TIP
🔥 Make sure you star the repo (opens new window) to keep up to date with new tips and tricks.
💡 Learn more : Read Replicas in Azure Database for MySQL (opens new window)
This post was brought to you by Kumar Allamraju (opens new window).
# How to create read replicas for Azure MySQL Database
# Read Replicas in Azure Database for MySQL
The read replica feature allows you to replicate data from an Azure Database for MySQL server to a read-only server. You can replicate from the master server up to five replicas. Replicas are updated asynchronously using the MySQL engine's native binary log (binlog) file position-based replication technology.
# Why would I need read replica?
The read replica feature helps you to improve the performance and scale of read-intensive workloads. Read workloads can be isolated to the replica instances, while write workloads can be directed to the master instance. A common scenario is to have BI and analytical workloads use the read replica as the data source for reporting.
Please note that the read replica feature uses MySQL asynchronous replication. This feature isn't meant for synchronous replication scenarios. There will be a measurable delay between the master and the replica instance. The data on the replica eventually becomes consistent with the data on the master.
You can also create a read replica in a different Azure Region when creating the read replica. This can help you to serve clients in different geographic regions more quickly.
In few steps we will learn to create a read replica for Azure managed MySQL database. This article assumes you have already created a Azure MySQL database instance. If not, pls refer to this posting (opens new window) to create a new MySQL server in Azure.
# Steps to create a read replica for Azure MySQL
- Sign into Azure Portal
- Select the existing Azure Database for MySQL server. This action opens the Overview page.
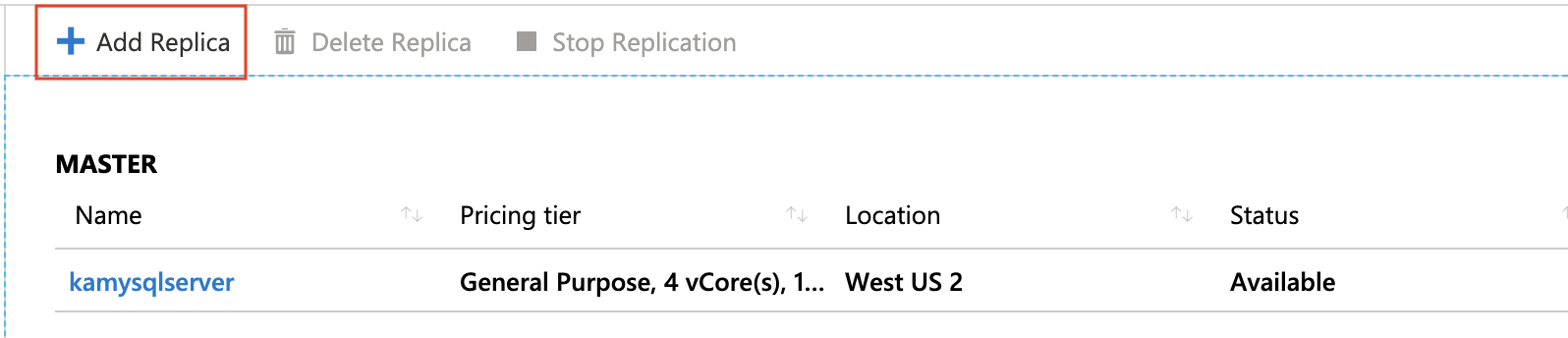
- Select Replication from the menu, under SETTINGS
- Click on + Add Replica
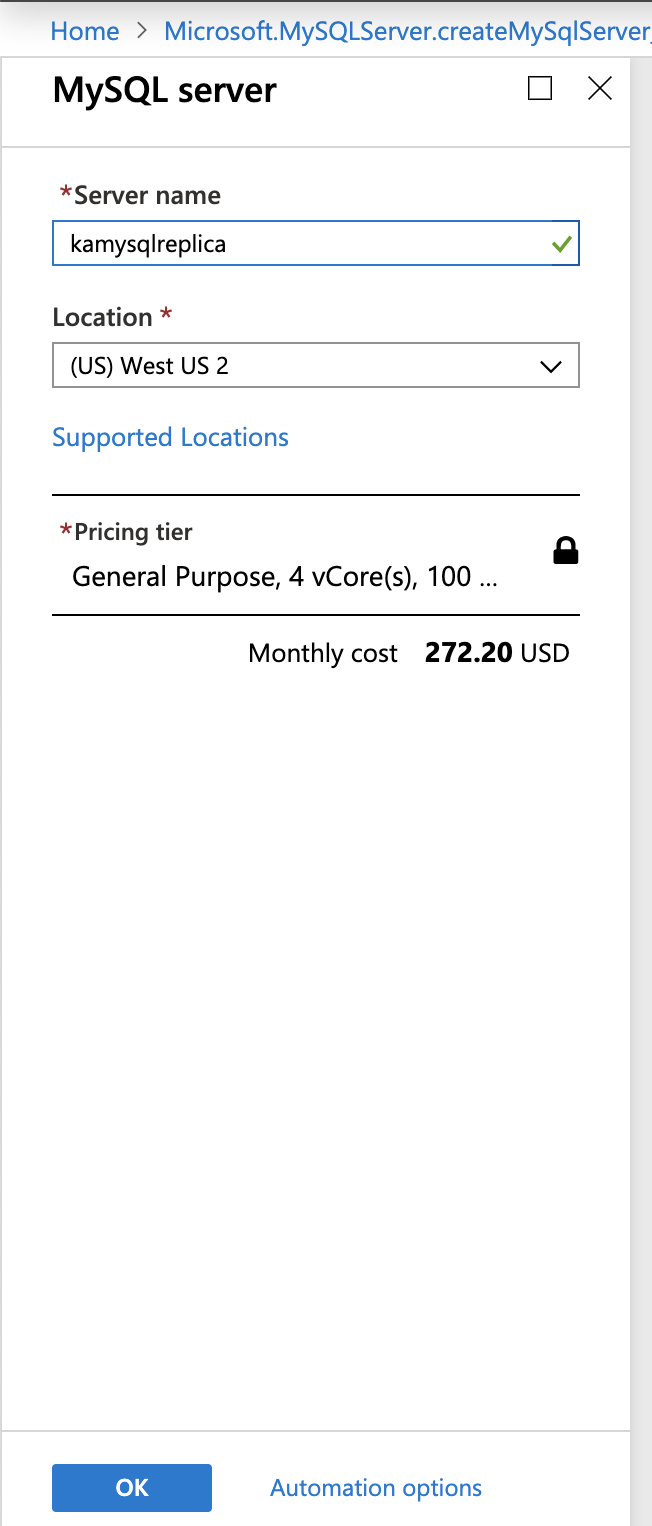
- Name the replica server and choose the target location. In this demo I chose the same location as master instance but you can also pick up a different region.
- The creation time depends on the amount of data on the master and the time since the last weekly full backup. The time can range from a few minutes to several hours. It's a recommended practice to create a read replica when you don't expect a heavy DB load. This is because the read replica creation process might cause I/O latency until it's completed.

- Once you are done exploring this feature, pls delete the read replica instance from Azure Portal to avoid compute and storage costs. Otherwise promote this feature to your Dev/QA/Test and eventually to production environment.
# Pricing
Replicas are new servers that are similar to regular Azure Database for MySQL servers. For each read replica, you're billed for the provisioned compute in vCores and storage in GB/ month.
# Conclusion
Database Read Replica(s) helps in decreasing load on the primary DB by serving read-only traffic. Read replicas allow you to elastically scale out beyond the capacity constraints of a single DB instance for read-heavy database workloads. Cross-region replication can be helpful for scenarios like disaster recovery planning or bringing data closer to your end users. In this article, we learned to create a read replica from an existing MySQL master instance in the same azure region or a different region.
