TIP
💡 Learn more : Azure HDInsight Documentation (opens new window).
# Getting Started with HDInsight
# What is Azure HDInsight?
Azure HDInsight (opens new window) is a managed cloud service for analyzing large sets of data. This big data is often collected rapidly and may be relatively unstructured. By itself this data might not be very useful, but when cleaned, analyzed, and presented, it can provide actionable insights. You can use Azure HDInsight to power machine learning, IoT, or data warehousing projects.
The service is available in most Azure regions and has the security and compliance standards you would expect from an Azure managed service. You can use whichever language you prefer to develop with. Python, Java, and C# are just a few examples.
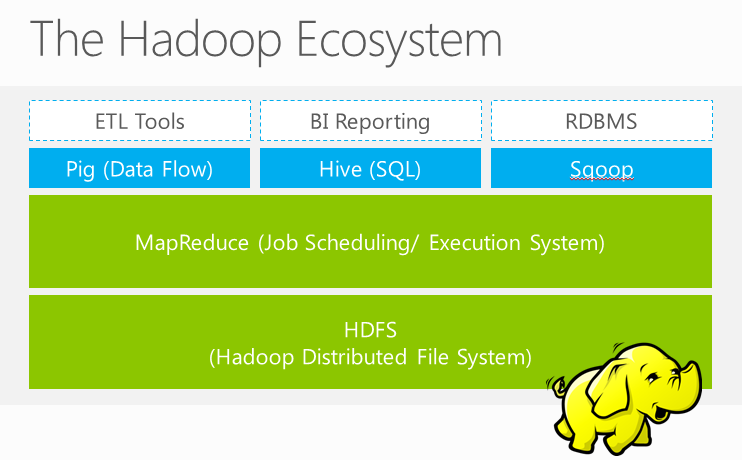
# The elephant in the room?
When you read about Azure HDInsight (opens new window) (or see it in the Azure portal, you'll probably notice a little elephant icon. This is the logo for Apache Hadoop, which is an open-source distributed data analysis solution (which MS contributes to).
Hadoop manages the processing of large datasets across large clusters of computers and it detects and handles failures. There are related projects in the Hadoop stack such as Hive, Spark, and Kafka that HDInsight also contains.
# Why Hadoop on Azure?
As we already know, Azure provides dynamic machines that are billed only when active. This enables elastic computing, where you can add machines for particular workloads or projects and then remove them when not needed. HDInsight can take advantage of this scalable platform. It can also capitalize on the security and management features of Azure, integration with Azure Active Directory and Log Analytics.
HDInsight can also integrate with familiar business intelligence tools such as Excel, PowerPivot, and SQL Server Analysis Services and Reporting Services. This is facilitated with special ODBC drivers.
# Hardoop for Devs
Hadoop uses the MapReduce (opens new window) programming model. This allows you to map (filter and sort) data sources and reduce (summarize, count, etc.) to produce meaningful output from a large unstructured data source. For developing with HDInsight, you can use Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, Eclipse, and IntelliJ development environments. You can create user-defined functions (UDFs) written in a number of languages for the Pig Latin programming language or use HiveQL, which is an SQL dialect, to treat the data like a relational model. A third tool, Sqoop (opens new window), allows you to export to a conventional relational database.
# Into the action - Setting up your cluster
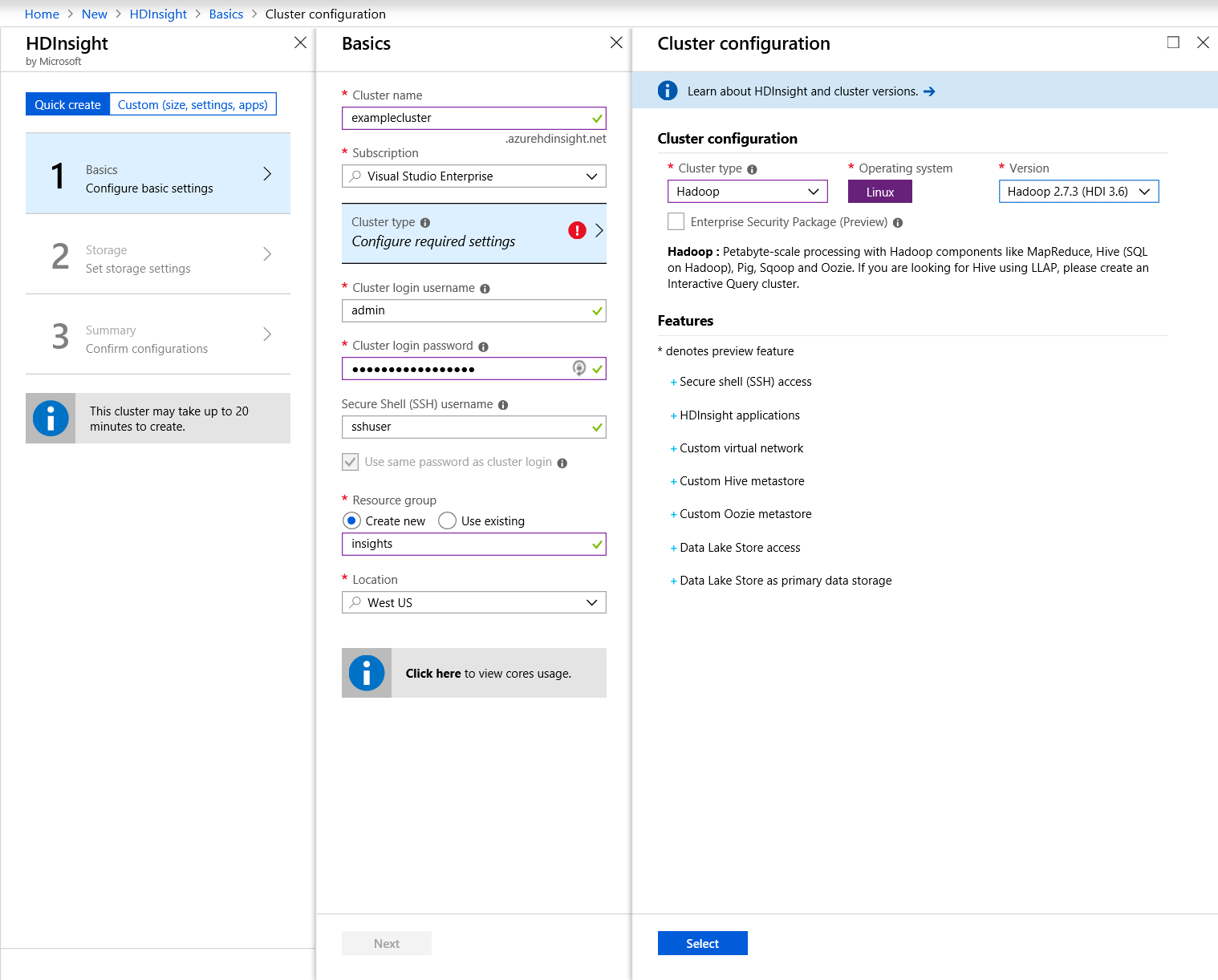
Adding a new HDInsight cluster is a three-step process. First, search the Azure Portal for HDInsight cluster and create a new cluster. We'll stay on the Quick create for this sample.
You must specify a unique name and login credentials and fill in the rest of the fields as you normally would.
When you get to cluster type, select Hardoop and leave the rest at their default values.
Note: It also supports the following types:
- Hadoop: Terabyte-scale processing with Hadoop components like Hive (SQL in Hadoop), Pig and Oozie.
- HBase: Fast and scalable NoSQL database. Data Lake Storage connectivity is available in preview for HDI 3.6.
- Storm: Reliably process infinite streams of data in real-time.
- Spark: Fast data analytics and cluster computing using in-memory processing.
- Interactive Query: In-memory analytics using Hive and LLAP.
- R Server: Terabyte-scale, enterprise-grade R analytics with transparent parallelization on top of Spark and Hadoop.
- Kafka: Fast, scalable, durable, and fault-tolerant publish-subscribe messaging system.
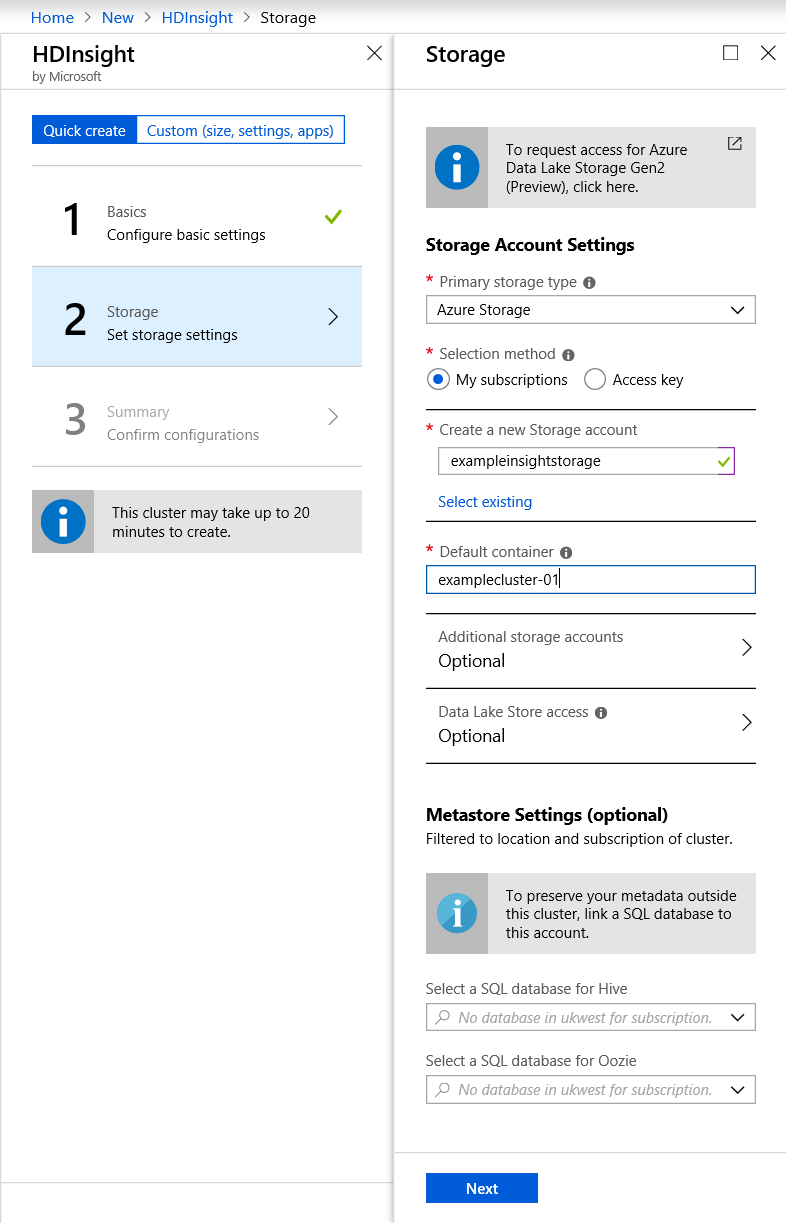
Next, you either select an existing Storage account or create a new one.
Finally, you are presented with a summary of the options you have chosen and an estimated running cost, per hour, for this configuration.
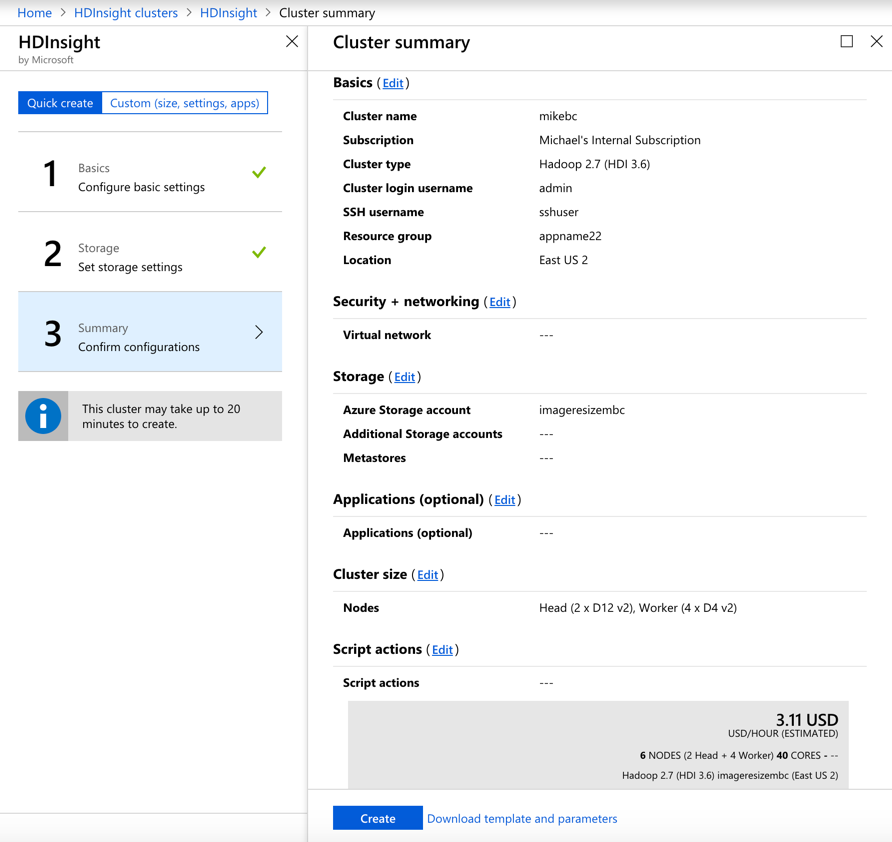
Once you click Create, the cluster nodes will be configured and you will be billed for the cluster until you remove it.
NOTE: It may take a while to spin this up. The information dialog says up to 20 minutes.
You can now open the cluster in the Azure Portal and do things such as scale up or scale out, manage policies (such as mask a column) or review audit logs.
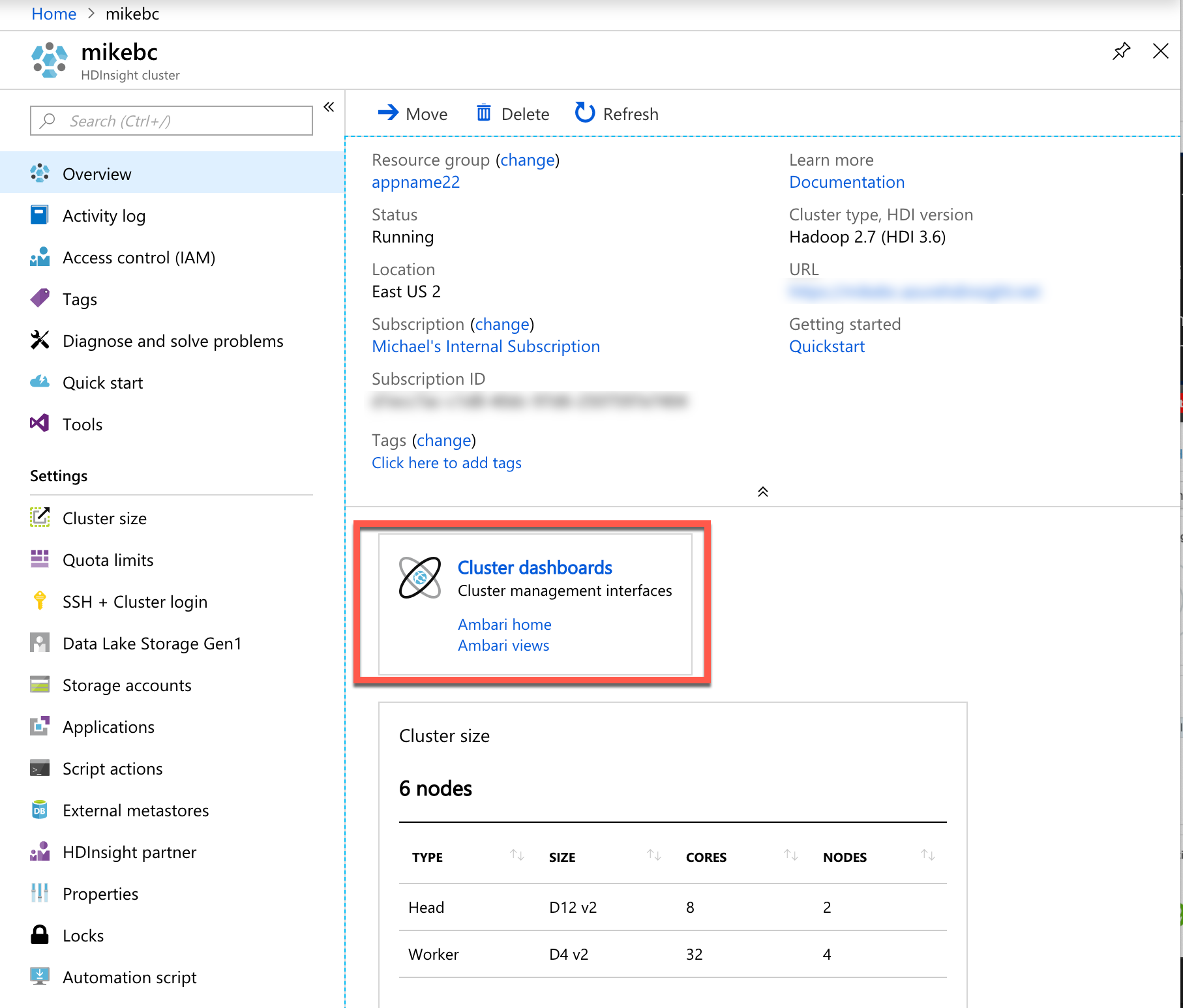
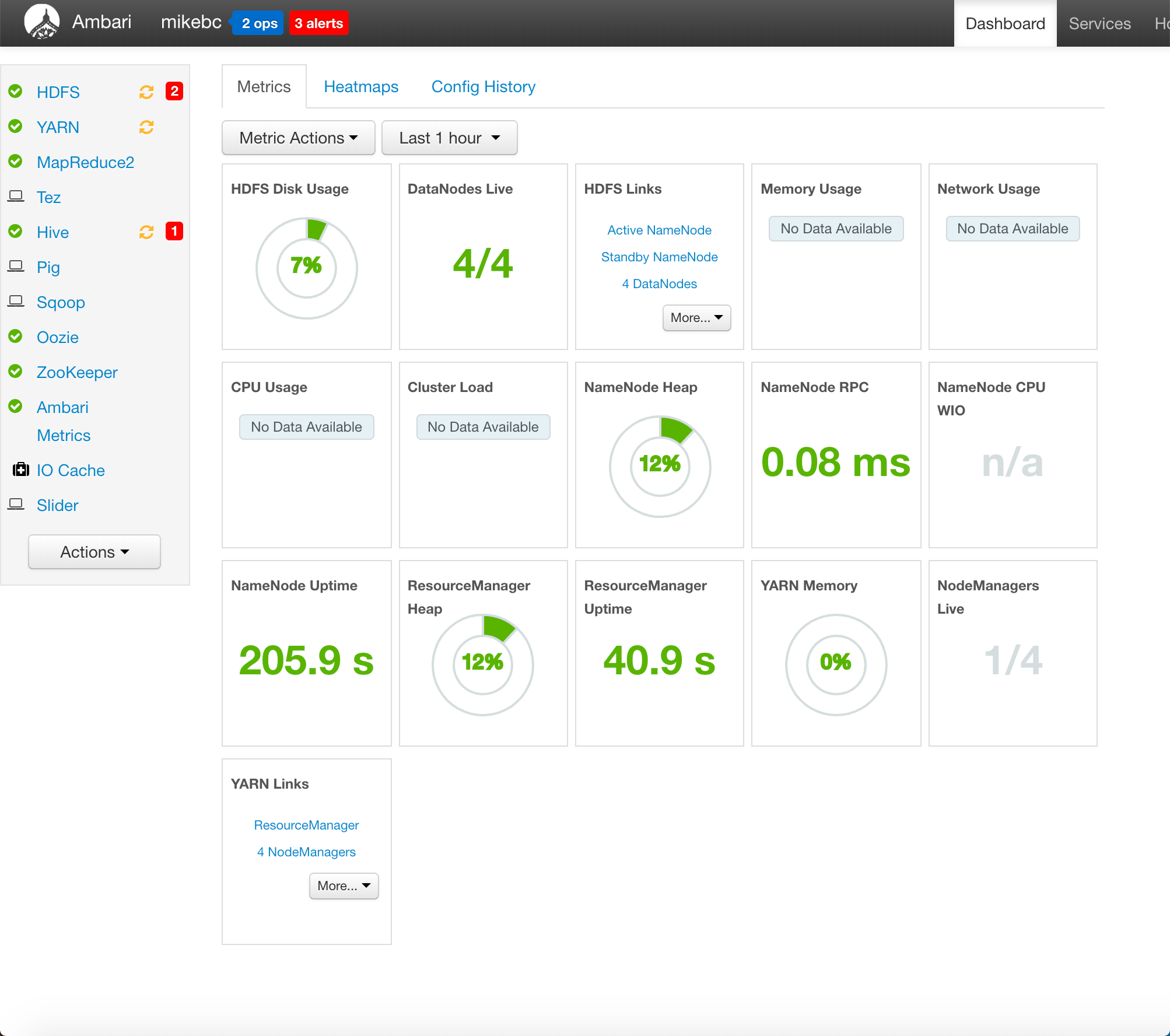
Click Cluster dashboards to open your Apache Ambari dashboard which simplifies Hadoop management with a GUI. You can use Ambari to manage and monitor Hadoop clusters. Developers can integrate these capabilities into their applications by using the Ambari REST APIs.
# Wrap-up
You can read about the Hadoop project in more detail here (opens new window). There is also a range of third-party applications to explore (opens new window).
