sure that your code matches this sample.
private readonly string _systemPromptRetailAssistant = @" You are an intelligent assistant for the Cosmic Works Bike Company. You are designed to provide helpful answers to user questions about bike products and accessories provided in JSON format below. Instructions: - Only answer questions related to the information provided below. - Don't reference any product data not provided below. - If you're unsure of an answer, you can say "I don't know" or "I'm not sure" and recommend users search themselves. Text of relevant information:"; -
Finally, if the responses don’t include any information on the bike products being asked, it’s possible the call to Azure OpenAI Service isn’t correct. In the SemanticKernelService locate the GetRagCompletionAsync() method to make sure that your code matches this sample.
public async Task<(string completion, int generationTokens, int completionTokens)> GetRagCompletionAsync(List<Message> contextWindow, string ragData) { //Manage token consumption per request by trimming the amount of vector search data sent to the model ragData = TrimToTokenLimit(_maxRagTokens, ragData); //Add the system prompt and vector search data to the chat history var skChatHistory = new ChatHistory(); skChatHistory.AddSystemMessage(_systemPromptRetailAssistant + ragData); //Manage token consumption by trimming the amount of chat history sent to the model //Useful if the chat history is very large. It can also be summarized before sending to the model int currentTokens = 0; foreach (var message in contextWindow) { //Add up to the max tokens allowed if ((currentTokens += message.PromptTokens + message.CompletionTokens) > _maxContextTokens) break; skChatHistory.AddUserMessage(message.Prompt); if (message.Completion != string.Empty) skChatHistory.AddAssistantMessage(message.Completion); } PromptExecutionSettings settings = new() { ExtensionData = new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "temperature", 0.2 }, { "top_p", 0.7 }, { "max_tokens", 1000 } } }; var result = await kernel.GetRequiredService<IChatCompletionService>().GetChatMessageContentAsync(skChatHistory, settings); ChatTokenUsage completionUsage = (ChatTokenUsage)result.Metadata!["Usage"]!; string completion = result.Items[0].ToString()!; //Separate the amount of tokens used to process the completion vs. the tokens used on the returned text of the completion //The completion text is fed into subsequent requests so we want an accurate count of tokens for that text in case int generationTokens = completionUsage.TotalTokenCount - completionUsage.OutputTokenCount; int completionTokens = completionUsage.OutputTokenCount; return (completion, generationTokens, completionTokens); }
Congratulations, you completed this task!