TIP
💡 Learn more : App Service Documentation (opens new window).
# Part 6 - An end to end scenario with Azure App Service, API Apps, SQL, VSTS and CI/CD
# A multi-part series showing an end-to-end possibility
Crystal Tenn (opens new window) and I teamed up to bring an E2E blog series that features an Azure App Service website that communicates with an API project, which communicates to an Azure SQL back-end. The app is a traditional To-Do application based on an existing sample that used ADO.NET, but adapted for Azure deploy and to Visual Studio 2017. The technology/tooling stack is Visual Studio, VSTS, C#, Angular, and SQL.
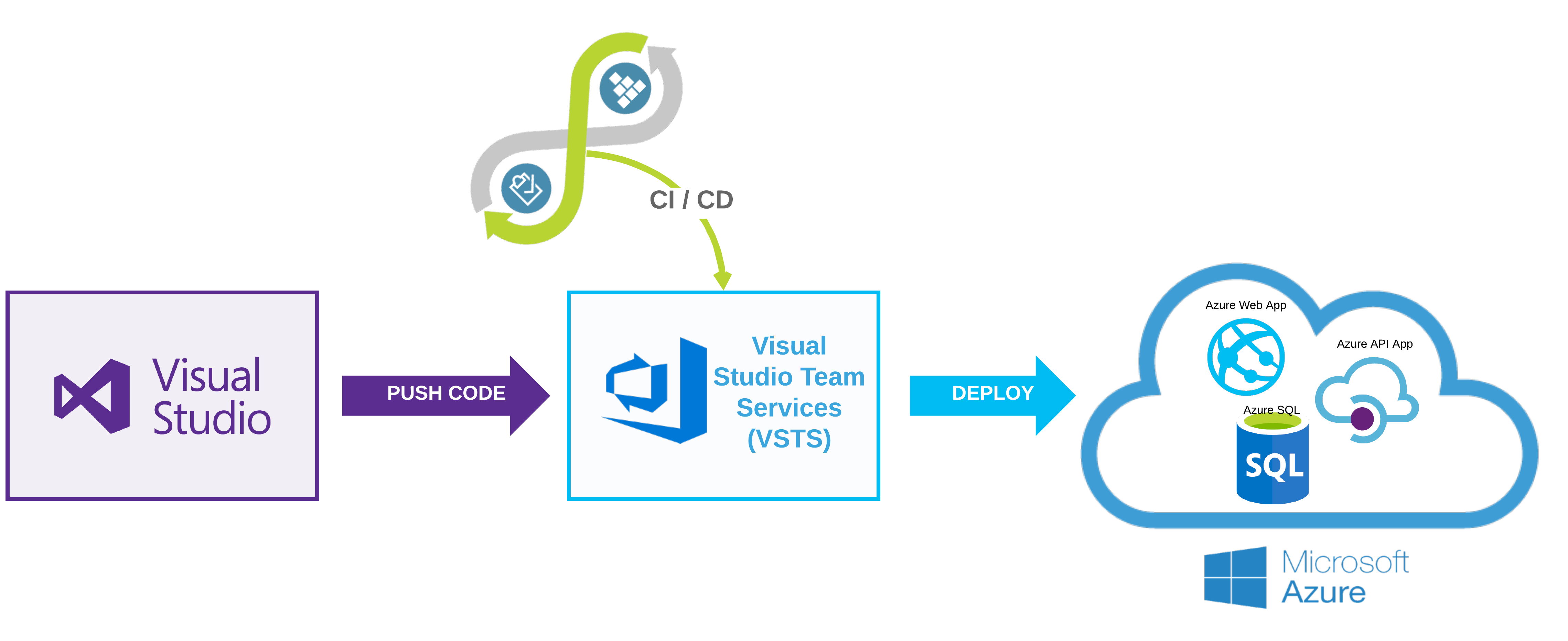
The process for the app is described below. In Visual Studio, you will start out with a working To Do list application. You will push the code to VSTS (Visual Studio Team Services). Then you will create a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) process in order to deploy to Azure. In Azure you will create 3 resources: Azure Web App, Azure API App, and an Azure SQL Server through this exercise.
- Local Setup - SQL Server (opens new window) - Locally connect a front-end website to an API, and connect the API to a SQL Server.
- Local Setup - Visual Studio and Swagger (opens new window) - Continue Part 1 and use a local instance of Visual Studio and Swagger to communicate to our db.
- Swagger - Learn how to use Swagger for API management (opens new window)
- Azure Deployment - Deploy the SQL database to Azure manually (opens new window)
- Azure Deployment - Deploy the front-end Web App and API App to Azure manually (opens new window)
- Adding the project to VSTS with Git (opens new window)
- VSTS Continuous Integration - Setup a CI Process in VSTS (opens new window)
- VSTS Continuous Deployment - Setup a CD Process in VSTS (opens new window)
- Cleanup - Cleanup and delete the Azure resources created in this tutorial (opens new window)
Keep in mind : While we won't be going into the deep specifics of how to code, you should be able to use this guide to look at several parts of the Azure technology stack and how you can best implement them in your organization.
Pre-requisite: Install Git (opens new window)
# Create the VSTS Account
1.) Sign up for VSTS if you do not have an account by clicking the Sign Up button (opens new window) on the homepage.
Make sure to use the same email address that you used for Azure.
2.) Create a new VSTS Account by hitting the button on the top right.

3.) After your account is created, then you'll see the following:
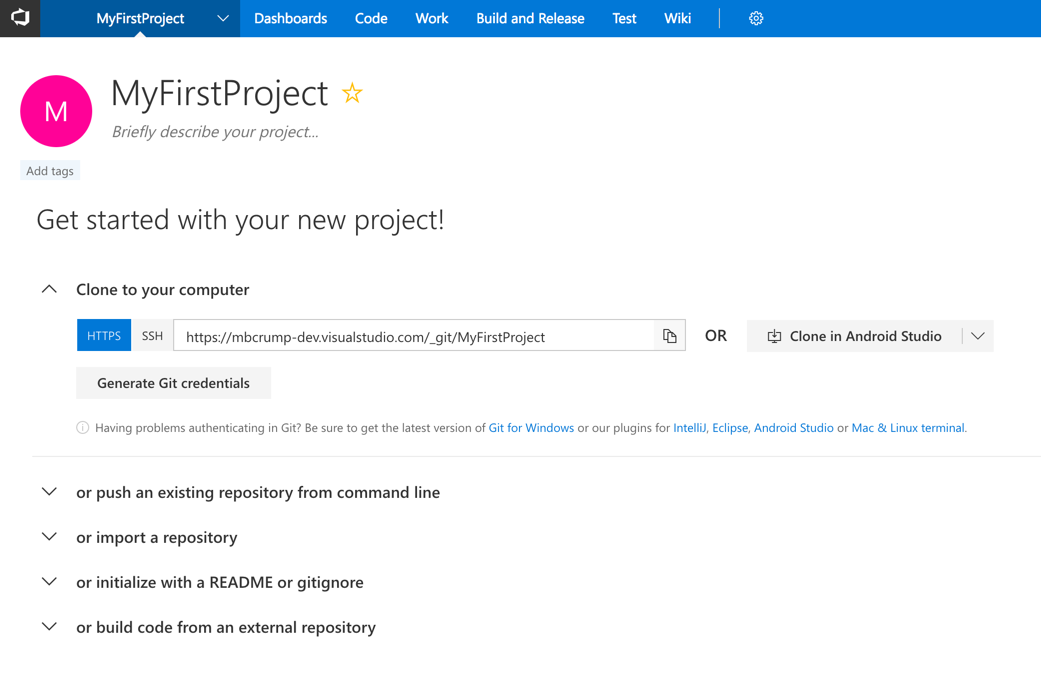
4.) You can optionally rename the project by clicking on the Gear icon and clicking on the Project Name. Note that if you do this, it updates all of your version control paths, work items, queries, and other team project artifacts to reflect the new name.
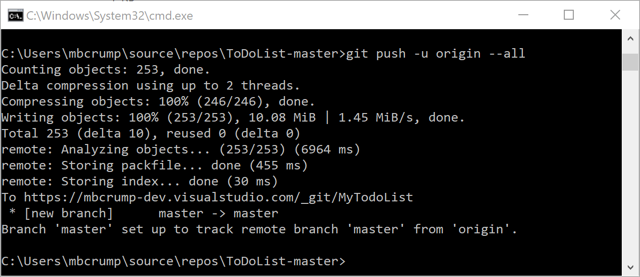
5.) Click on the push an existing repository from the command line and copy the copy to notepad.

6.) If you've already installed Git (opens new window), then run navigate to your Visual Studio solution and run the following commands in order. You'll need to change the 4th command to the URL you copied earlier
git init
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git remote add origin https://YOURPROJECT.visualstudio.com/_git/AzureWebApp
git push -u origin --all
2
3
4
5
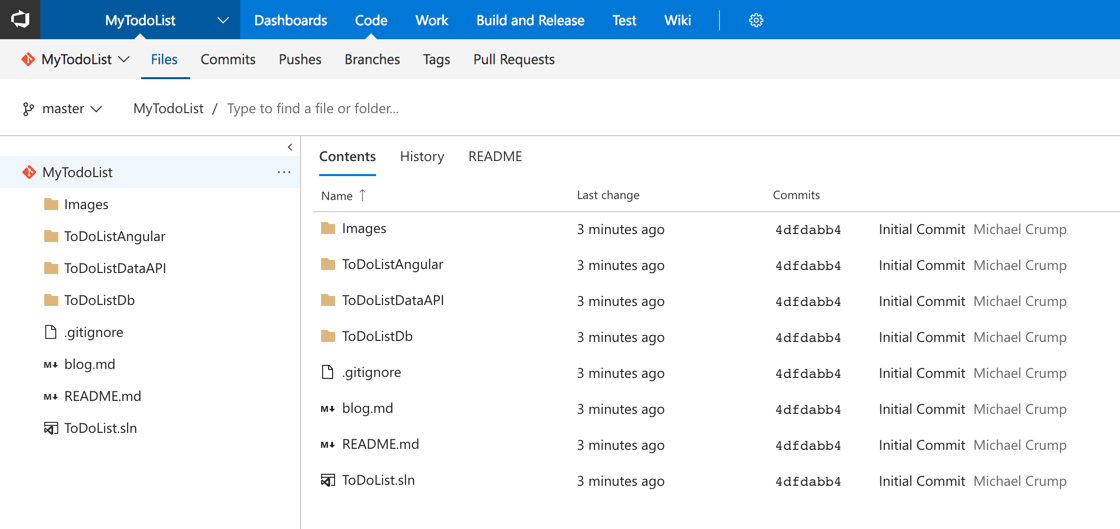
7.) Go to VSTS and click Code, you should see your code there: